A dense diamond nanoneedle array for delivering fluorescent probes and drugs to a large number of cells for use on gene and cell therapy.
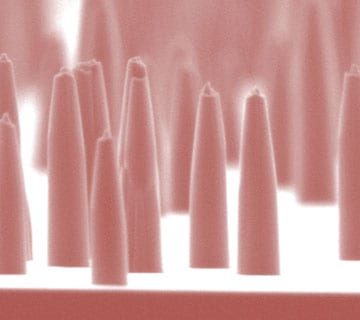

A dense diamond nanoneedle array for delivering fluorescent probes and drugs to a large number of cells for use on gene and cell therapy.
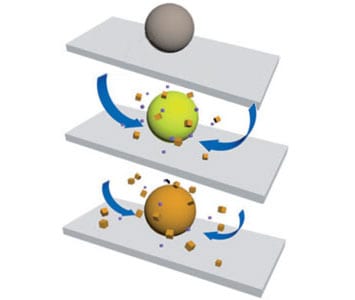
A microscopic pump starts up when irradiated with UV light but its material continues to work when the stimulus is removed.
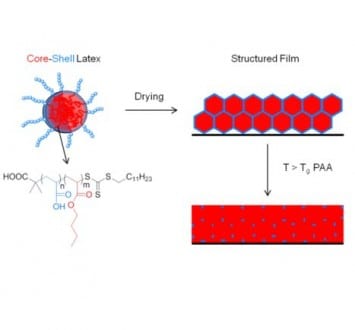
Researchers from France prepared exceptionally stiff and tough polymer films with a very low volume fraction of percolating phase.
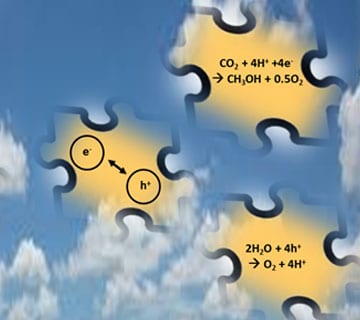
Sustainability – solar fuels from the sun, not fossil fuels from the earth.

A topical issue of Angewandte Chemie and a GDCh Colloquium in Darmstadt, Germany.

Recent research into combining graphene, graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide with polymers for use as barrier materials is reviewed.

A terahertz laser developed at the Paul Scherrer Institute makes it possible to control a material’s magnetisation at a timescale of picoseconds.

Experts from Michigan Technological University review the recent developments in molecularly imprinted nanoparticles by surface imprinting techniques.

Bio-optical methods have been an essential tool for biological observation and clinical diagnosis, and optoacoustic (photoacoustic) imaging is now emerging.

Special polydimethylsiloxane-coated deformed microcavity acts as an optical “whispering gallery”.