The month’s top articles from the field of nanooptics, optoelectronics, metamaterials, optical devices, detectors & sensors, micro/nano resonators and more.
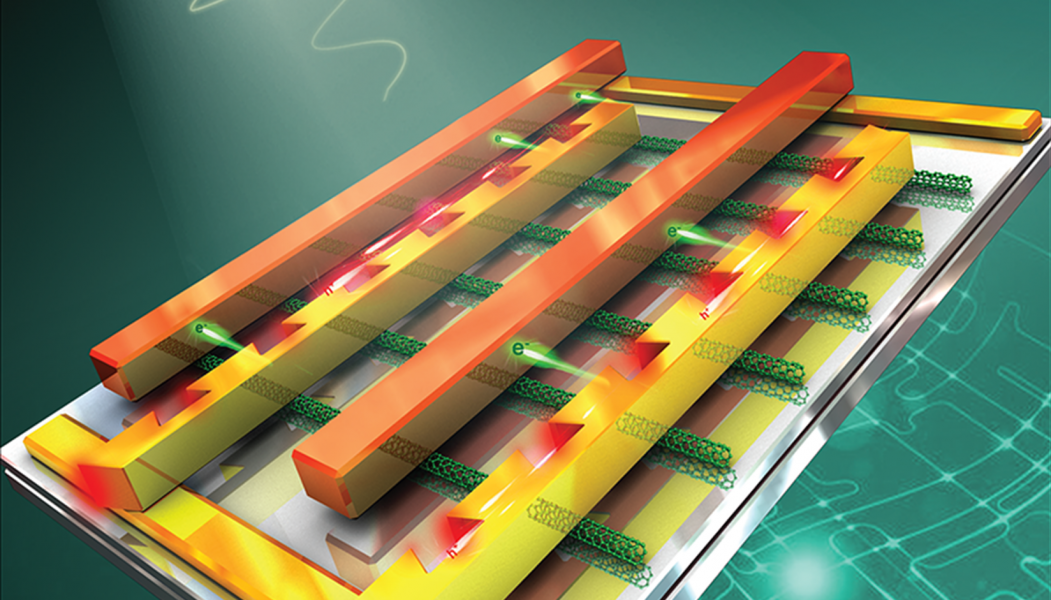

The month’s top articles from the field of nanooptics, optoelectronics, metamaterials, optical devices, detectors & sensors, micro/nano resonators and more.
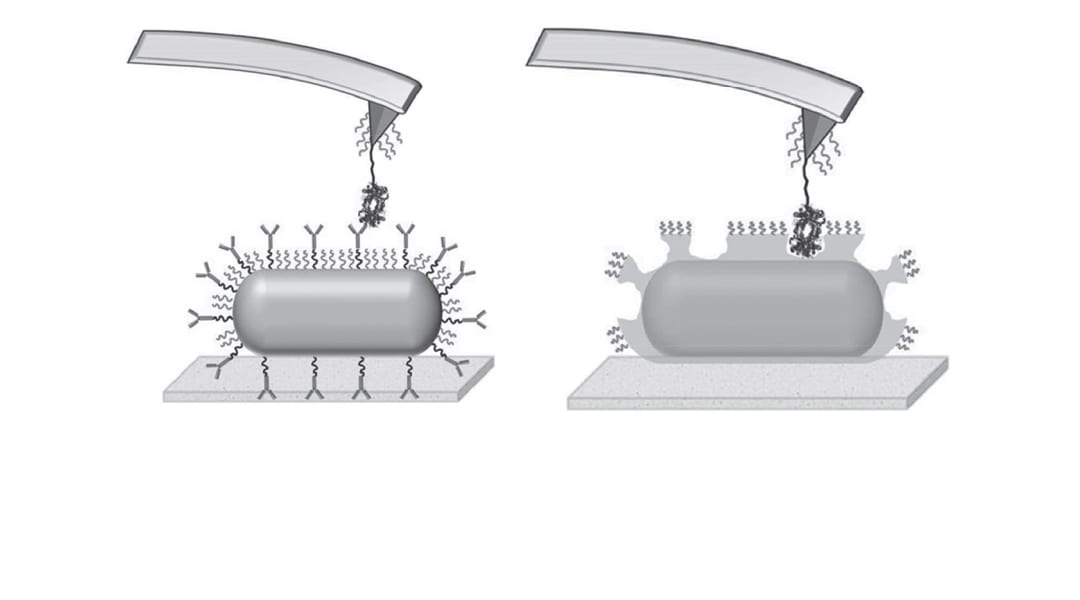
Biosensors using natural and artificial antibodies show different responses. Both systems are tracked with pico-newton resolution to find out why.
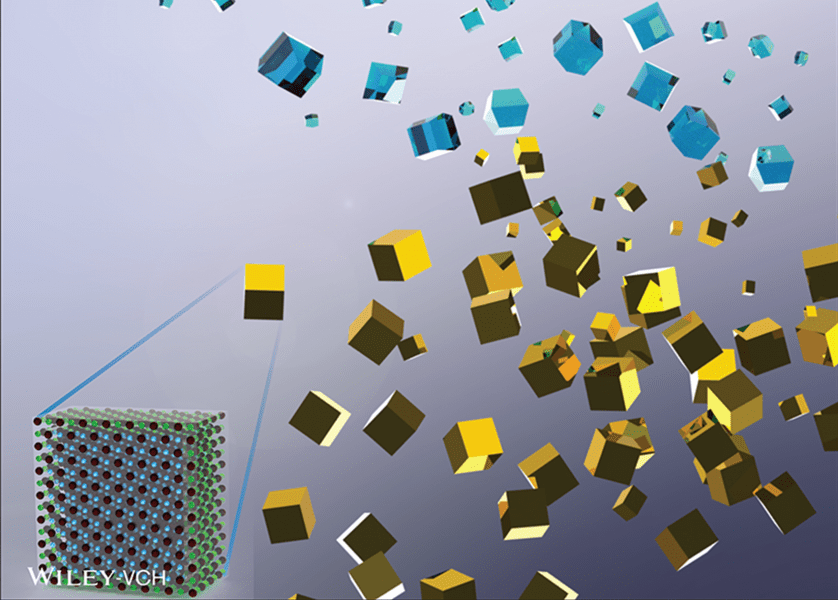
Researchers demonstrated a new approach to fabricate large-scale, complex nano-architectures of refractory plasmonic transition metal nitrides.

Researchers have used hydroprinting – a new and versatile technique – to prepare conductive features on 3D objects.
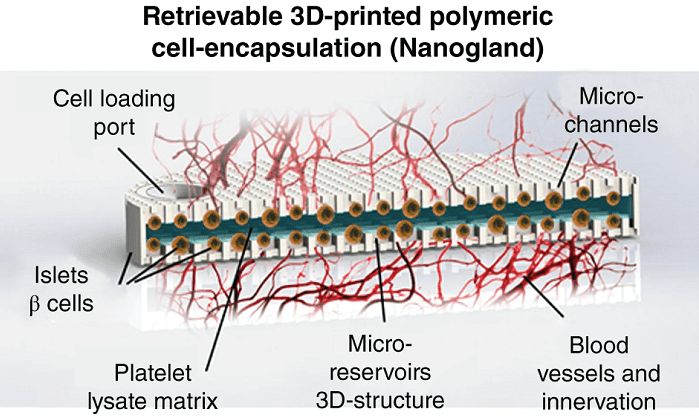
Nanofluidic implantables represent a recent advance in a broad effort for developing personalized, point-of-care medical technologies.

Specially designed carbon nanotube nanomotors undergo rotary motion in water, driving external mechanical loads on the nanoscale.
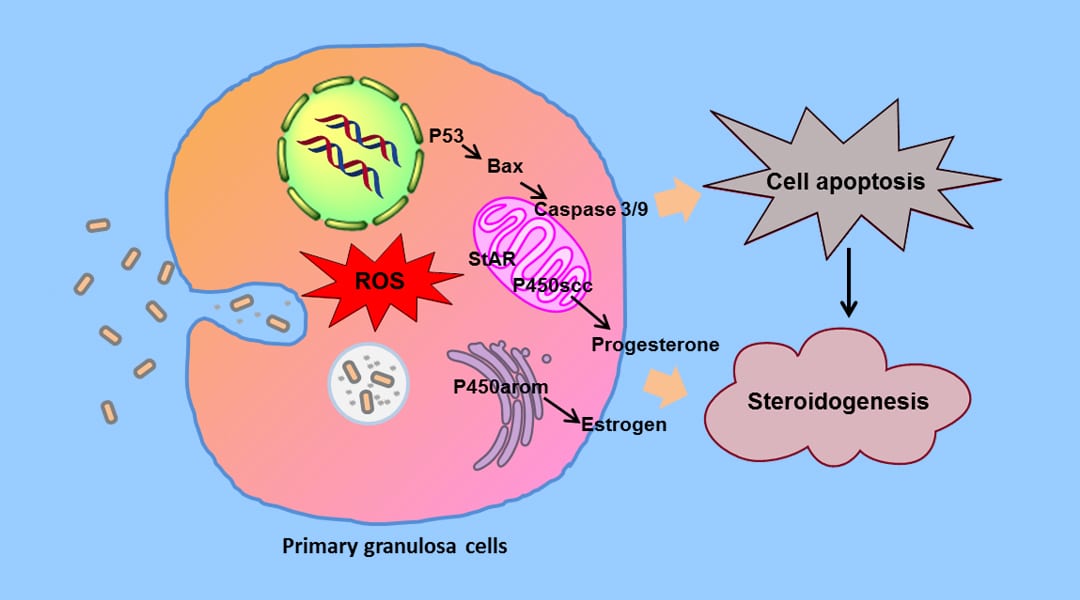
A study that looks at how silver nanomaterials could affect the female reproductive system.
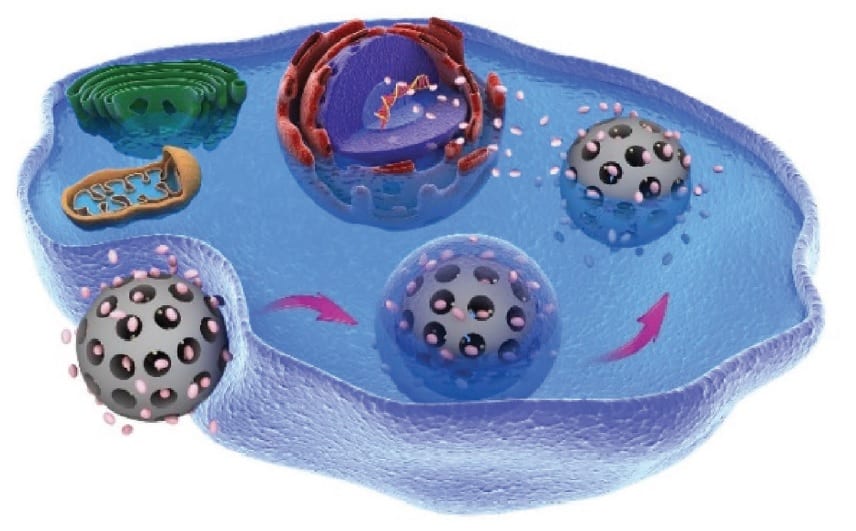
Antitumour platform comes of age: this system gets the responsible drug to keep itself in check for transport and delivery.
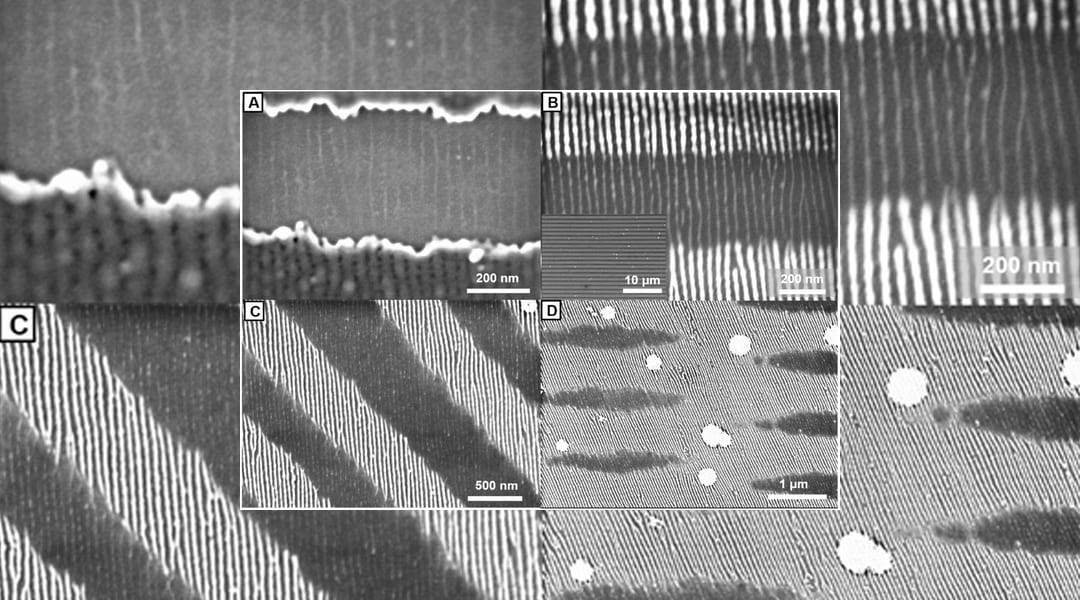
This old dog has a new trick: an adapted lithography technique allows precise variation of the composition of 1D materials during fabrication.
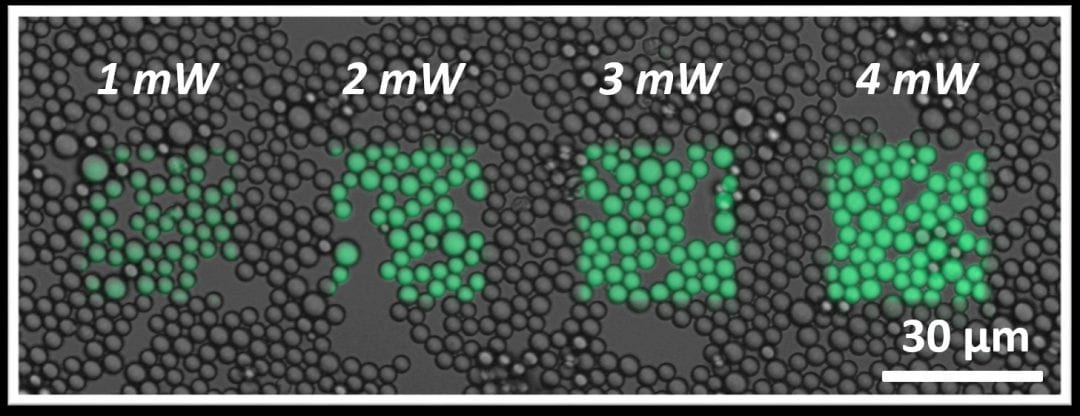
The NITEC reaction is explored with tetrazole-functionalised microparticles, and demonstrates micrometer-scale resolution as a surface-patterning technique.