Minute fossils from the depths: Deep life on Earth thrives, is fossilized, and may help us identify life elsewhere.
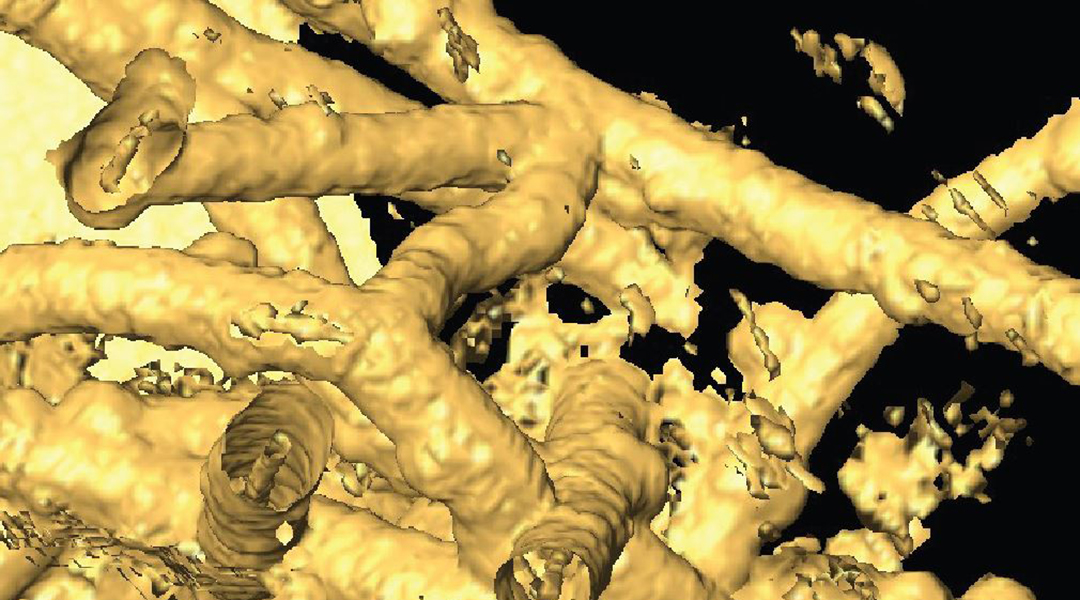

Minute fossils from the depths: Deep life on Earth thrives, is fossilized, and may help us identify life elsewhere.

A plethora of exciting applications in biology has been found for Parrondo’s paradox, in which losing strategies can be combined to produce winning outcomes.
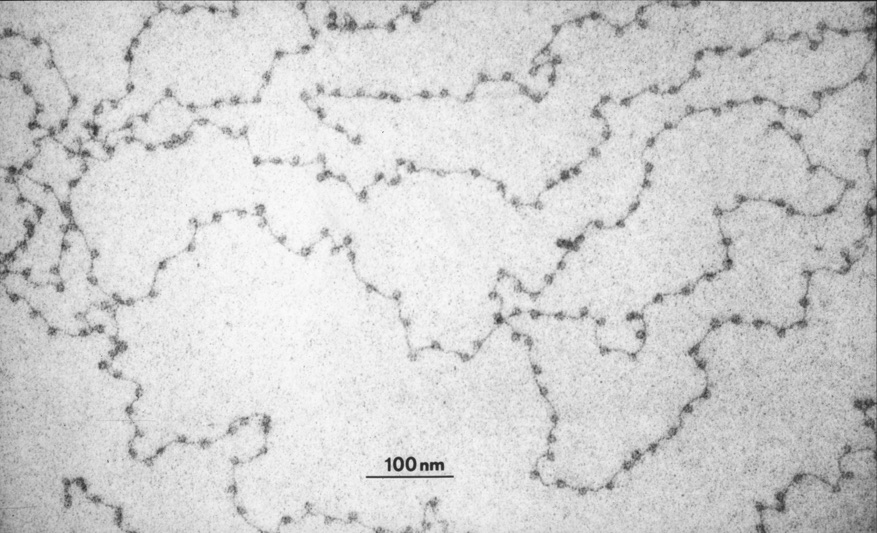
It is now possible to distinguish the pattern of DNA fragments of normal cells from cancerous cells within the blood of individuals with surgically-operable early stage cancers.1 Regions of the genome have their own local differences in cancer-specific,...
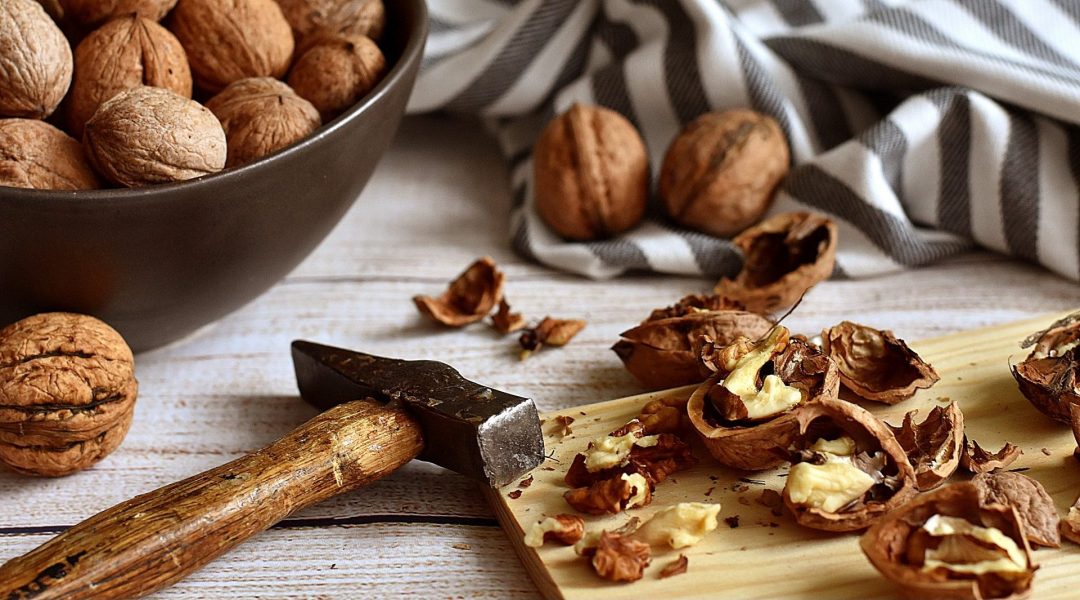

A novel cell type with interlocked packing found to be responsible for the hardness of walnuts’ shell

The domestication of crops is a directed evolutionary process that has lasted for most of human history. It has allocated naturally occurring mutations that encode traits for higher production, better taste, and convenient cultivation. These traits can better manage...
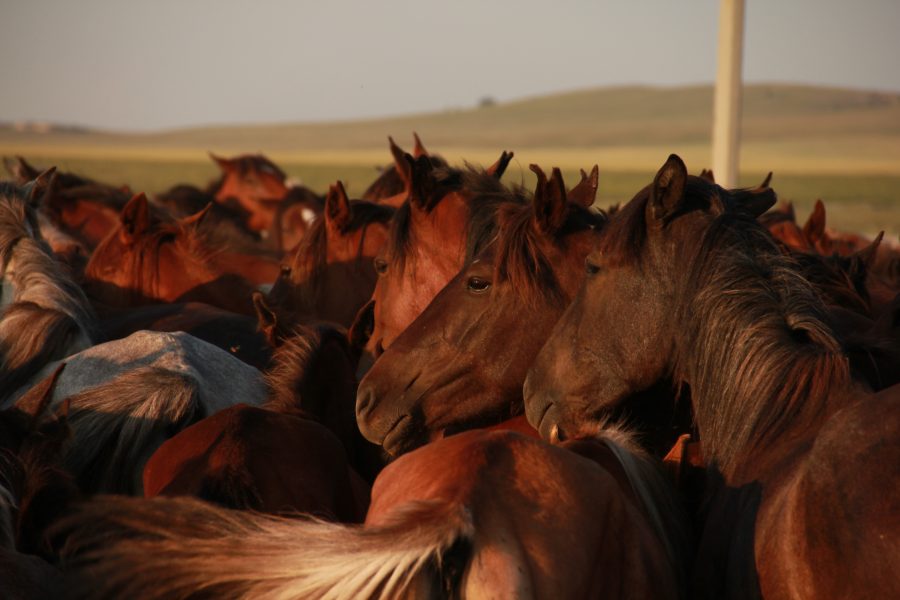

By a process of elimination, ancient DNA sequences are clarifying the history of horse culture.1 Domestic horses were genetically very diverse for the last five millennia. However, in the last thousand years, this pool of diversity is shallower due to breeding for...
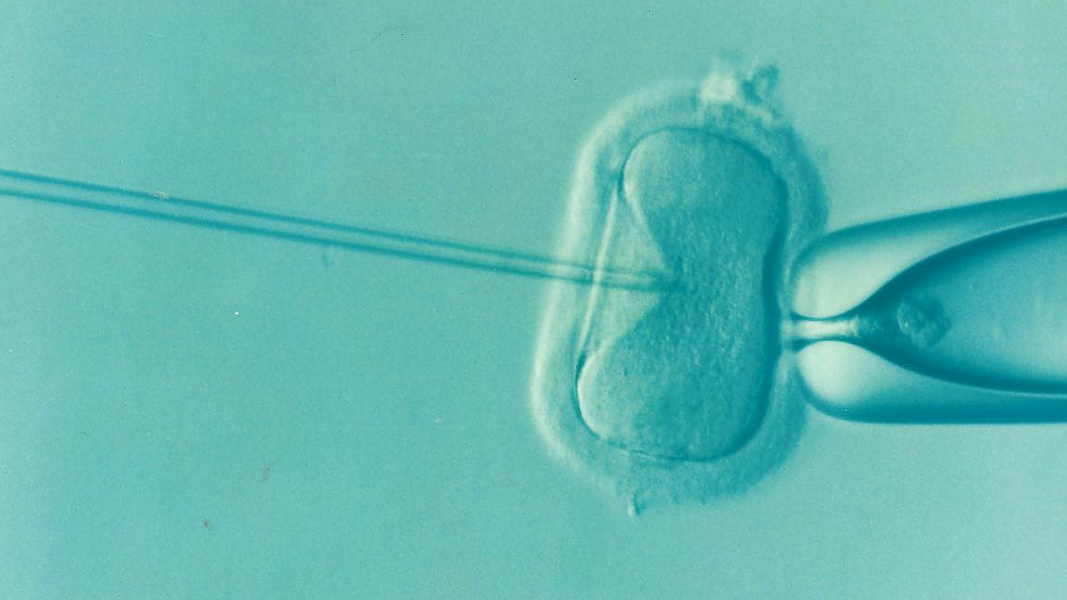
Machine-learning applied to IVF.
Members of the Max Planck Research Network in Synthetic Biology put together a special issue on synthetic cells for Advanced Biosystems.

Scientists measured nanoscale structural alterations in the brains of mice after chronic corticosterone administration using a novel nanoscale optical imaging technique and gene expression analysis.
How T cells maintain homeostasis and maximize the size of the peripheral T cell pool are important questions that have fascinated both immunologists and mathematicians.