Drug-free macromolecular therapeutic systems can target and kill cancer cells without causing the side-effects of the drugs currently in clinical use.
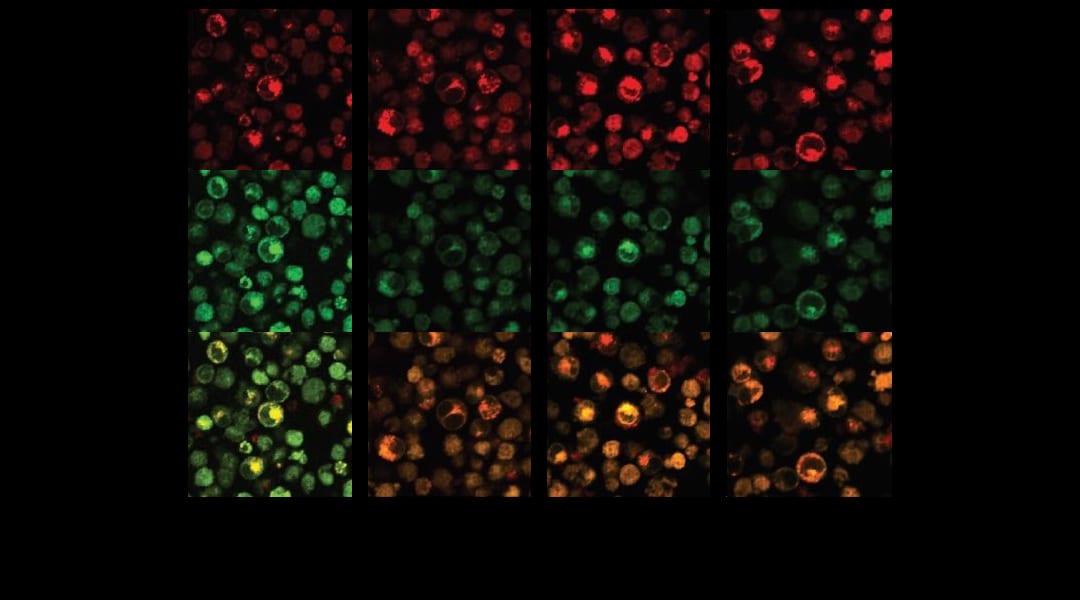

Drug-free macromolecular therapeutic systems can target and kill cancer cells without causing the side-effects of the drugs currently in clinical use.
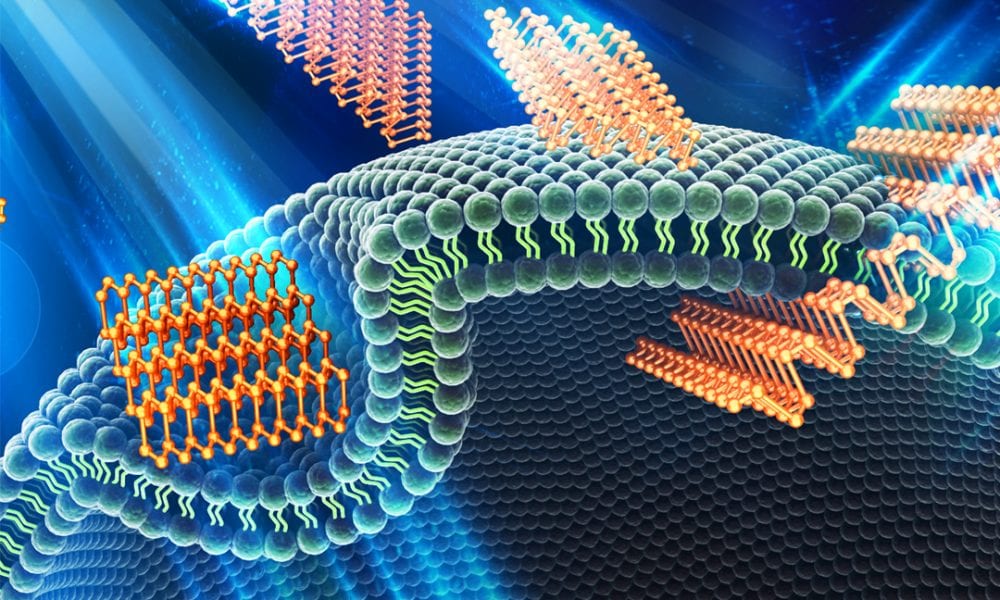
The concentration-, size-, and cell type-dependent response to layered black phosphorous is explored to maximise its potential and avoid future problems.

Soft microswimmers that use a combination of acoustic and magnetic fields to demonstrate motion with precise manoeuvrability in a blood vessel.
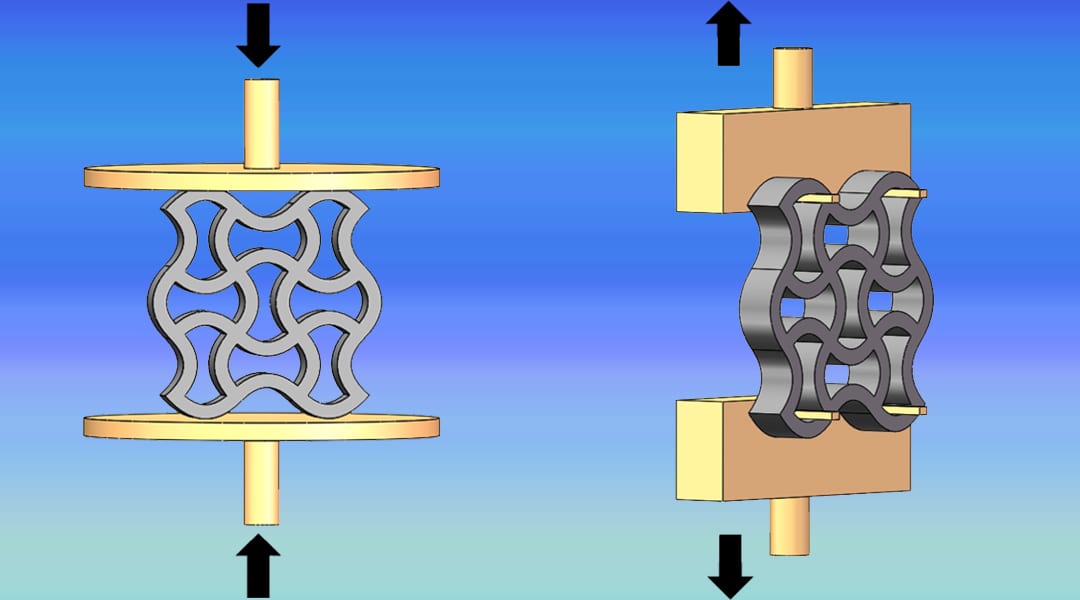
Control over macro- and microstructures, density, conductivity, and Poisson ratio is enabled by this new combined metallic aerogel production technique.
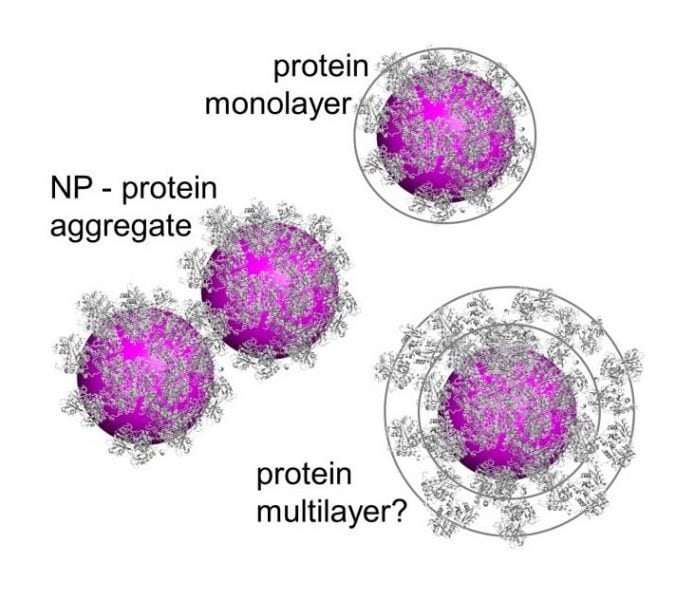
A biomolecular adsorption layer (corona) forms on essentially all nanoparticles immersed in biological fluids, and governs their interactions with the biological environment. Key aspects of protein corona formation and its structure and dynamics have yet remained elusive and call for further investigations.
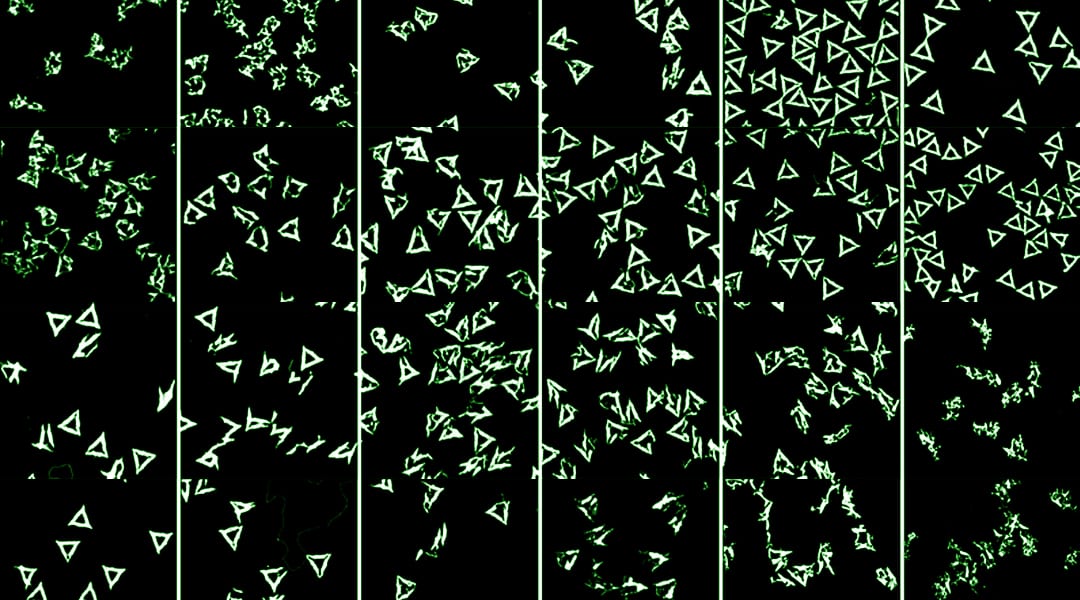

The stability of DNA origami under strongly denaturing conditions is investigated.
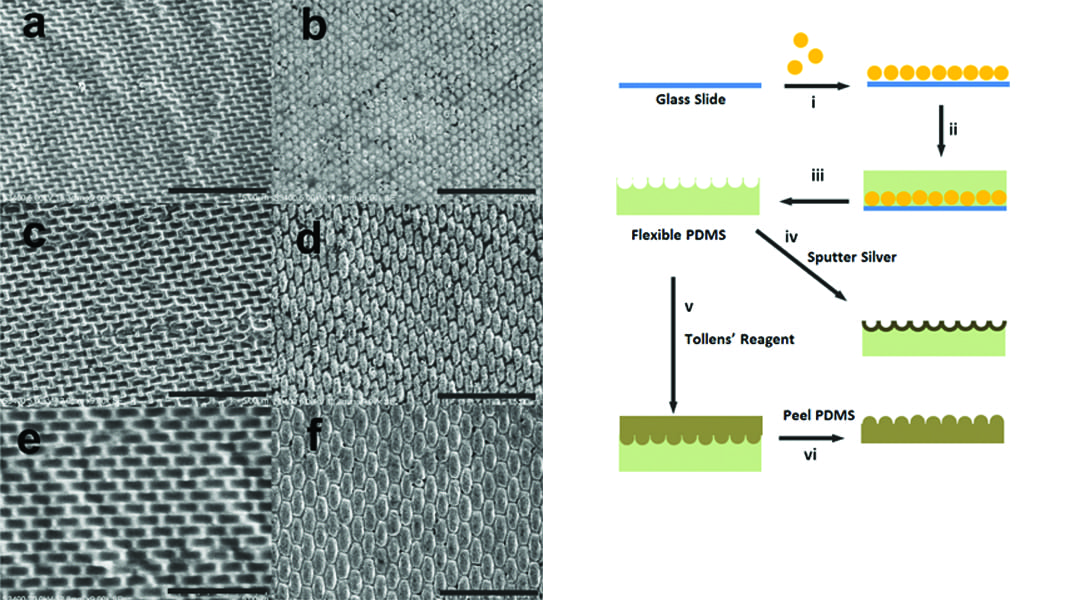
A unique and versatile approach to creating ordered silver nanostructures is presented that allows for feature shape alteration in a simple and inexpensive manner.
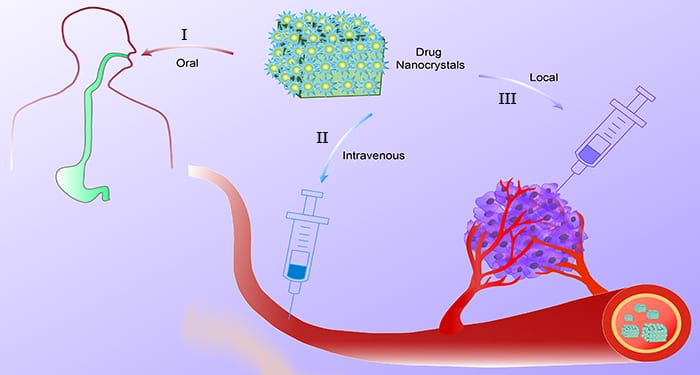
Drug nanocrystals deliver drugs via oral, intravenous, and local administration and show promise towards treating cancer more effectively.
An advanced 4D bioprinting approach uses shape-morphing, biopolymer hydrogels to form the basis for blood vessels and other tubular structures in artificial tissues and organs.
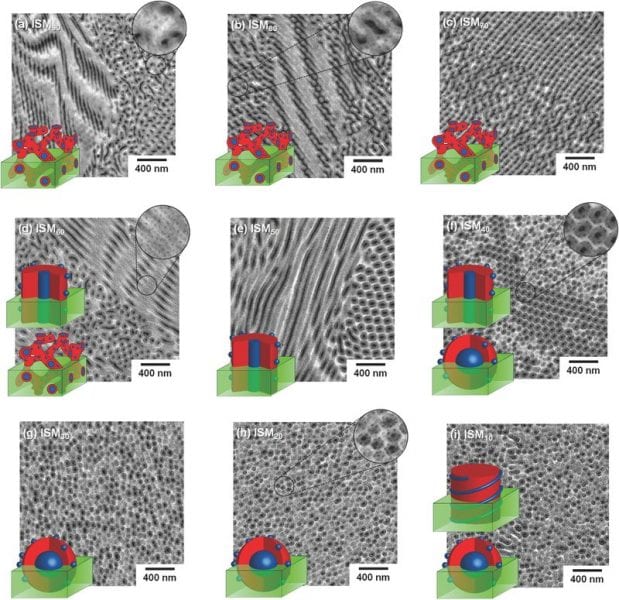
Abetz Volker and his team demonstrate how complex nanostructures can be achieved by polymer blending.