Latest

Hollow planets could help find primordial black holes
Small primordial black holes could have consumed the interiors of planets or asteroids, leaving their outer shells intact.

Haruka Sasaki, uncovering the link between melatonin and asthma
Haruka Sasaki is researching how melatonin impacts asthma to create new treatments for life-threatening nocturnal attacks.
Live imaging of nanoscale biological processes achieved for the first time
Scientists have built a microscope capable of live imaging of biological processes in such detail that moving protein complexes are visible.
Blood pressure drug shown to treat triple-negative breast cancer in mice
A new study reveals that lacidipine, a common antihypertensive medication, slows tumor growth in triple-negative breast cancer.
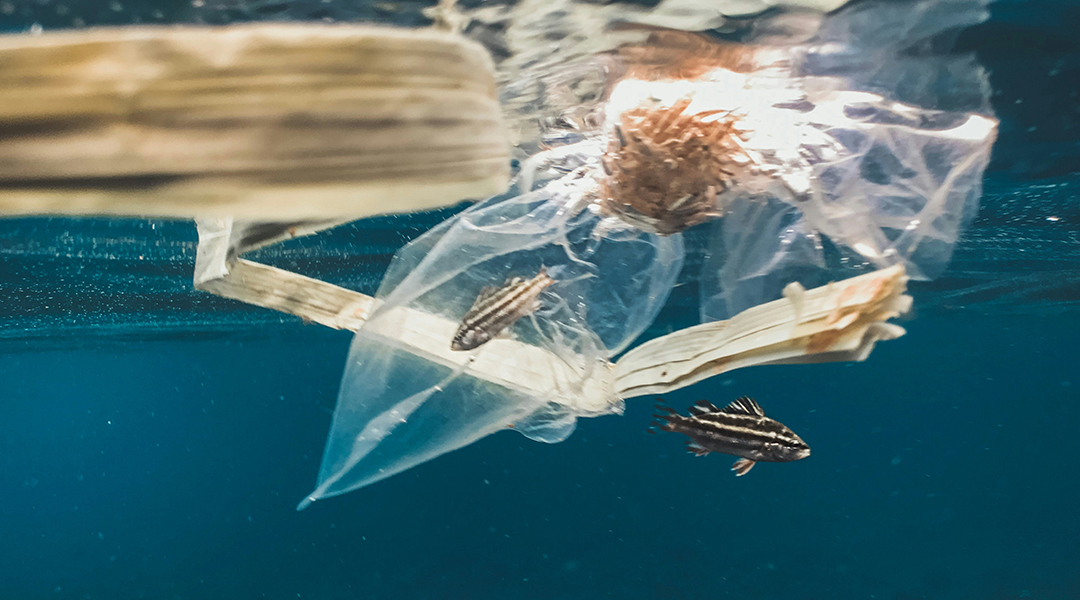

New plastic material fully degrades in the ocean
A new material designed to dissolve only in salt water could help us prevent the accumulation of microplastics in the seas.
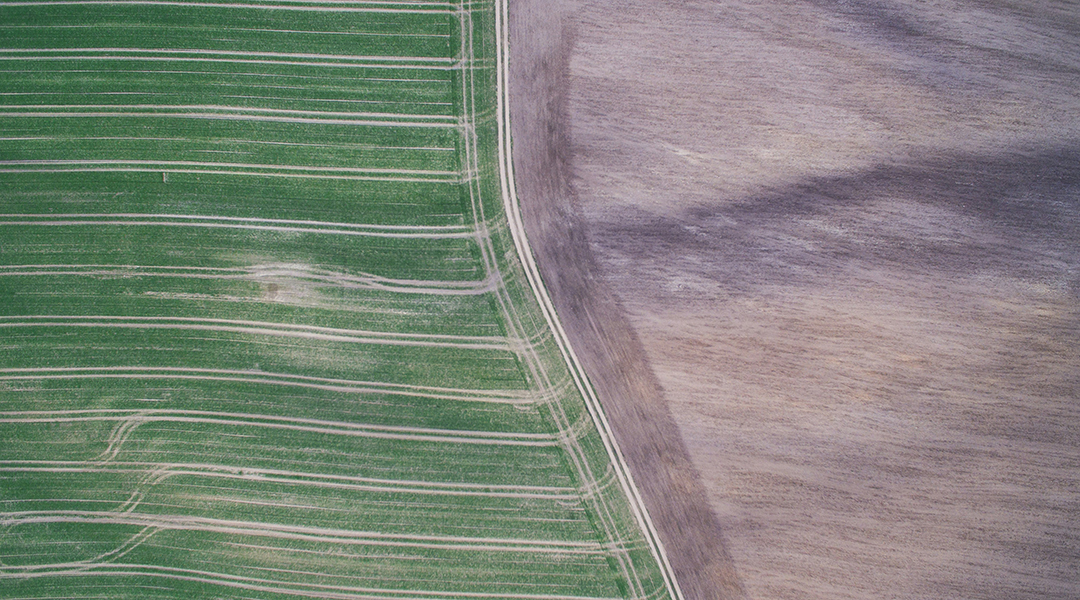

Modern crop seeds are not ready for climate change
Traditional means farmers used to use for seed selection and preservation may help us cultivate more resilient food in a changing climate.
Gold nanoparticles help hydras regrow their heads
Gold nanoparticles and near-infrared light speed up regeneration and reproduction in hydras, providing insights for regenerative medicine.
ASN Weekly
Sign up for our weekly newsletter and receive the latest science news directly to your inbox.
Sniffing out lung diseases with a portable E-Nose
Revolutionizing respiratory disease detection with a portable E-Nose for non-invasive breath analysis.
One step closer to sustainable fuels with a low-cost, solar-driven photoreactor
An innovative photoreactor concept achieves commercially viable performance indicators for a broad variety of solar-driven reactions.
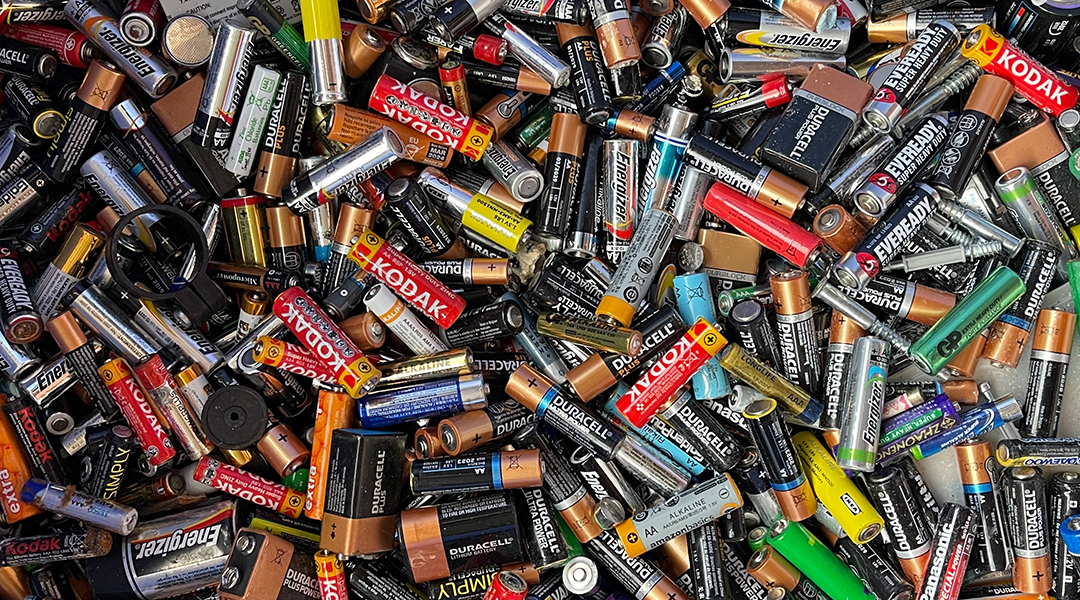

Tough but stretchable material could improve rechargeable lithium batteries
A tough gel electrolyte protects lithium metal anodes for safer and more efficient rechargeable batteries.
A synthetic nanoenzyme helps combat IBD
To minimize inflammation in IBD, scientists have developed a synthetic enzyme that targets multiple problematic pathways.
Scientists detect the X-ray signature of a single atom
A new technique can detect the X-ray signature of an individual atom, even determining the structure of its electron orbits.
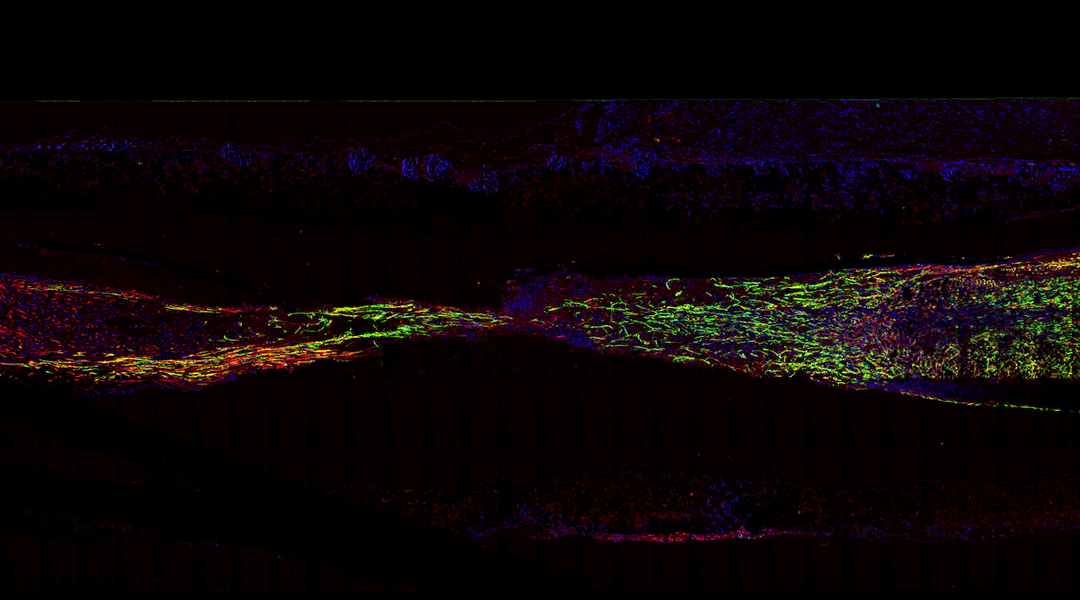
A biodegradable scaffold repairs nerve damage in mice
A fully biodegradable nerve scaffold not only helps regenerate damaged nerves, but negates the need for retrieval procedures.

Climate modeling turns to clouds to unravel a long-standing enigma
Clouds have scrambled climate models for decades and researchers are doing something about it.
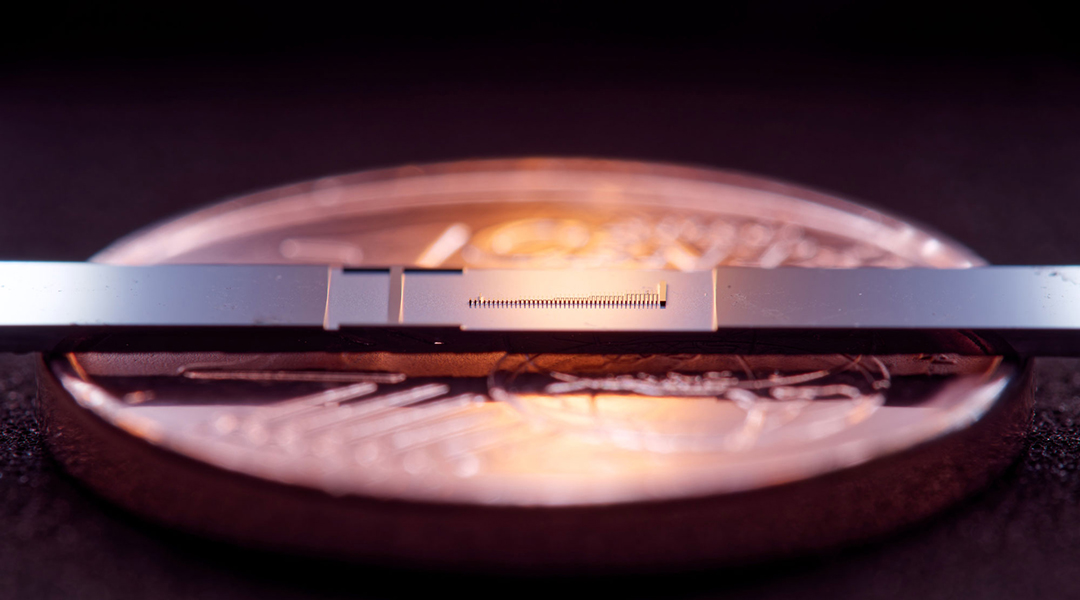
A big step for little particle accelerators
Scientists build a particle accelerator that fits on a dime, and it works!
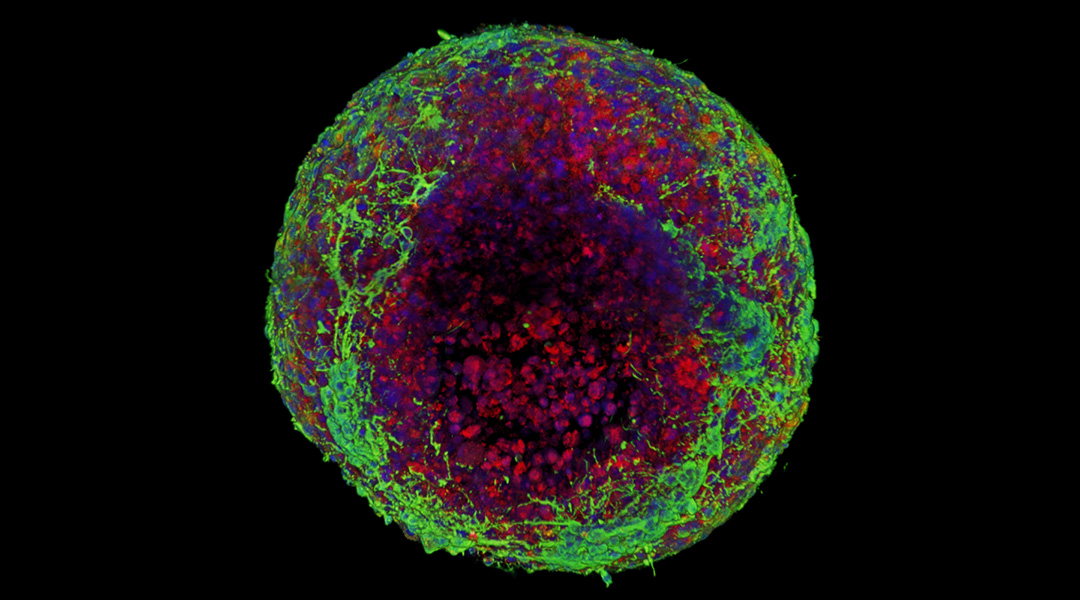
Creating realistic “squishy” brain tissue in the lab
Growing brain tissue requires capturing the realistic “squishiness” and cohesion between cells, but how each cell type contributes has been a mystery.
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
New local anesthetic delivery system offers longer lasting pain relief, fewer side effects
Hydrogel-based microspheres better control the release of drugs, providing better post-op pain relief and fewer side effects.
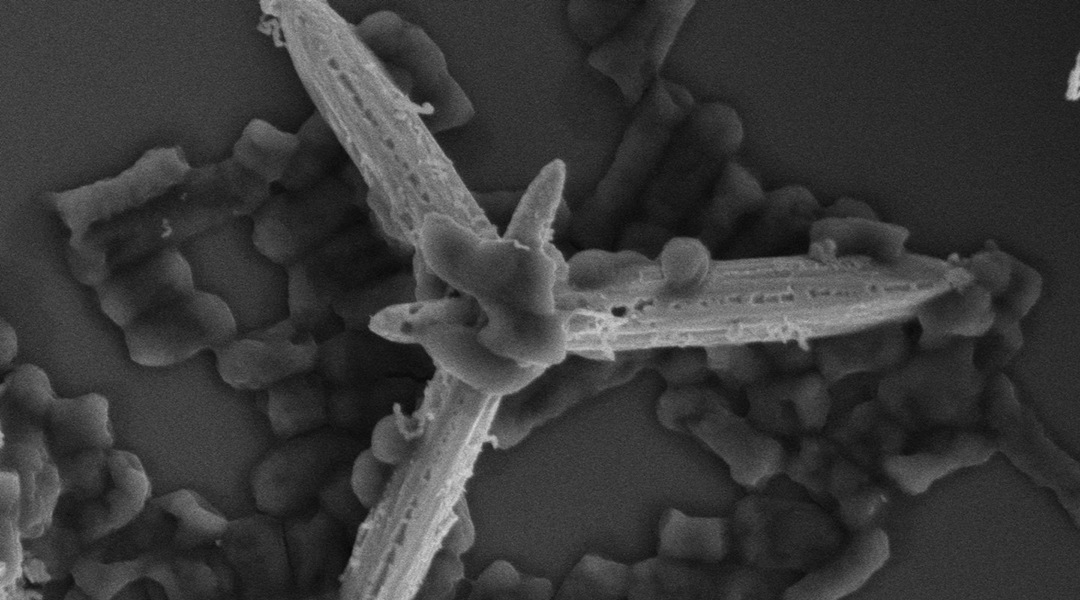
Tiny, self-propelled machines might be key to fighting antimicrobial resistance
Microscopic machines powered by light are a “double threat” to bacteria and could help combat the growing problem of drug resistance.
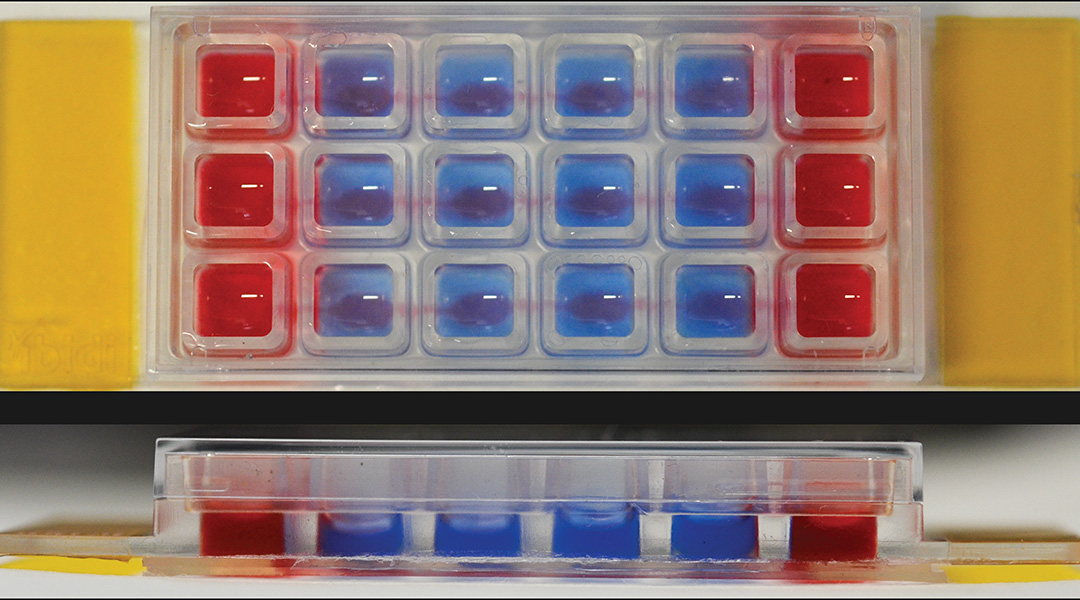
Gut-on-a-chip helps get to the bottom of inflammatory bowel disease
A microfluidic chip could help researchers uncover the unknown underlying mechanisms that cause inflammatory bowel disease.

A lung-mimicking sealant helps repair surgical leaks
A superior surgical sealant mimics the structural and mechanical properties of lung tissue to repair air leaks after surgery.

An artificial nose that sniffs like a wine taster
Precisely copying the capabilities of a biological nose with an artificial one is a lofty but potentially world-changing goal.

Fitness trackers powered by sweat
The generator harnesses energy from water and is built with a fiberform material derived from the straps of disposable medical masks.

Cellulose could replace plastics in flexible electronics
Discover how cellulose may revolutionize flexible electronics, replacing plastics in eco-friendly, sustainable substrates for innovative devices.
How label-free, super-resolution imaging will push microscopy’s limits
New research lays out the future of a pioneering form of electromagnetic imaging.

Are golf courses an alligator’s paradise?
To understand the impacts of golf courses on wildlife, researchers are exploring how these novel habitats are affecting fundamental animal behaviors.

Boosting lateral solar cells
A new design approach and specialized organic material helps improve the efficiency of lateral solar cells, turning energy generation on its side.
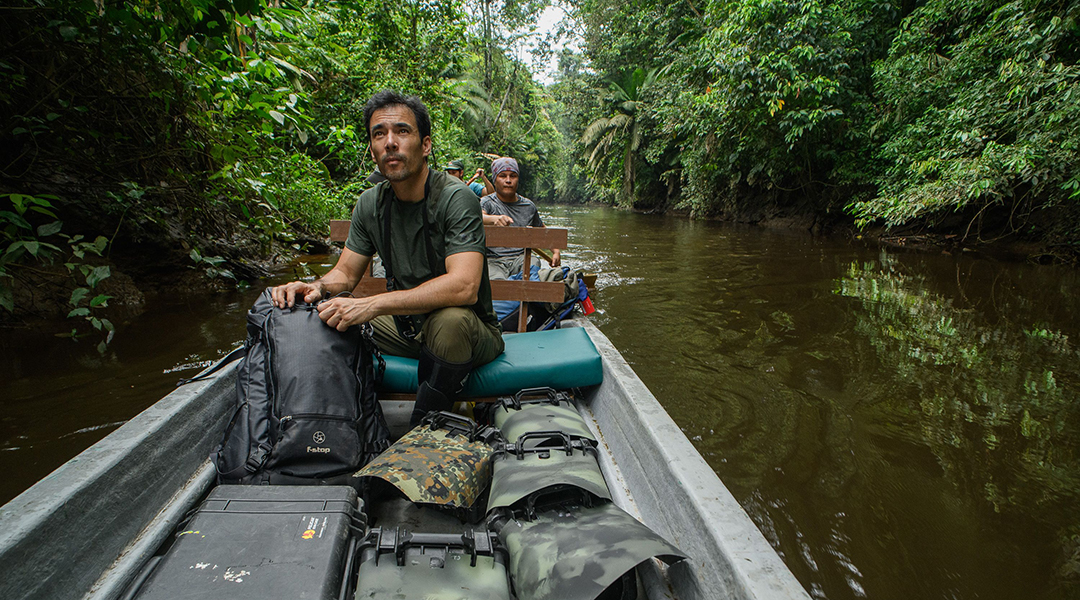

Through the lens of rainforest conservationist and photographer Chien Lee
Not just pretty pictures: Borneo-based wildlife photographer and conservationist Chien Lee has a deeper message.

Ozone pollution disrupts genes controlling circadian rythyms
Study finds air pollution, specifically ozone exposure, has a disruptive affect on the genes responsible for circadian rhythms in the lungs.

Harnessing entanglement and curved spacetime to make quantum radar a reality
Scientists investigate the synergy of entanglement and curved spacetime in advancing quantum radar technology for precise distance measurement.
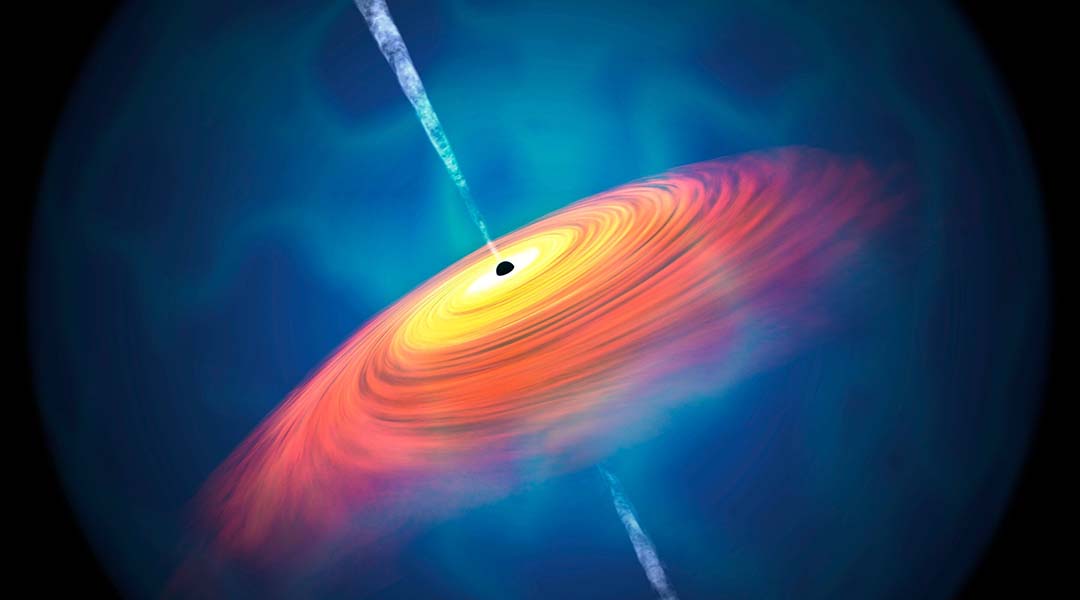

Subaru Telescope shatters limit, observes supermassive black holes in the early Universe
Scientists have only observed supermassive black holes one billion years after the Big Bang, but astrophysicists have now breached this barrier.
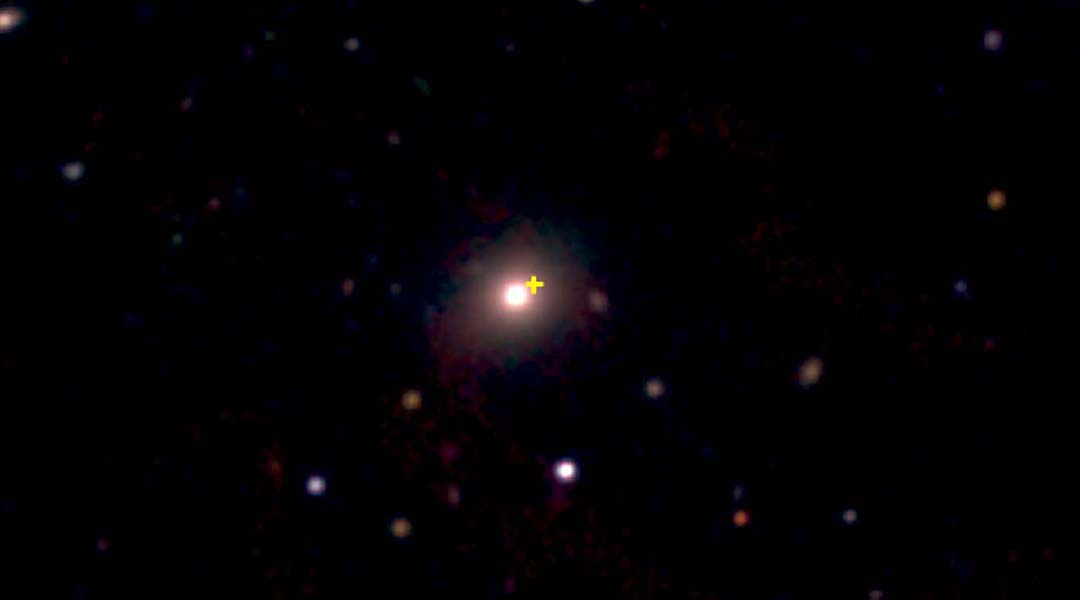

Cosmic explosion is one of the most powerful and rapid blasts ever seen by astronomers
The rare but extreme blast that outshone most supernovas originated two billion light years away and has been classed as a “Luminous Fast Cooler”.
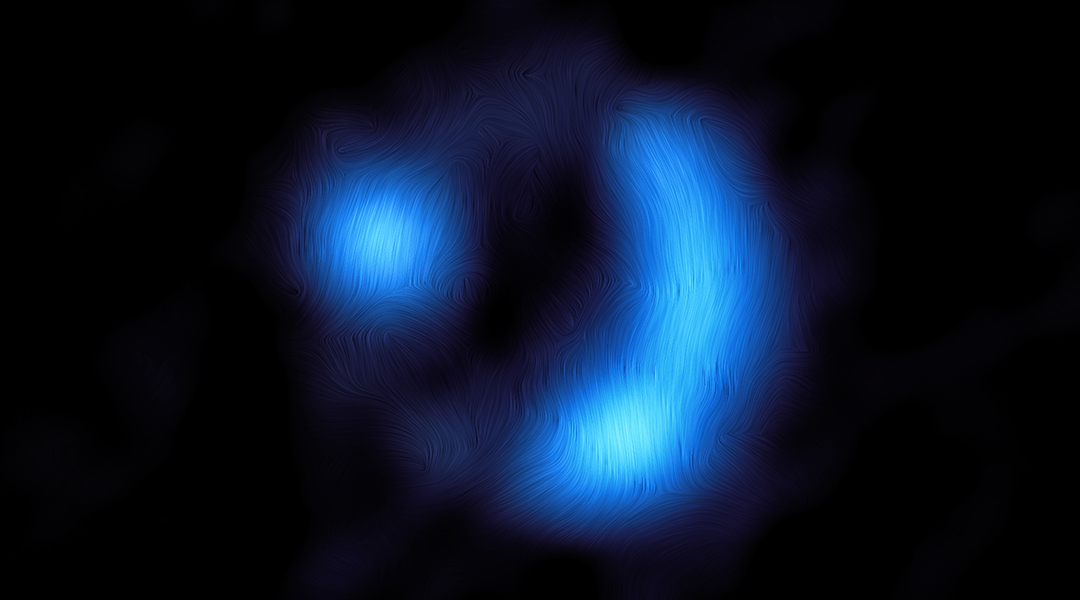
Astronomers observe a galaxy’s magnetic field in the very early Universe
The galaxy 9io9 is seen as it was when the cosmos was just 2.5 billion years old, making this the earliest galactic magnetic field ever observed.