A new, flexible, and self-powered sensor made by magnetoelectric materials can convert mechanical stimuli to electrical signals for robots with a “soft touch”.
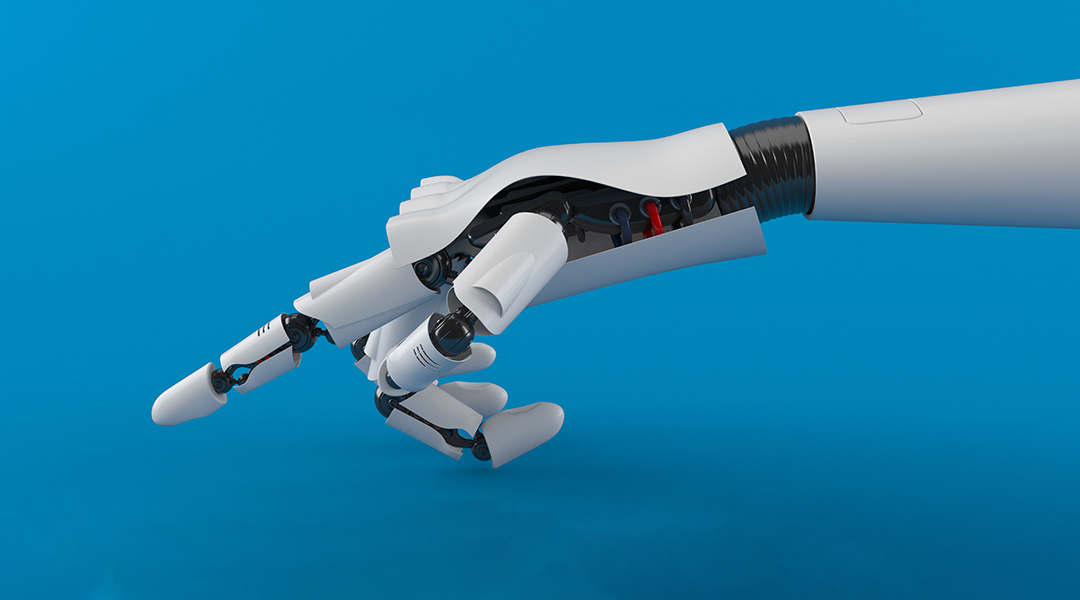

A new, flexible, and self-powered sensor made by magnetoelectric materials can convert mechanical stimuli to electrical signals for robots with a “soft touch”.
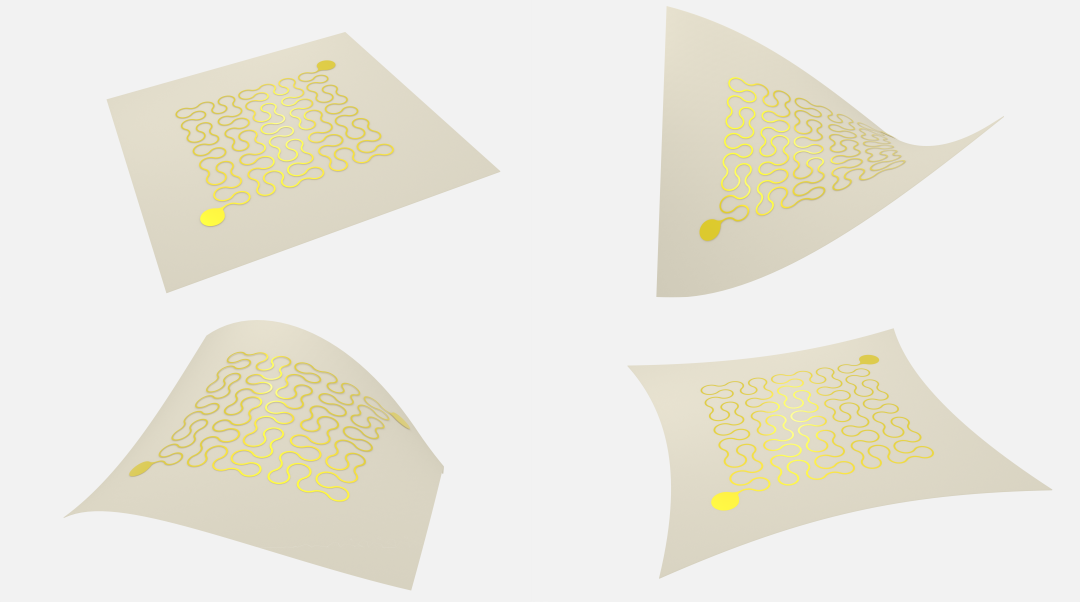
To mimic the fluid and versatile movement of soft-bodied animals, soft robots require their own “muscles” to function.

Hello HAL, do you read me HAL?

Will artificial intelligence expand and enhance its teaching prowess to the point where it can replace the professor in his or her traditional role?

Masking heat signatures from prying eyes, researchers develop a new material that functions as a cloaking device.

Researchers at Dartmouth have developed a miniature robotic bug that has a flexible body, is easily maneuverable, and can be completely flattened without damaging its functionality.

AI is being leveraged to provide machines with the capacity to match or even outperform humans in many endeavors. So what does this mean for the synthetic chemist?

Smart contact lenses could revolutionize the way in which we monitor brain activity and diagnose neurological diseases.

How do we reproduce the memory and processing capabilities of the human brain?

UCF researchers develop a device that mimics brain cells used for human vision. The invention may help to one day make robots that can think like humans.