Scientists have developed a CRISPR-based diagnostic that detects pathogens in blood with million-fold greater sensitivity—without the need for DNA amplification.

Scientists have developed a CRISPR-based diagnostic that detects pathogens in blood with million-fold greater sensitivity—without the need for DNA amplification.
New probe system offers real-time protein mapping within living cells, unlocking insights into cellular function and disease mechanisms.

Scientists achieve threefold speed boost for DNA nanomotors and applied them to breakthrough virus detection for SARS-CoV-2 and RSV tests.
Microscopic robots made out of a patient’s own cells may be able to work inside the body to repair damage, scope out signs of disease, or fight off infections.

Molecules isolated from a rare cyanobacteria found in Japan found to have UV-absorbing, antioxidant, and anti-aging properties.
When building a functional model of the brain, it’s crucial to think about more than just neurons.
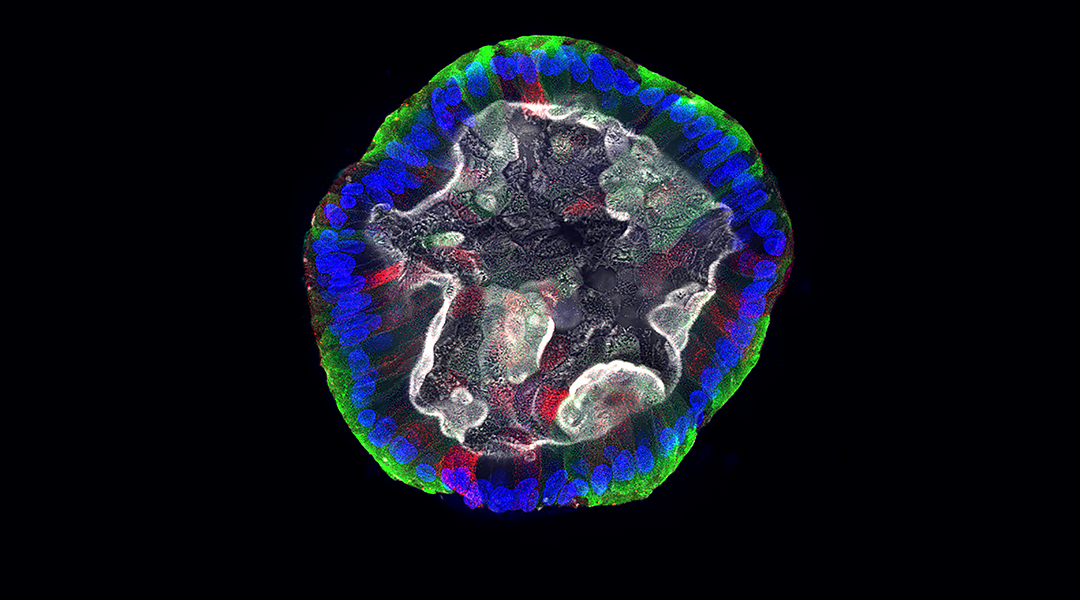
Addressing the lack of diversity in drug testing, scientists are using organoids from voluntary donors to enhance equity and inclusion.

Bacteria residing inside tumors provide a surprisingly powerful immunotherapy platform to combat different cancers.
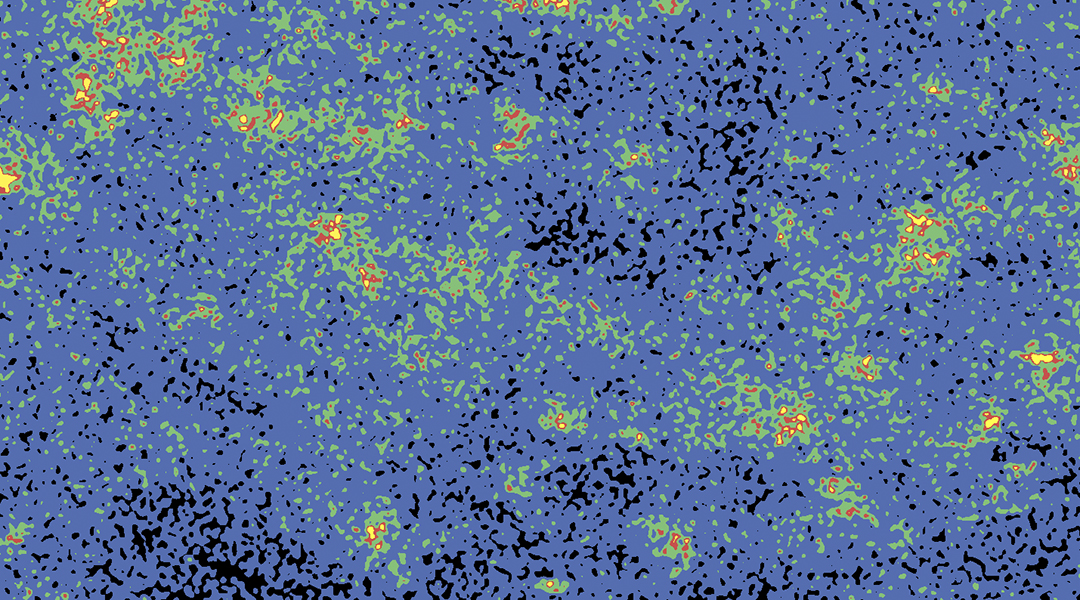
Catalysts that mimic antioxidase enzymes show promise in treating inflammatory diseases, such as gum disease, lupus, or cancer.
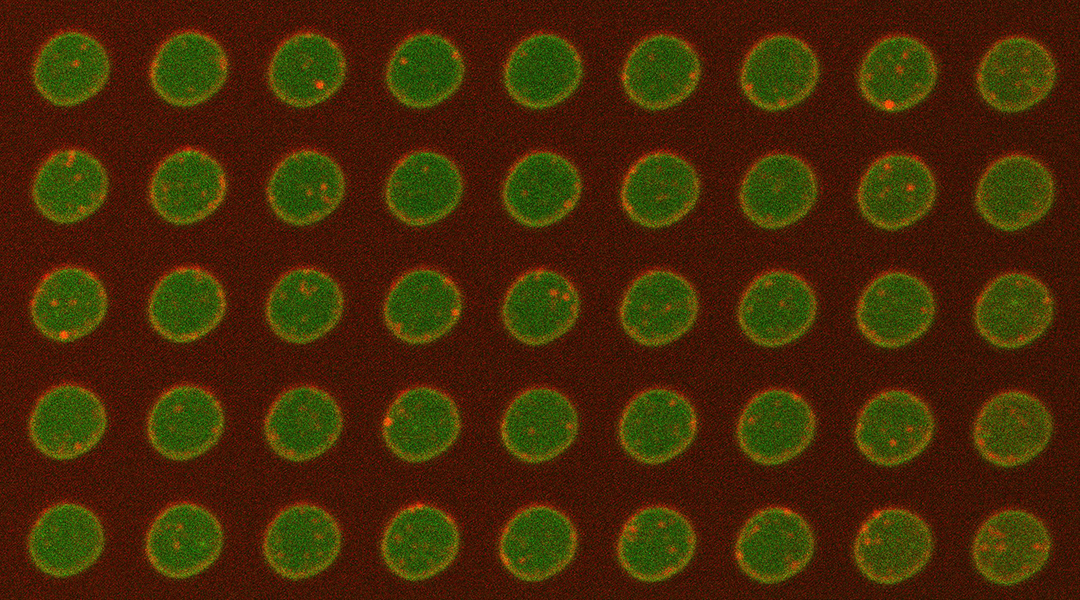
Compared to other platforms, this new “on-a-chip” system allows membrane proteins to be studied in their natural state.