A new device setup enables an interface between biomolecules and electronic materials for biohybrid electronics.


A new device setup enables an interface between biomolecules and electronic materials for biohybrid electronics.
A miniaturized, tetherless needle offers a safe means of performing surgery, treating cancer, and performing diagnostic tests.

Study participants were more comfortable with voice-based AI companions compared to robots that act and look like humans.

Researchers calculate the automation risk of almost 1000 existing occupations and provide alternatives based on skill set.
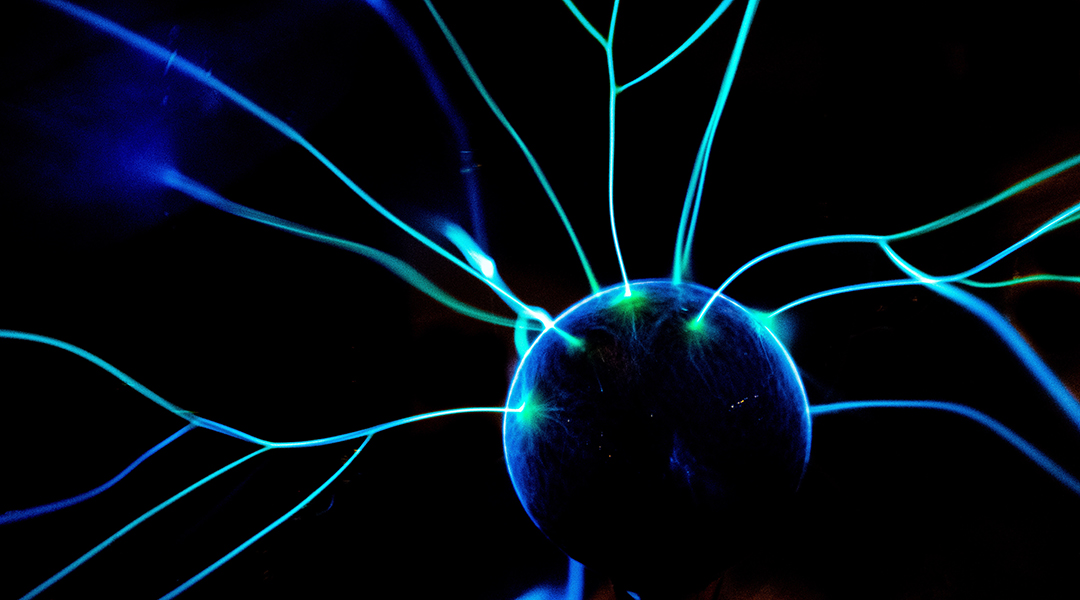

Memristor-based sensing devices generate biological-like electrical signals that mimic those found in the brain for better computing.
A new approach to in-memory computing proposes a new set up to create an artificial synapse that can both store and process data.
With a re-imagined architecture, these new Schottky diodes are being developed for better communication devices.
Researchers in Shanghai report a potential therapeutic based on Prussian blue to tackle Parkinson’s disease.
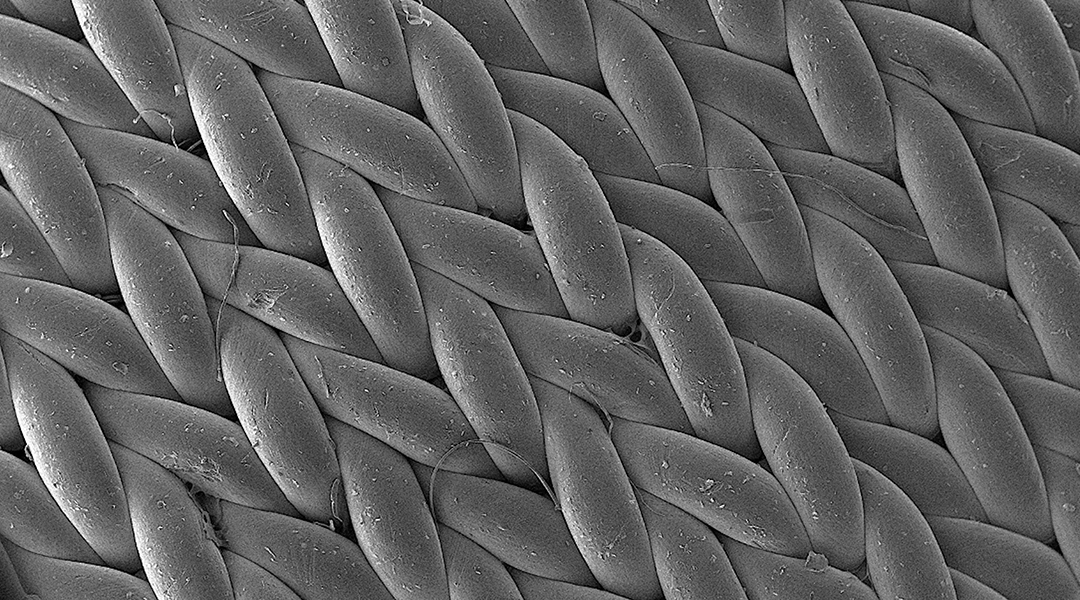

Wearable devices for health monitoring don’t have to be limited to just smart watches and fitness trackers.
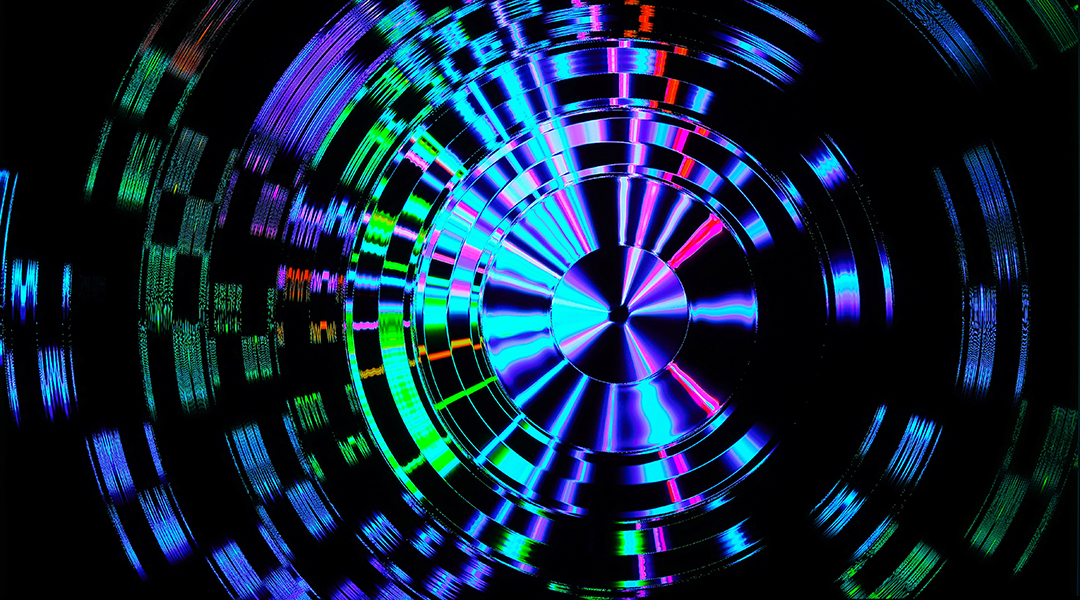

A set of quantum computers was put to the test by playing the notorious triangle game.