Developing better protective equipment requires new materials that better disperse energy.
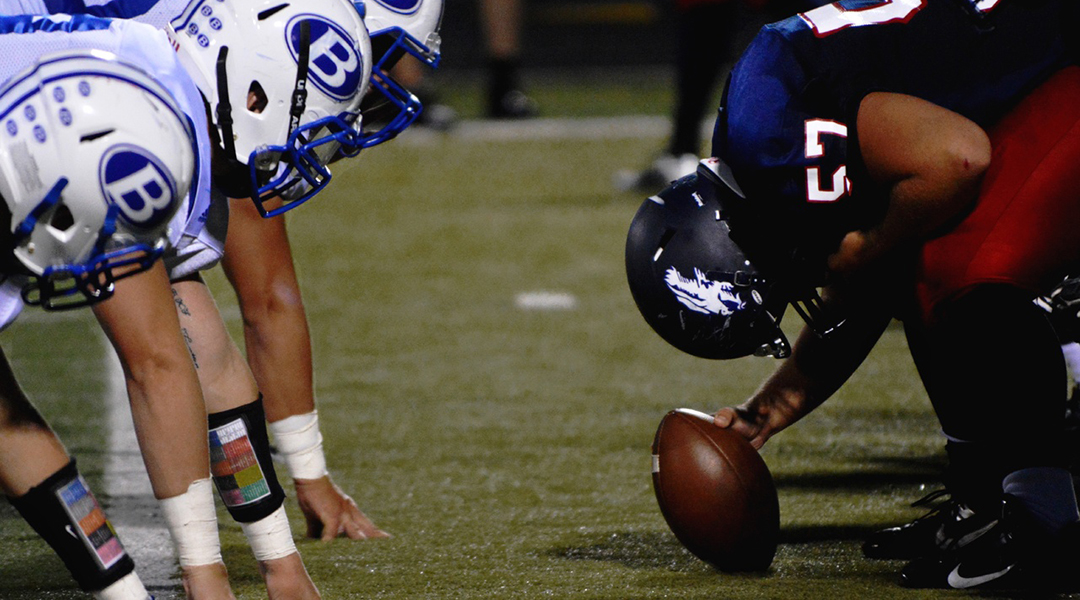


Developing better protective equipment requires new materials that better disperse energy.
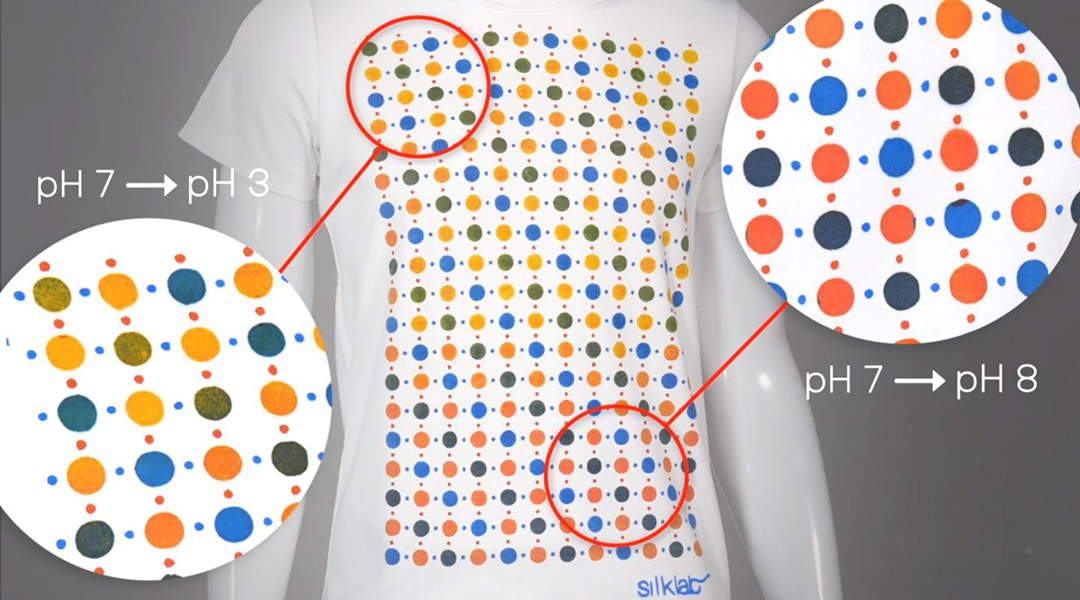
Bioactive inks printed on wearable textiles can map conditions over the entire surface of the body, including possible pathogens.
New quantum algorithms will have dramatic impact in computational molecular biology and bioinformatics and promise to impact a number of life science applications.
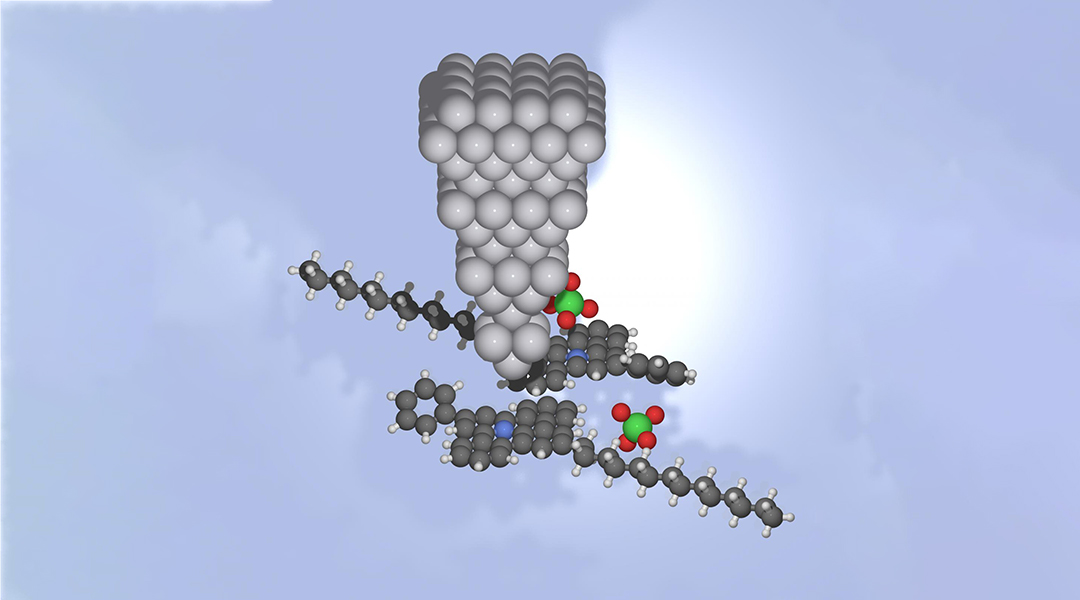
Researchers have discovered a single-molecule “switch” that can act like a transistor and offers the potential to store binary information.

A transparent and stretchable touch sensor could enable robust touch input mapping under either static or dynamic deformation.
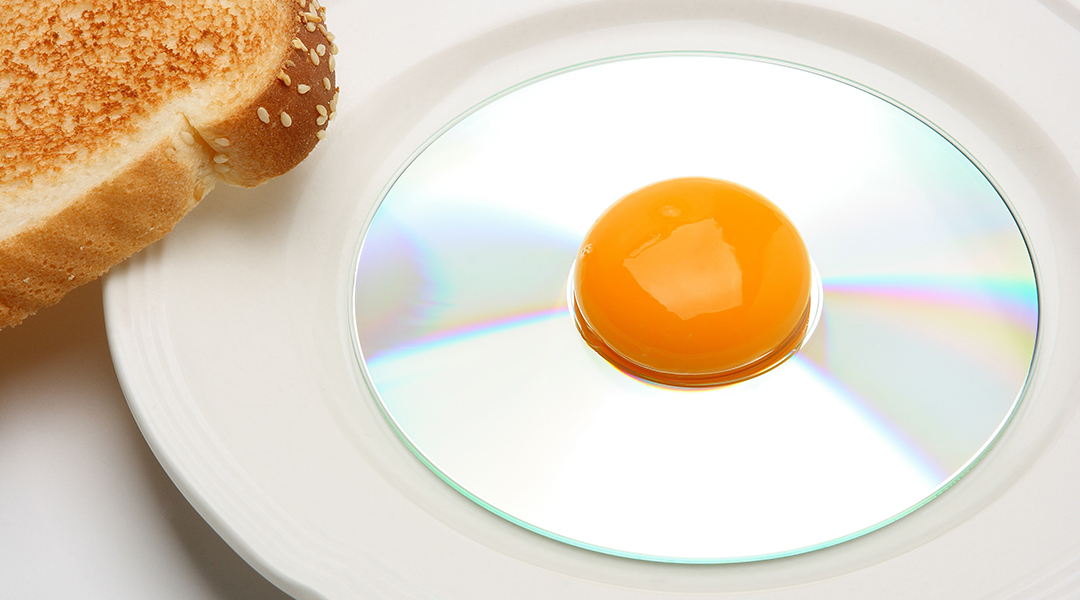

From cracking eggs to plating the finished dish, a team of engineers have trained a robot to prepare omelettes that actually taste good.
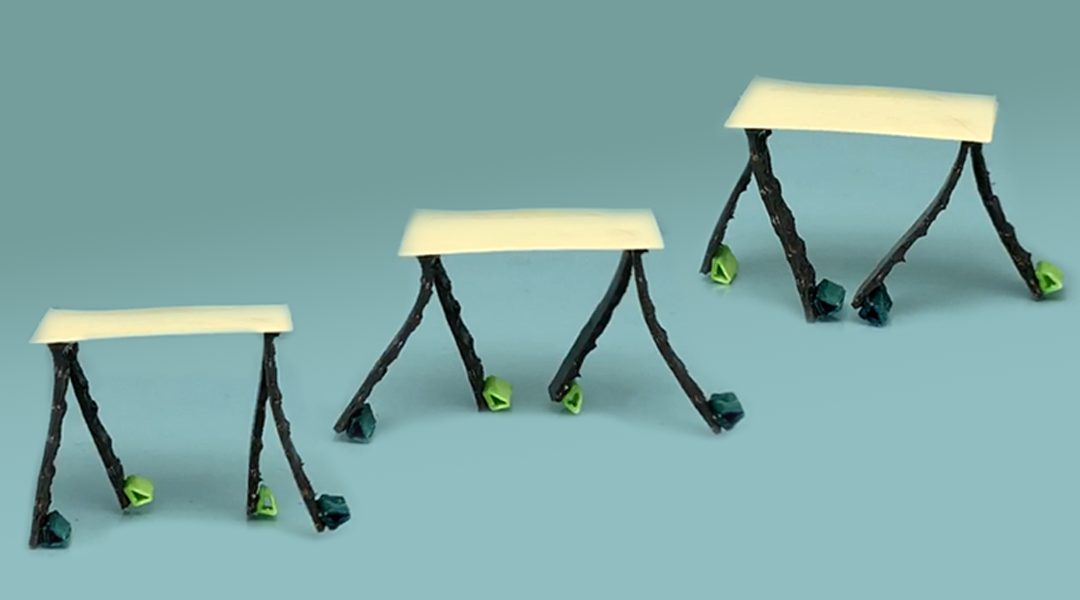

An automatic design approach with a new 3D-printing method is established to fabricate soft composites that can change to predetermined shapes and generate controllable robotic motions under a magnetic field.

Zinc metal batteries built using a novel hydrogel electrolyte show remarkable performance and processability, making them suitable for the next generation of wearable energy storage devices.
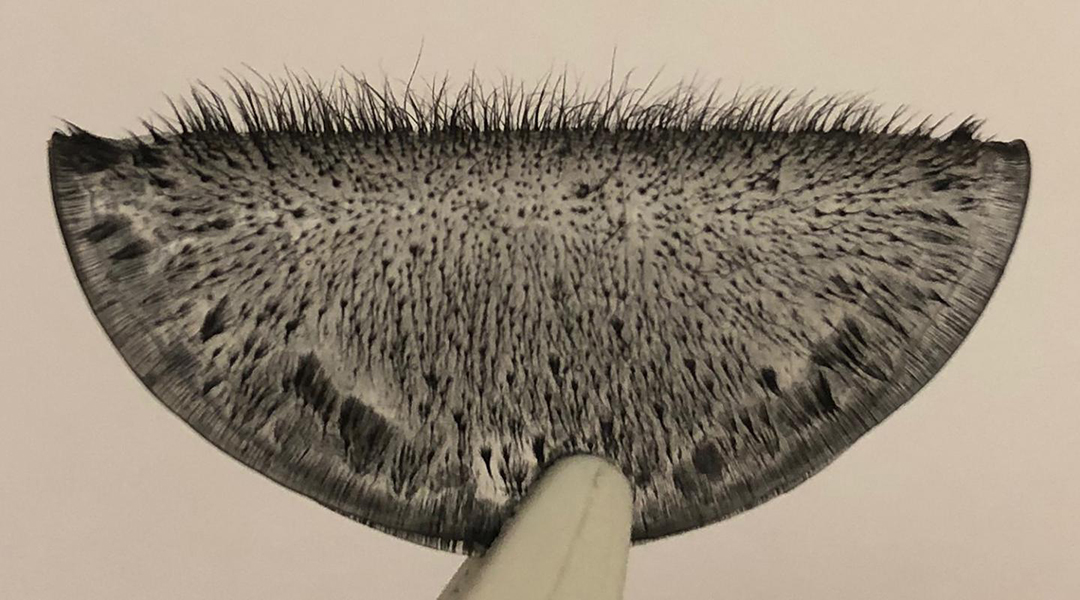

Researchers create an artificial array of magnetic cilia that could contribute to advancing the capabilities of soft robotics.

As the way in which we work, socialize, and live becomes ever-more digital, enabling faster internet speeds and bandwidth capacity while using existing infrastructures promises a new dawn of the digital age.