Made of self-assembling nanoparticles and a microgel, this new material could overcome limitations in 3D bioprinting.


Made of self-assembling nanoparticles and a microgel, this new material could overcome limitations in 3D bioprinting.
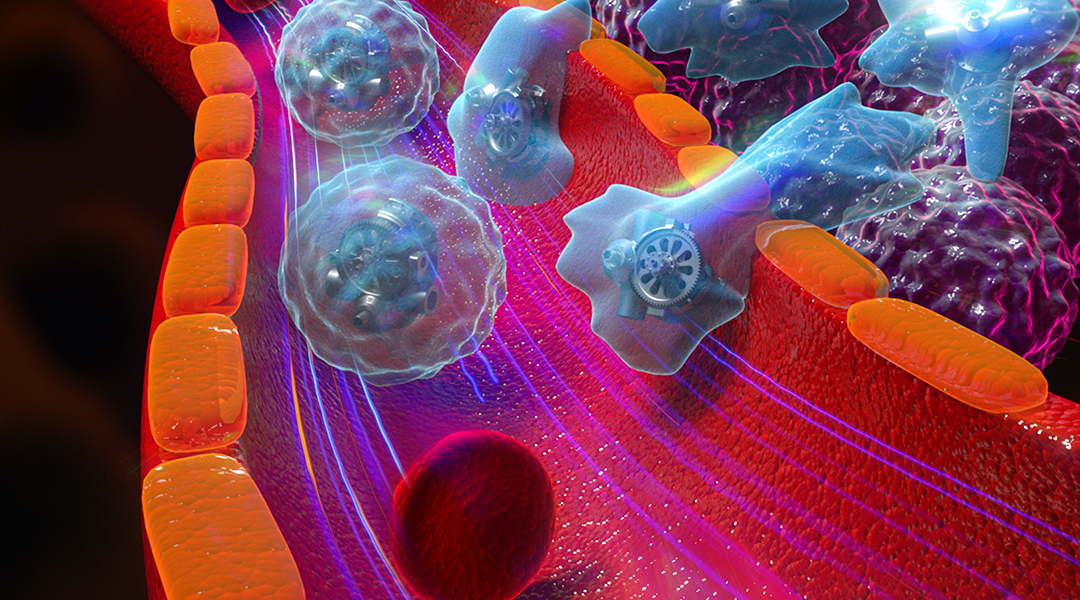
Swimming cellbots capable of autonomous motion and drug encapsulation can deliver their payload at desired sites.
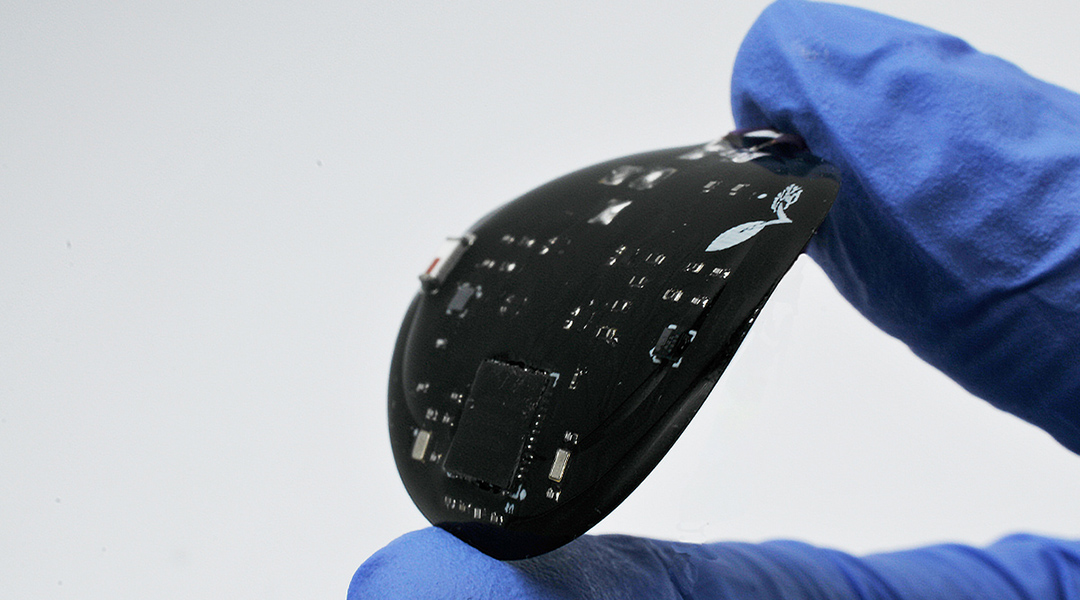

A team led by Wubin Bai developed a novel wearable sensor patch that provides a safe, real-time, less invasive and low-cost way to track a patient’s recovery.
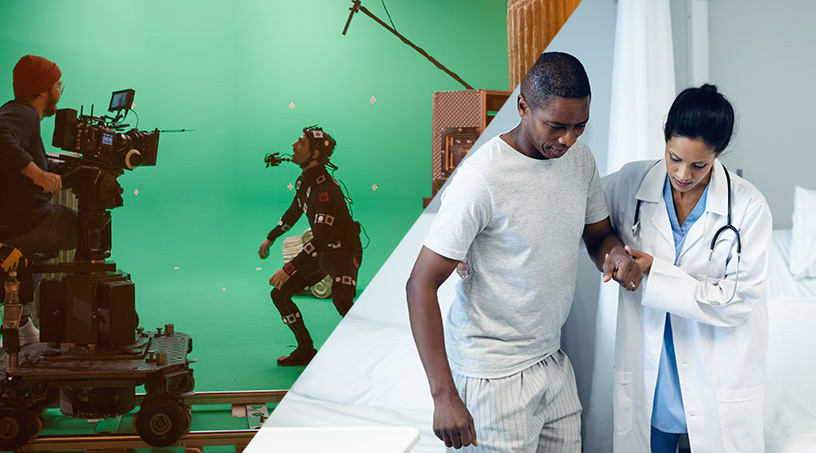

The Hollywood technology that brings impossible creations to life onscreen could bring better, fairer care to patients around the world.
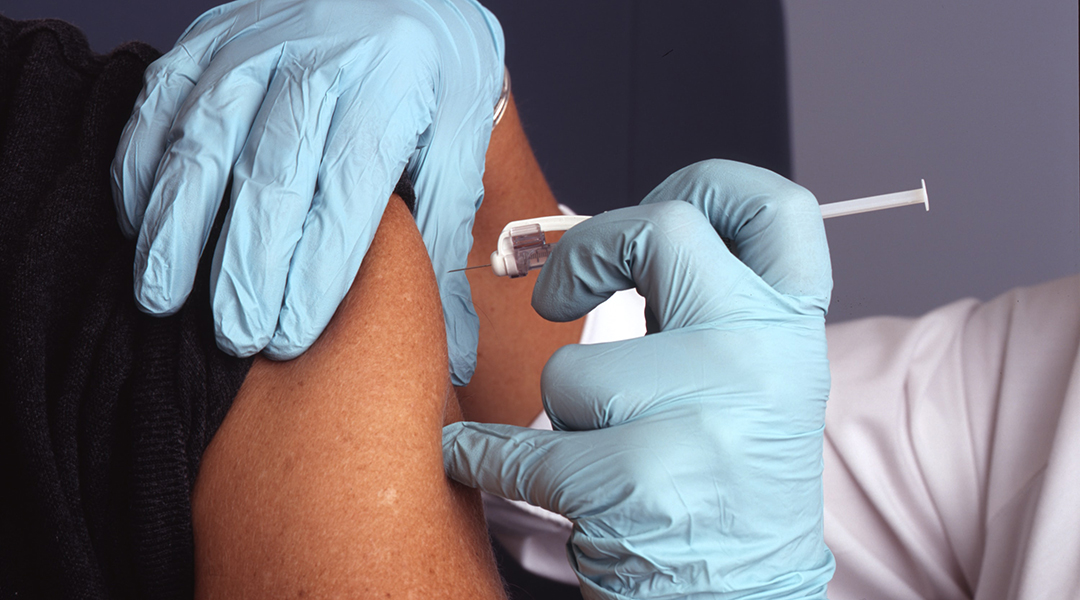
A rare type of antibody found in some individuals could help develop an HIV vaccine to target highly diverse viral strains.
Implants containing cyanobacteria help produce oxygen within heart tissue to repair damage done after a heart attack.
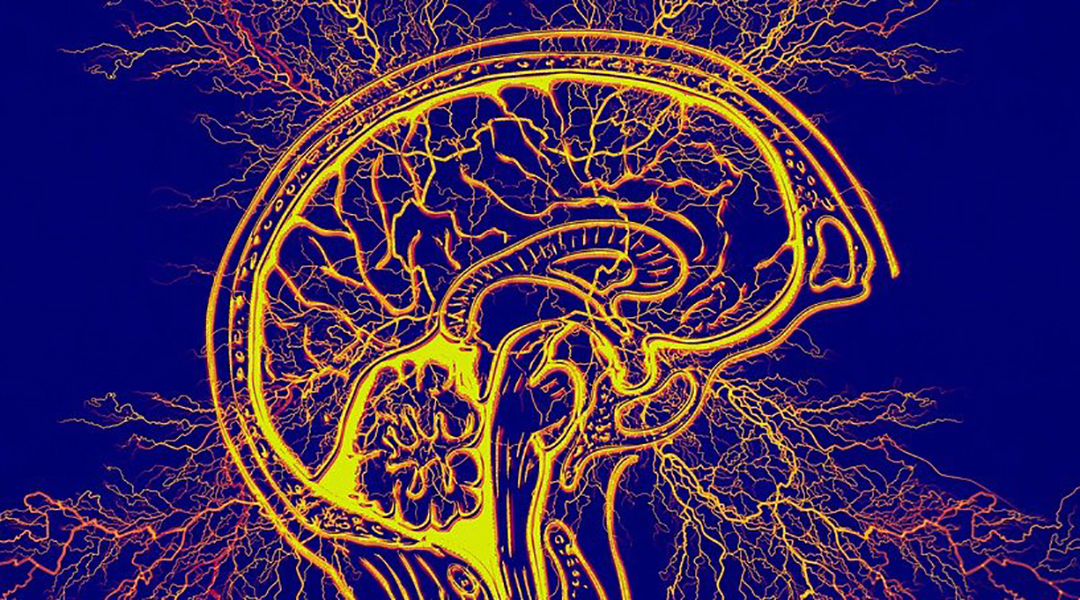
Early results for an anti-seizure drug administered as a nasal spray show a more targeted approach to helping get seizures under control.
Clumping proteins act as vaccine adjuvants, activating immune signalling pathways triggered by cell stress.
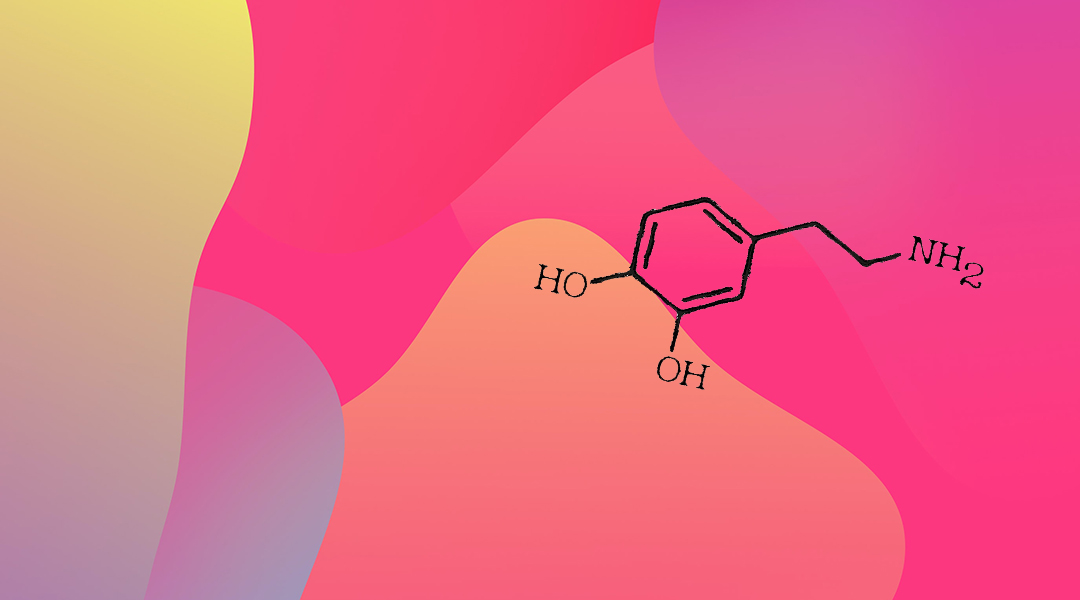
Dopamine might play a more complex role than was previously assumed when it comes to learning and reward association.
With more research, there is a potential for vaccines to have both adaptive and trained immunity to fight different diseases.