Haydale Limited believe new method will supply commercial quantities, announce distribution deal with Cheaptubes Inc.


Haydale Limited believe new method will supply commercial quantities, announce distribution deal with Cheaptubes Inc.
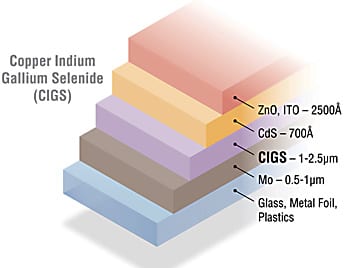
Effort to accelerate the deployment of CIGS manufacturing will play a critical role in building a competitive U.S. photovoltaic industry.

The German engineering company transfluid pledges that process integration for spherical head sealing on steel tubes can save money and avoid weak points.
Selective and effective: silicon nanowires as photoelectrodes for carbon dioxide fixation
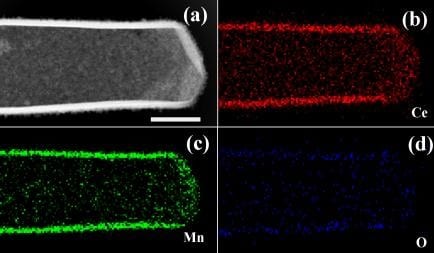
Canadian researchers develop a synthesis method for created hollow, structured binary metal oxides.
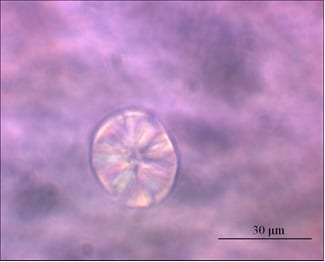
Glass ceramics are of great interest for the development of optical elements with meter-scale dimensions for high power laser facilities.

Advanced Optical Materials Issue 2 is live, with 12 papers from top research groups and covering all aspects of light–matter interactions.
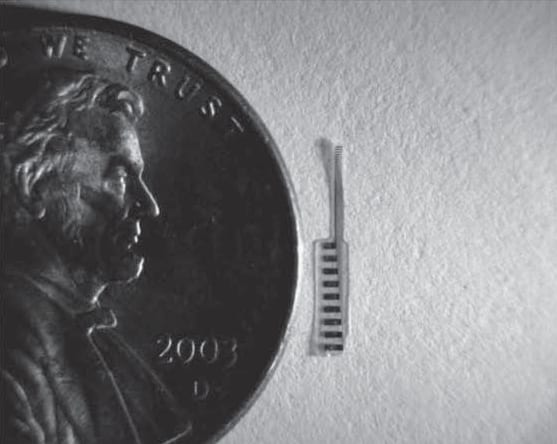

University of Texas researchers develop materials that are stiff for initial implantation, and then soften to better match the mechanical properties of brain tissue.
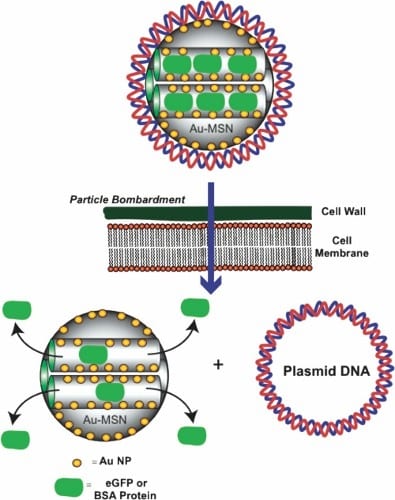
Researchers at Iowa State University demonstrate the ability to simultaneously deliver proteins and DNA into plant cells.
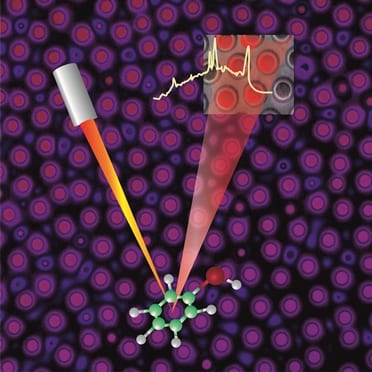
Hierarchical electrohydrodynamic pattern formation enables the fabrication of multiscale 3D structured arrays as SERS-active platforms.