Heat-based carbon nanotube/PDMS sensor developed at University of Michigan could detect terahertz radiation in real-time.


Heat-based carbon nanotube/PDMS sensor developed at University of Michigan could detect terahertz radiation in real-time.
Joint project aims to optimize materials and formulations for improved performance and cost for roll-to-roll manufacturing, including for OLED devices.
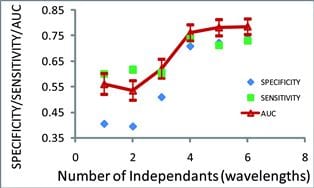
A novel screening approach for discriminating dysplasia from metaplasia in Barrett’s Esophagus using diffuse reflectance spectroscopy.
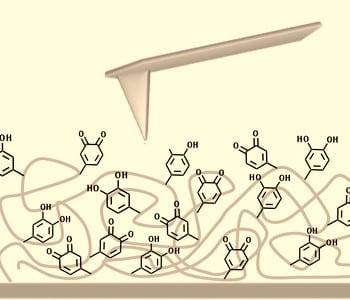
Team reports a catechol-based SAM technique to produce more homogeneous catechol-containing surface with improved adhesion properties.
A research group has uncovered the unique structural, electronic, optical, and defect properties of halide peroveskites.

A combination of nanotechnology and a unique twisting property of light could lead to new methods for ensuring the purity and safety of pharmaceuticals.
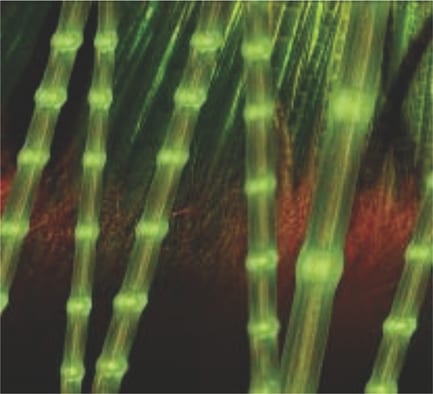
A biomimetic one-step fabrication approach is utilized to generate bamboo-like hybrid fibers at the micro- and nanoscale.

Silica-coated gold nanorods with absorption at precisely 780 nm cause action potentials in nerve cells when exposed to laser light.
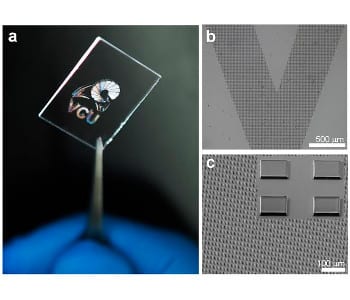
Researchers from Virginia Commonwealth University have found a way to fabricate precise, biocompatible architectures of silk proteins at the microscale.
A mechanism of growth of anisotropic metal oxides that was predicted 20 years ago has been observed for the first time.