Latest
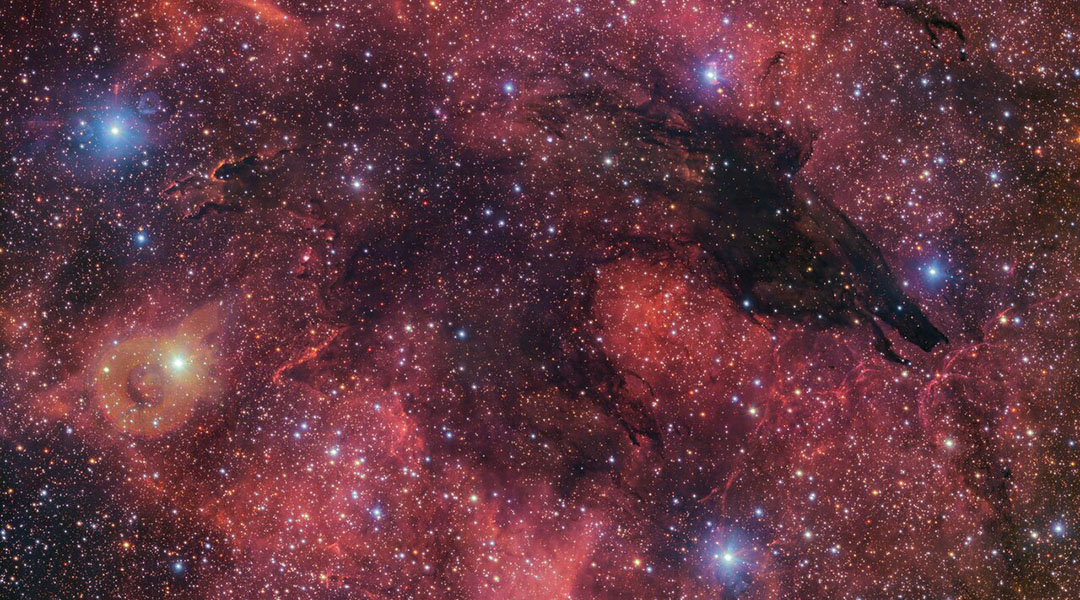

ESO reveals spectacular “Dark Wolf Nebula” in time for Halloween
This image of a dark nebula creates the illusion of a wolf-like silhouette against a colorful cosmic backdrop.
Machine learning spots single photons to accelerate quantum communication
Machine learning is bringing forth the future of secure communication, swiftly identifying single photons that hold the key to quantum tech.

String theory provides a new take on the expansion of the Universe
String theory could reshape our understanding of the Universe’s accelerating expansion and unlock the mysteries of dark energy.

Do voice assistants help alleviate loneliness?
Scientists explored whether evidence backs up the growing belief that voice assistants like Alexa can alleviate loneliness, especially in the elderly.
Researchers explain the intricate interactions that shape DNA organization
Scientists uncover how the complex interactions between nucleosomes influence DNA’s organization in chromosomes.
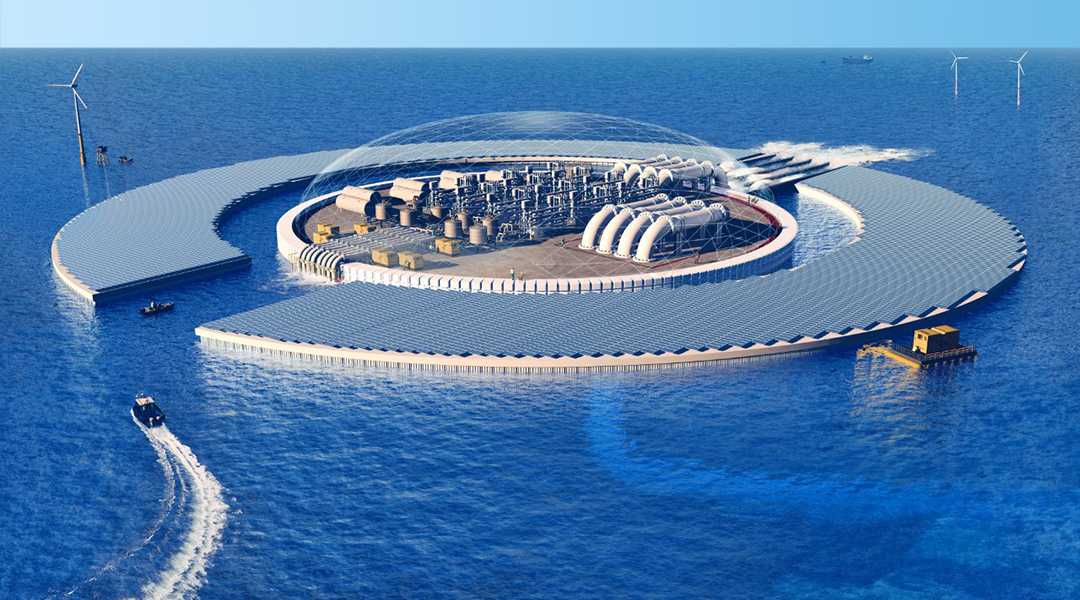

Offshore oceanic CO2 capture
An out-of-the box approach to carbon sequestration proposes an off-shore solution and a fascinating adjunct to direct air capture.
Uncovering the secrets of cellular organization
A 3D hydrogel model provides key insights into how cells sense and respond to elements of their environment.
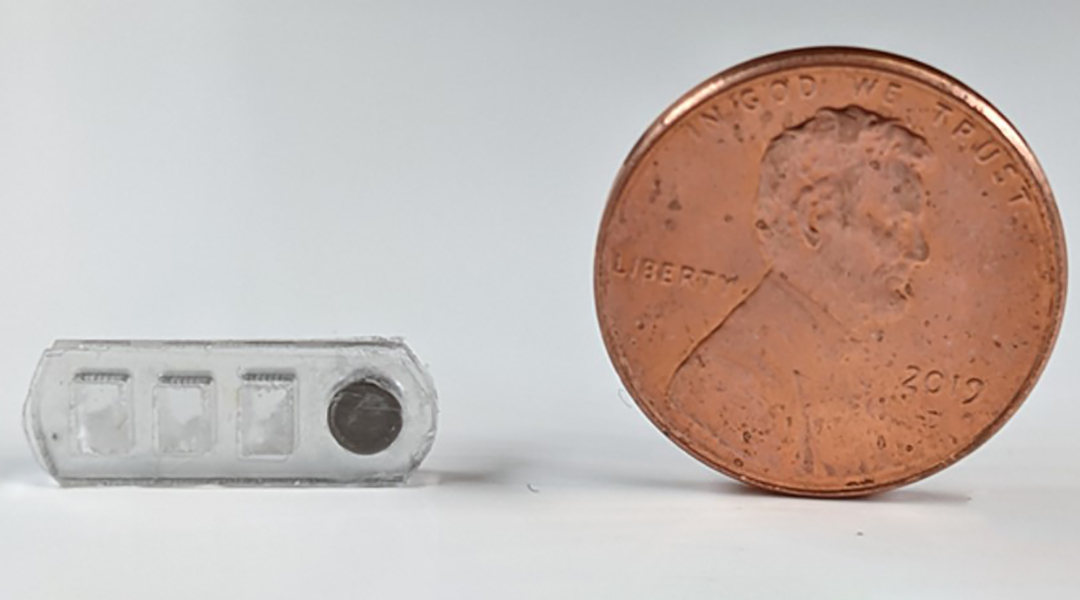
A robotic pill monitors disease in the gut
A robotic pill capable of collecting biomarkers, including proteins and bacteria, from the gut provides an easy-to-use disease screening tool.

3D printing the perfect piece of chocolate
Researchers explore how manipulating the properties of chocolate metamaterials can change our enjoyment of it.
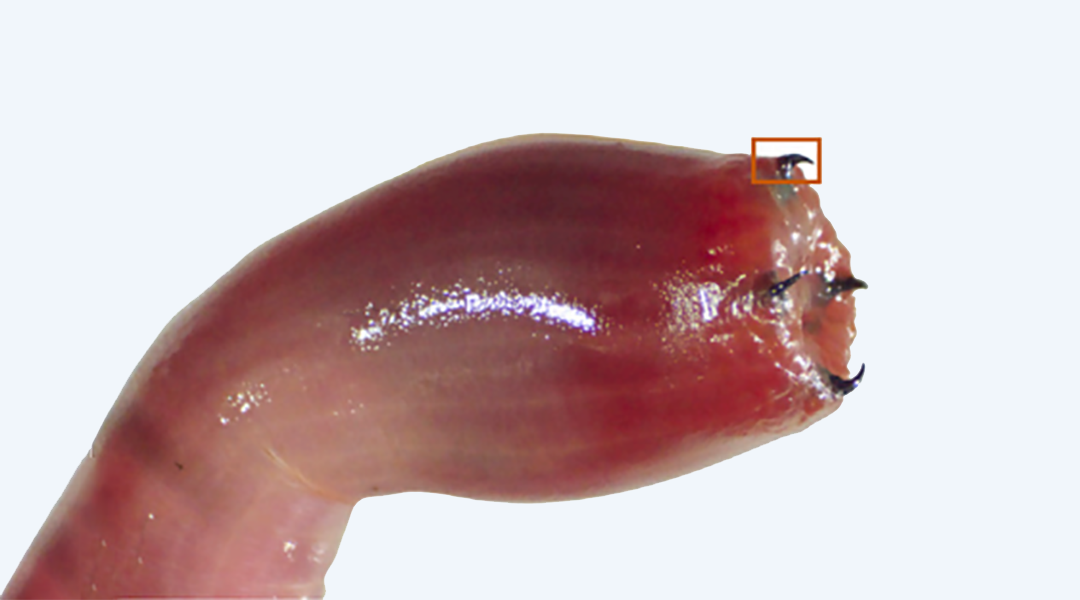
How bloodworms build their copper teeth
Scientists uncover how one small protein juggles multiple roles in shaping the bloodworm’s fang-like copper teeth.
ASN Newsletter
Sign up for our newsletter and receive the latest science news directly to your inbox.
Beam me up to 5G, Schottky
With a re-imagined architecture, these new Schottky diodes are being developed for better communication devices.
Parkinson’s disease treatment based on artificial enzymes
Researchers in Shanghai report a potential therapeutic based on Prussian blue to tackle Parkinson’s disease.
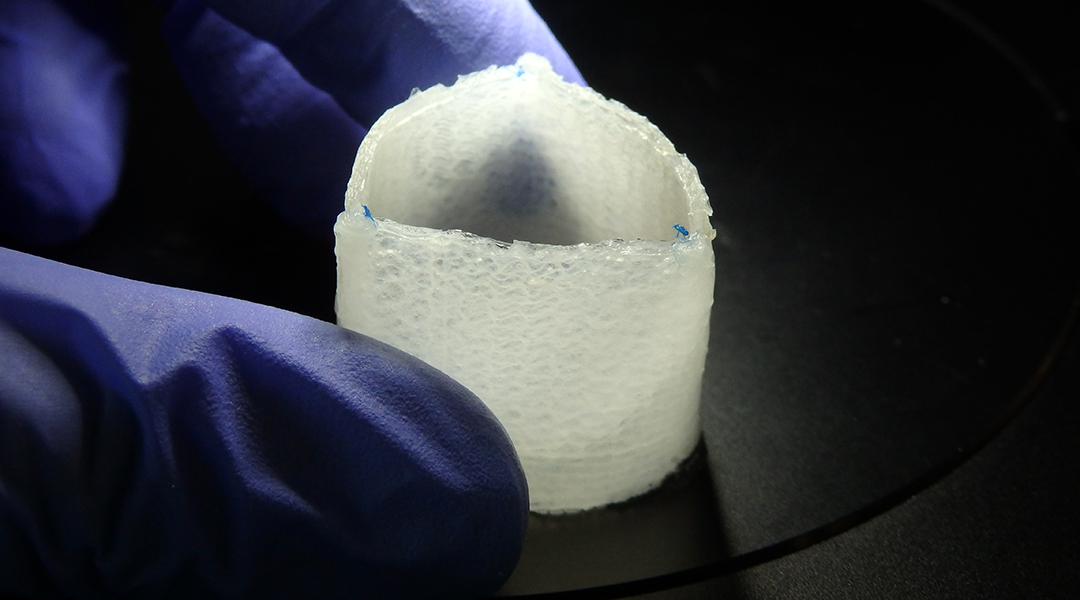
Artificial heart valves that evolve into a patient’s own tissue
To avoid the need for repeated surgery, scientists are developing durable artificial heart valves from regenerated tissue.

Smart knitted garments monitor the heart
Wearable devices for health monitoring don’t have to be limited to just smart watches and fitness trackers.

Quantum advantage tested in quantum games
A set of quantum computers was put to the test by playing the notorious triangle game.

Scientists test the link between tiny subconscious gestures and stress
Capable of measuring stress through micro gestures “EmoSense” could find its way to wearable electronics in the future.
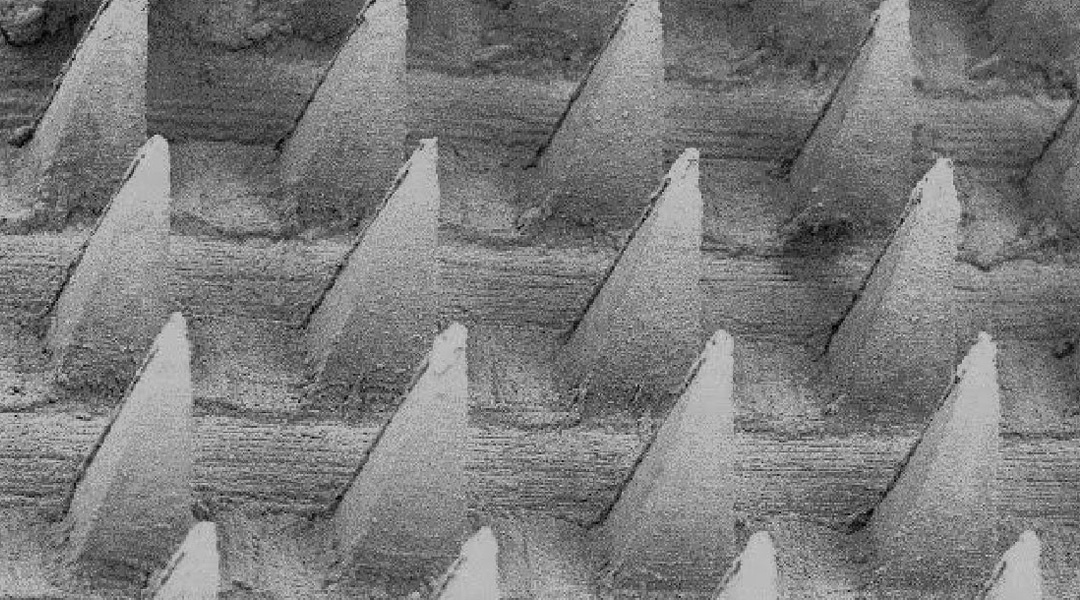
Making long-term microneedle therapies safer
Researchers demonstrate a technique for reliably coating microneedles with antibacterial agents
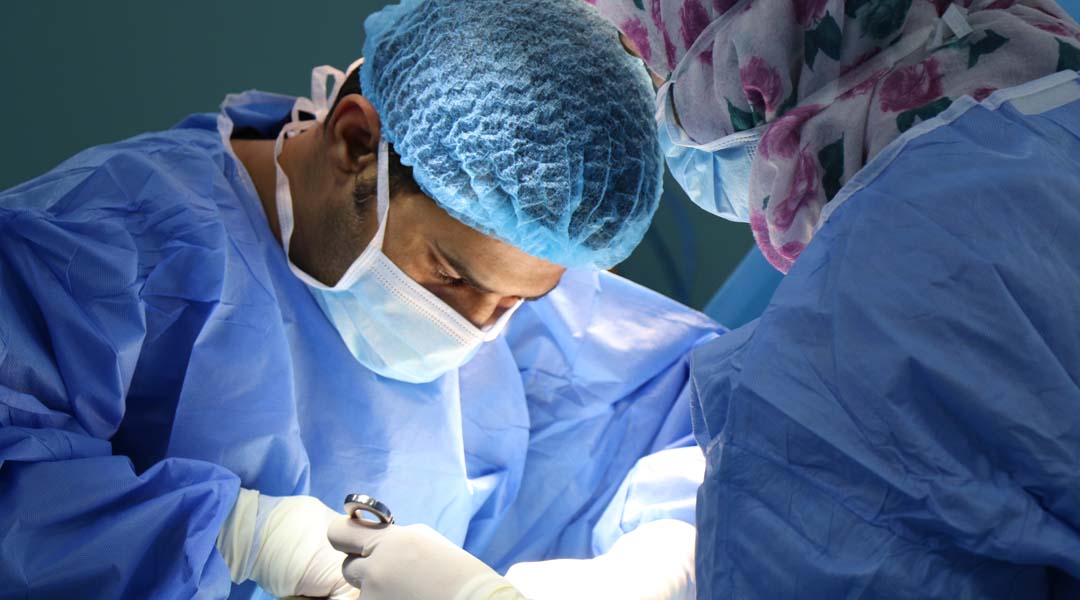
Sealant with integrated sensors rapidly detects leaks after stomach surgery
An acid sensitive hydrogel makes it possible to detect dangerous leaks before they cause damage.

Ozone pollution disrupts genes controlling circadian rythyms
Study finds air pollution, specifically ozone exposure, has a disruptive affect on the genes responsible for circadian rhythms in the lungs.
Scientists test the link between tiny subconscious gestures and stress
Capable of measuring stress through micro gestures “EmoSense” could find its way to wearable electronics in the future.
Making long-term microneedle therapies safer
Researchers demonstrate a technique for reliably coating microneedles with antibacterial agents
Sealant with integrated sensors rapidly detects leaks after stomach surgery
An acid sensitive hydrogel makes it possible to detect dangerous leaks before they cause damage.
Ozone pollution disrupts genes controlling circadian rythyms
Study finds air pollution, specifically ozone exposure, has a disruptive affect on the genes responsible for circadian rhythms in the lungs.
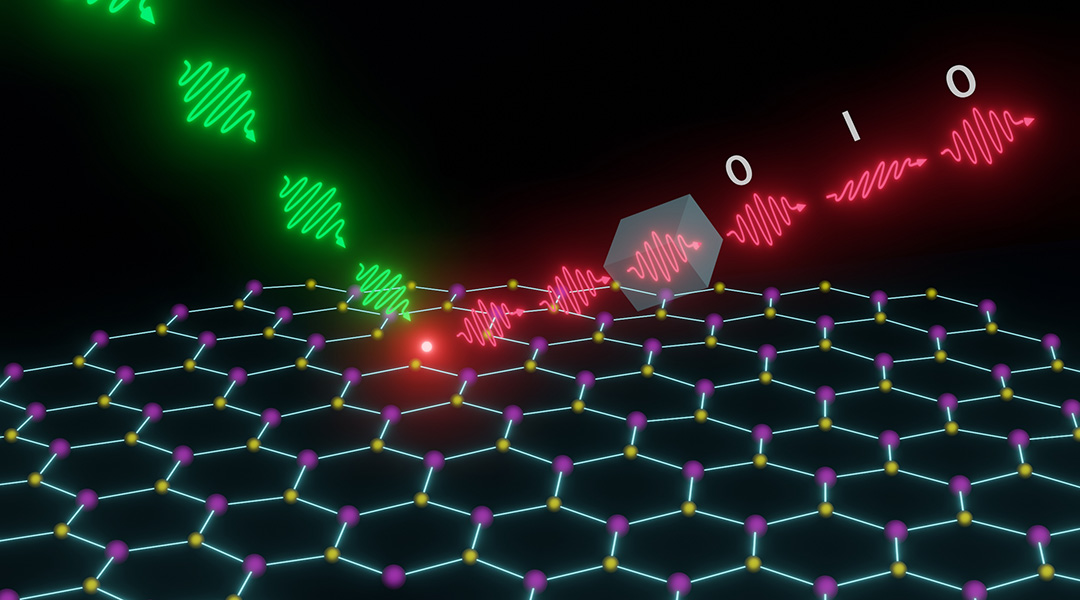
Single photons light up quantum encryption
Exploiting defects in 2D hexagonal boron nitride to create reliable single photons, researchers have upped their quantum encryption game.

Science fiction to reality: Space-based solar power
With climate change, the weaponization of energy, lower satellite launch costs, incentives to harness space-based solar power are on the horizon.
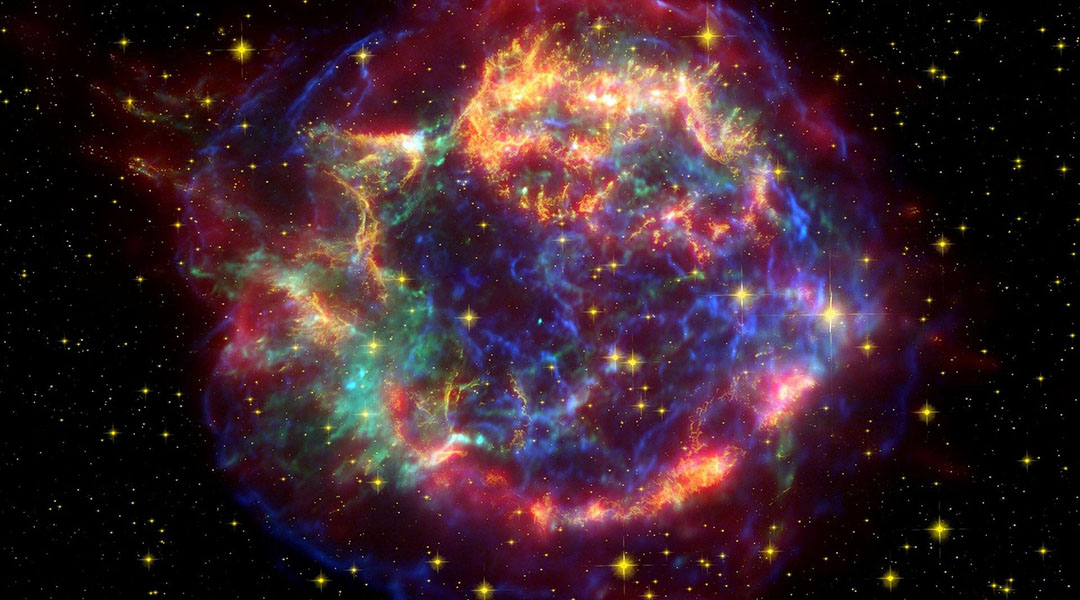
A bright future for supernovae
Researchers have found that supernovae explosions are preceded by observable radiation whose features should make it possible to distinguish the radiation of a future supernova from other light sources in space.

Dark matter from quantum gravity
Researchers at the Southern University of Science and Technology in China ask if gravitons can be promising candidates for dark matter components.
Single photons light up quantum encryption
Exploiting defects in 2D hexagonal boron nitride to create reliable single photons, researchers have upped their quantum encryption game.
Science fiction to reality: Space-based solar power
With climate change, the weaponization of energy, lower satellite launch costs, incentives to harness space-based solar power are on the horizon.
A bright future for supernovae
Researchers have found that supernovae explosions are preceded by observable radiation whose features should make it possible to distinguish the radiation of a future supernova from other light sources in space.
Dark matter from quantum gravity
Researchers at the Southern University of Science and Technology in China ask if gravitons can be promising candidates for dark matter components.
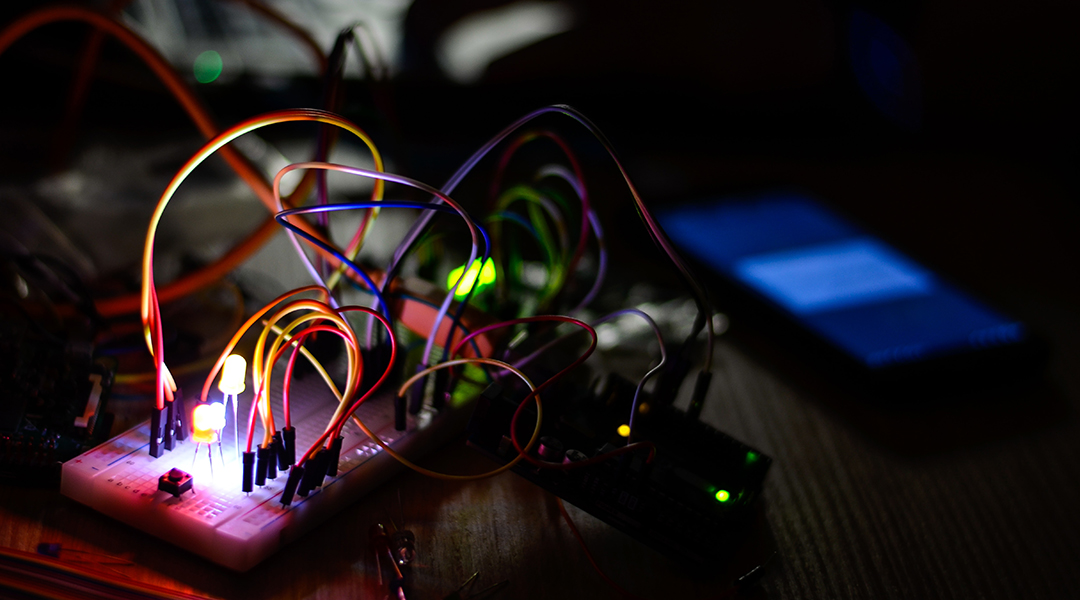
Using light to power wireless brain-like computers
An optical device uses light-based signals for computation and communication and is a vital step toward advanced neuromorphic computers.
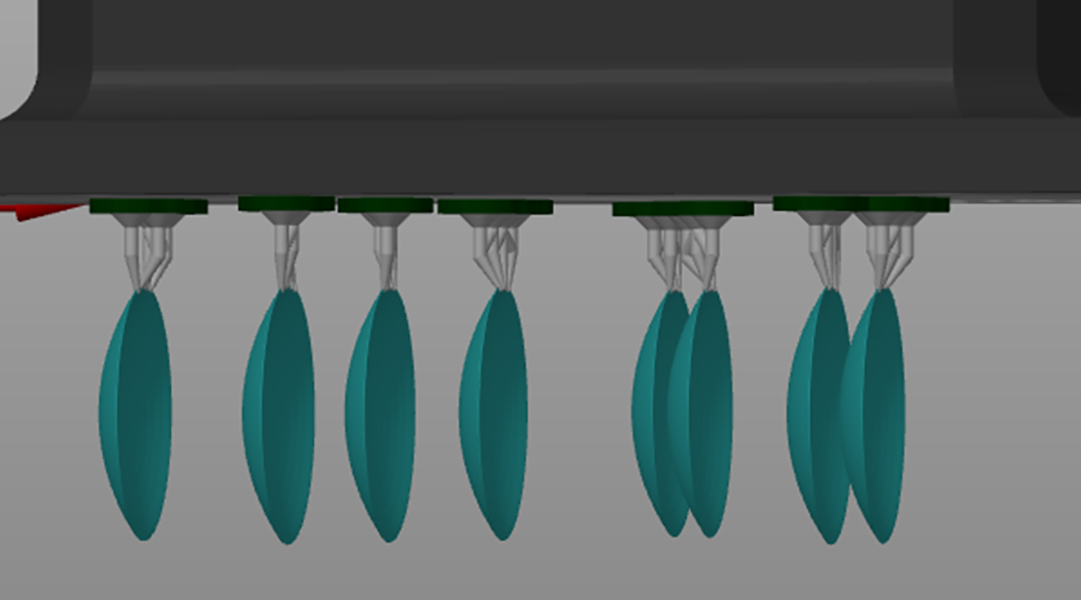
Low-cost contact lenses to tackle color blindness
Scientists used 3D printing and an inexpensive ink to make colored contact lenses that could improve color distinction in color-blind people.
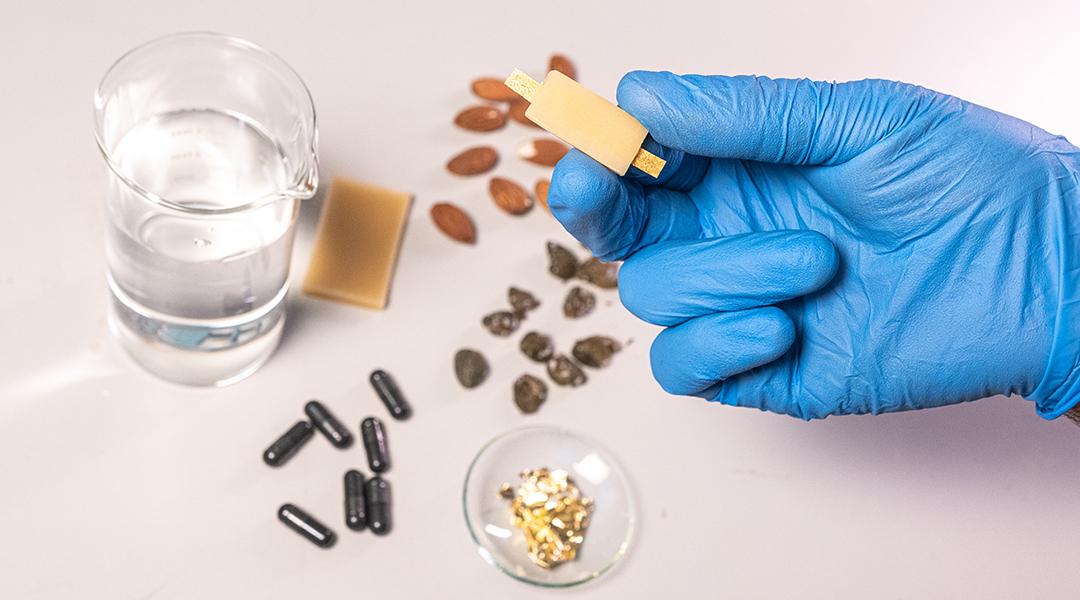

A battery made from food makes edible electronics palatable
An edible and rechargeable battery to power devices used for GI tract monitoring, therapeutics, and analyzing food quality.
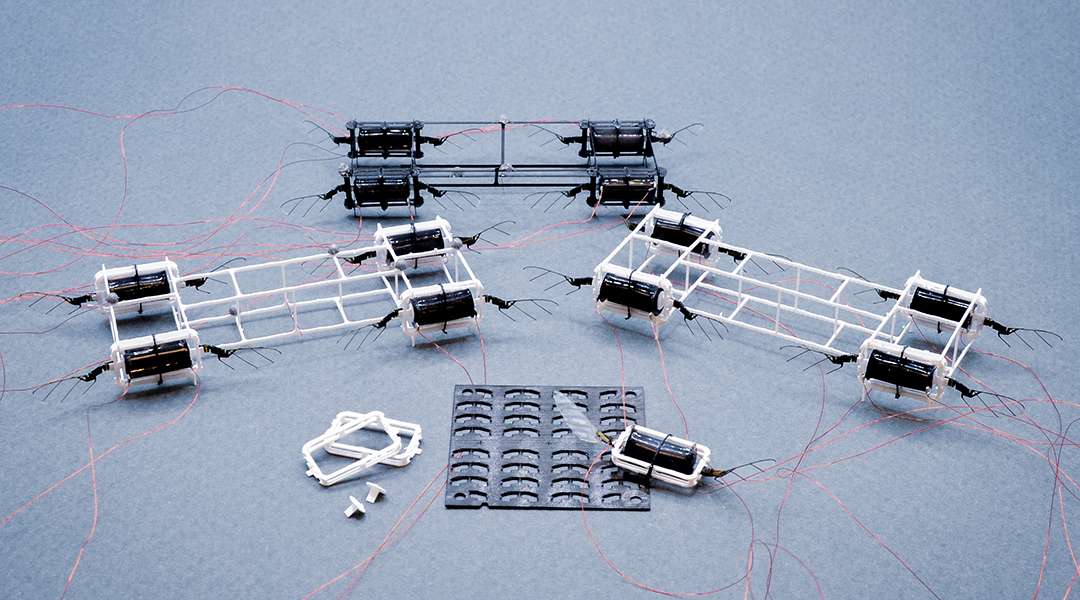
Robotic insects that fly in teams to lift objects
To make swarms of honeybee-sized robots, researchers propose new design and fabrication methods to cut down on time and resources.
Using light to power wireless brain-like computers
An optical device uses light-based signals for computation and communication and is a vital step toward advanced neuromorphic computers.
Low-cost contact lenses to tackle color blindness
Scientists used 3D printing and an inexpensive ink to make colored contact lenses that could improve color distinction in color-blind people.
A battery made from food makes edible electronics palatable
An edible and rechargeable battery to power devices used for GI tract monitoring, therapeutics, and analyzing food quality.
Robotic insects that fly in teams to lift objects
To make swarms of honeybee-sized robots, researchers propose new design and fabrication methods to cut down on time and resources.

Plant immunity to fungal pathogens developed millions of years ago
As plants evolved to live on land, so too did their immune systems, offering protection against dangerous fungi.
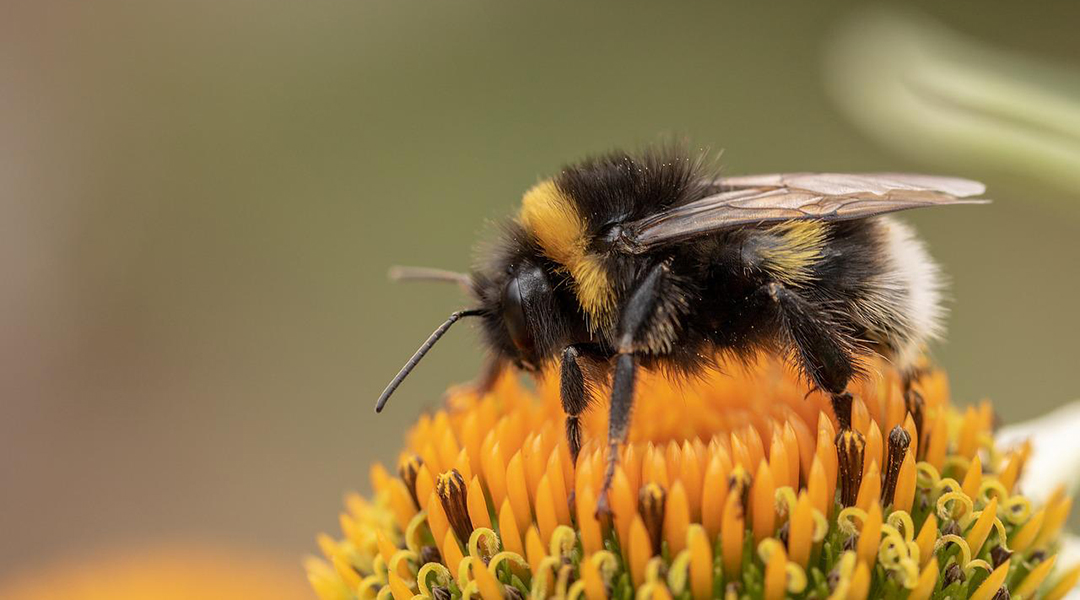

Isolated bumblebees become socially awkward
Low levels of socialization are sufficient in maintaining typical behavior and brain development in bumblebees.
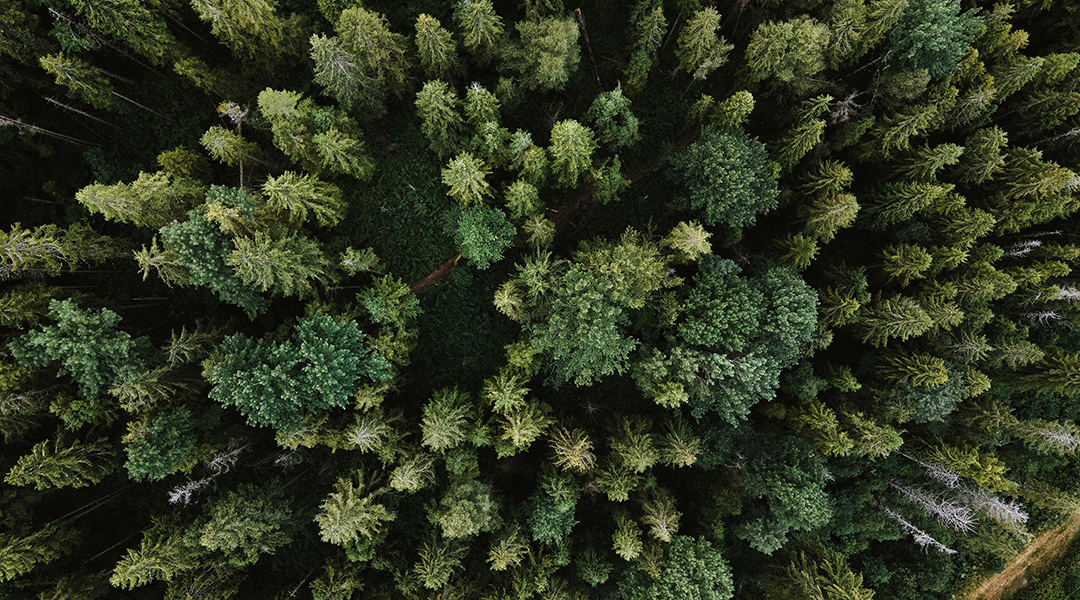

Forest restoration benefits depend on location
The long-term benefits of global forest restoration to support biodiversity and ecosystems depends on climate and forest type.
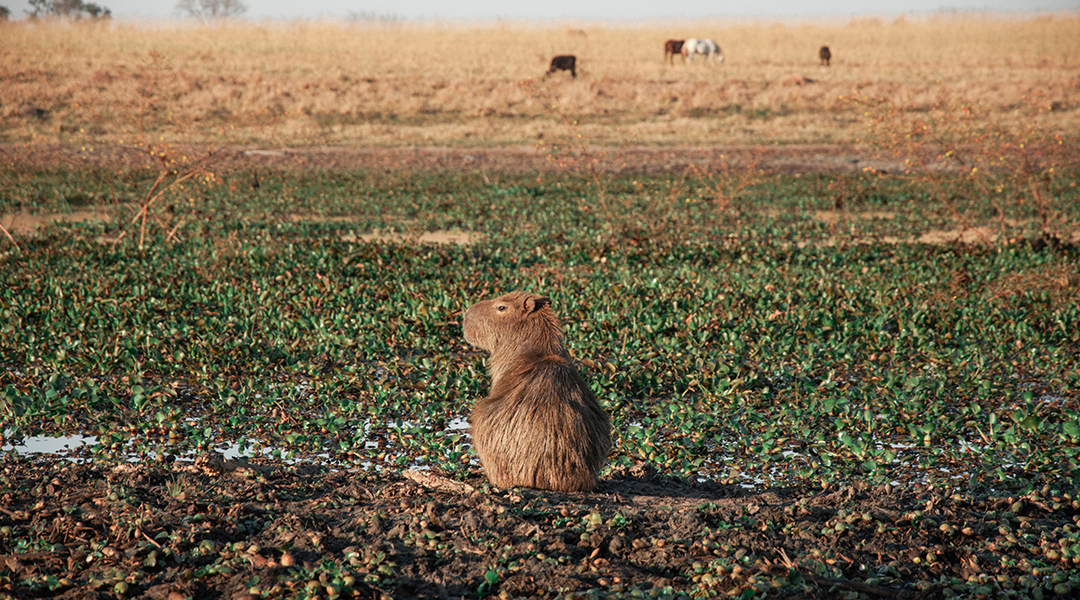

How the capybara could improve biofuels
Unique enzymes found in the gut of sugarcane-eating capybaras could help convert agricultural waste into low-carbon biofuels.
Plant immunity to fungal pathogens developed millions of years ago
As plants evolved to live on land, so too did their immune systems, offering protection against dangerous fungi.
Isolated bumblebees become socially awkward
Low levels of socialization are sufficient in maintaining typical behavior and brain development in bumblebees.
Forest restoration benefits depend on location
The long-term benefits of global forest restoration to support biodiversity and ecosystems depends on climate and forest type.
How the capybara could improve biofuels
Unique enzymes found in the gut of sugarcane-eating capybaras could help convert agricultural waste into low-carbon biofuels.
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.