Using a computer model to plan electricity grids in developing countries, researcher Christina Dominguez traveled to Kenya to get an idea of how people live without electricity and what developments access to the power grid can trigger.
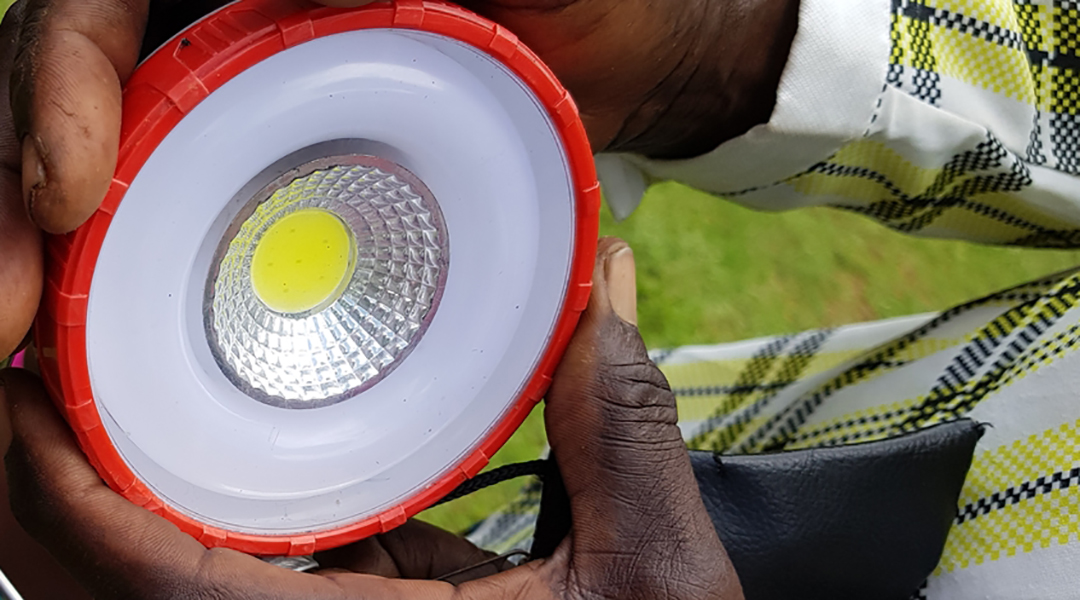


Using a computer model to plan electricity grids in developing countries, researcher Christina Dominguez traveled to Kenya to get an idea of how people live without electricity and what developments access to the power grid can trigger.
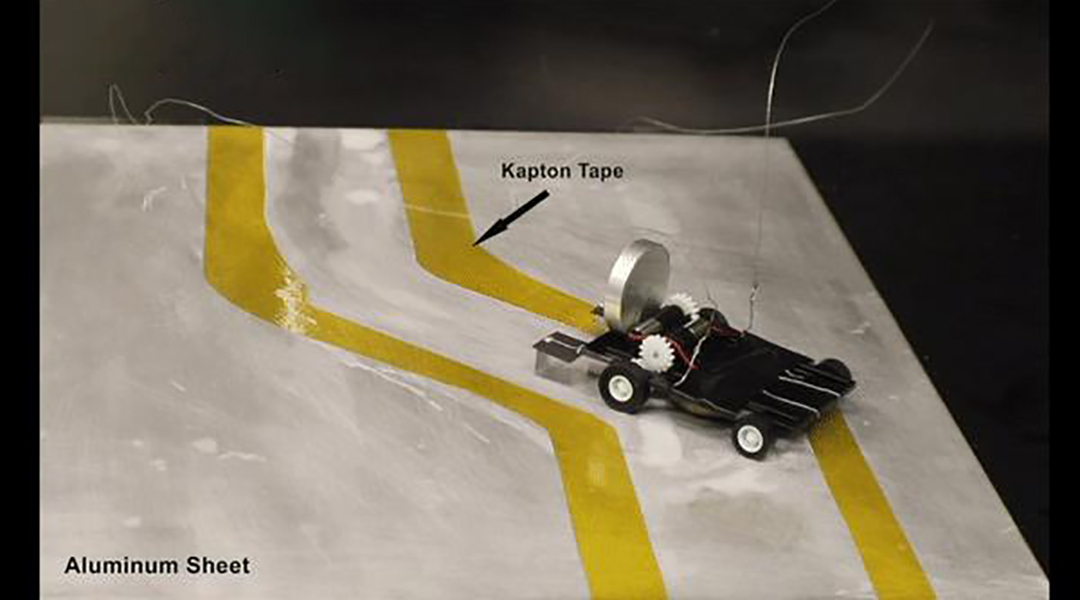
The “metal-eating” robot can follow a metal path without using a computer or needing a battery.
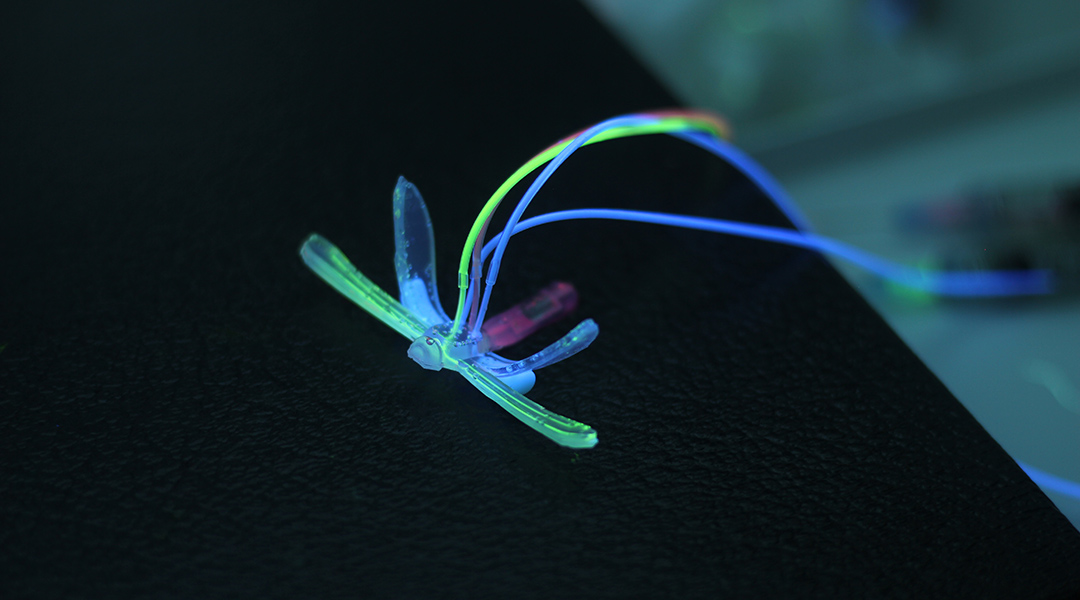
Electronics-free DraBot uses air pressure, microarchitectures, and self-healing hydrogels to watch for changes in pH, temperature, and the presence of contaminants.

The demands of quality forensic science demonstrate the impact of regulatory activities and external factors on the work of forensic science providers.
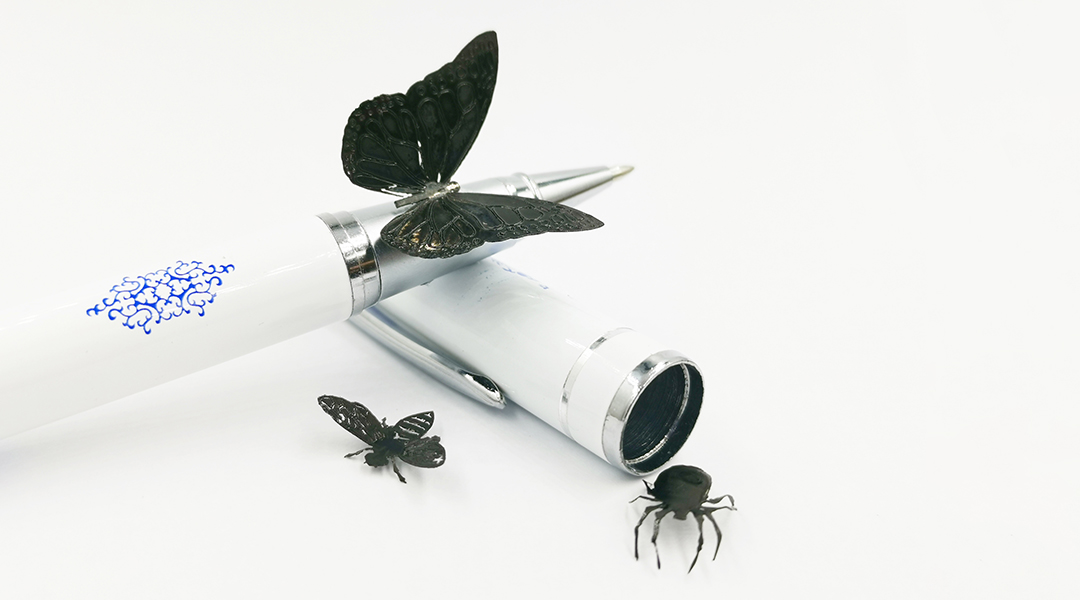

Researchers recreate the somatic nervous system in robots, allowing them to convert feeling into movement under different stimuli.
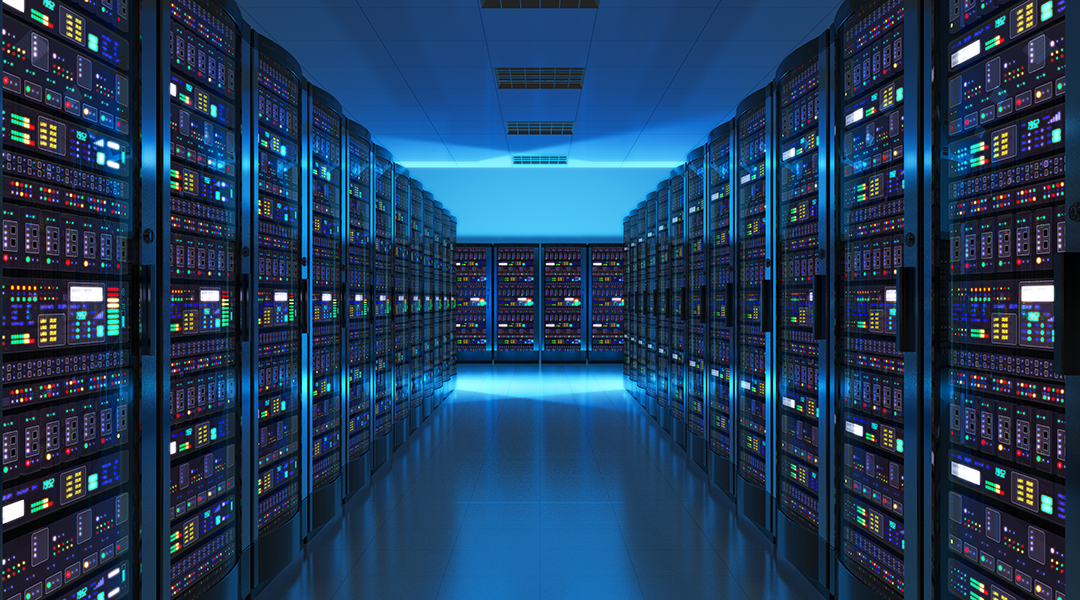

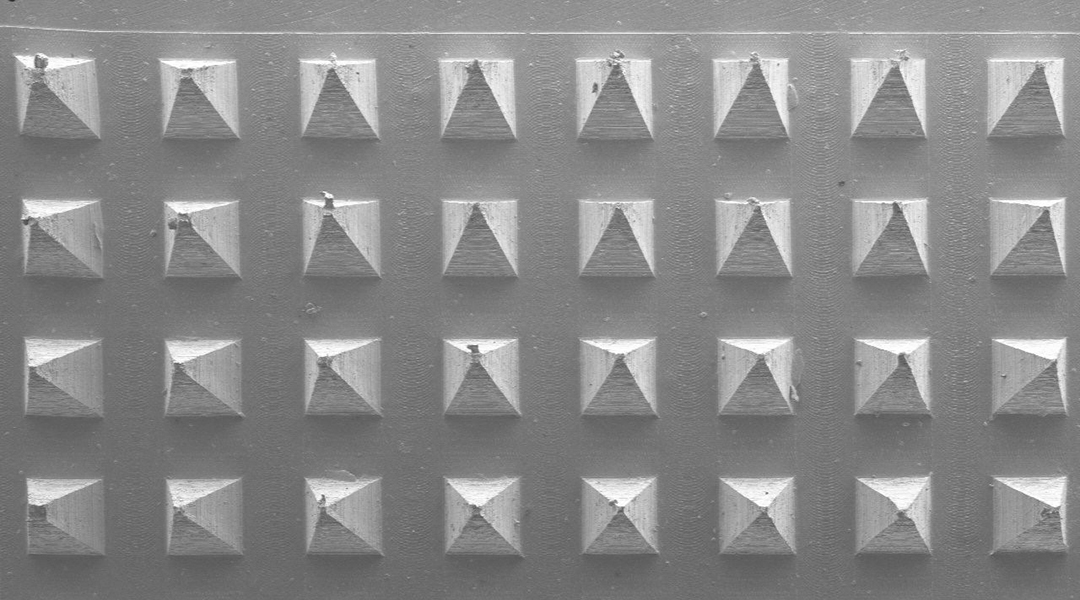
A new device significantly decreases unwanted current leakage from memory devices, which could help reduce the greenhouse gas emissions of future data centers.
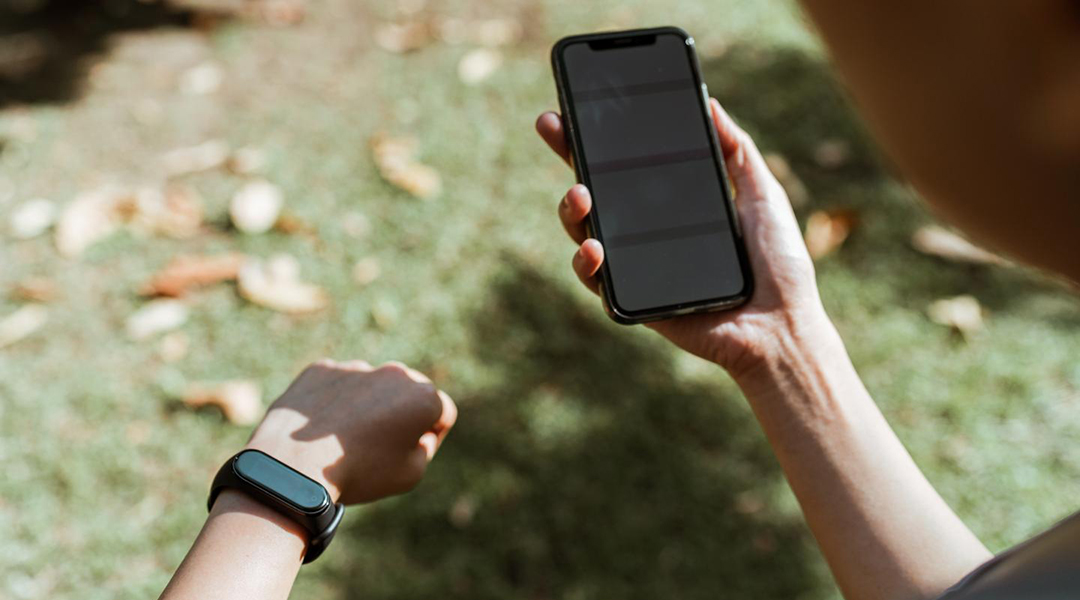

“Cool gadgets” takes on new meaning as scientists develop a radiative cooler that keeps wearable device temperature down, even under direct sunlight.
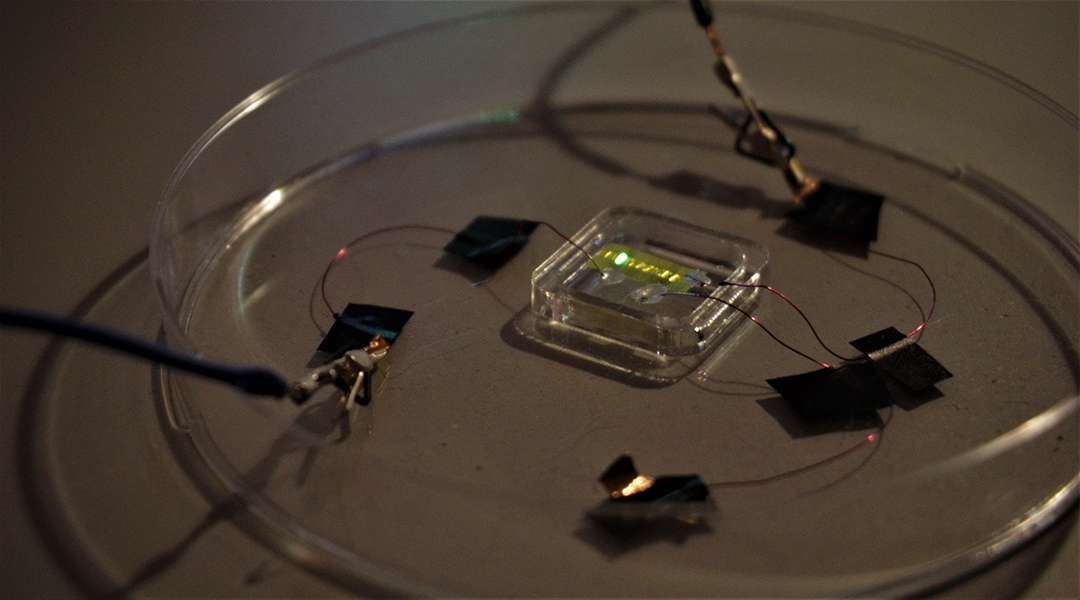
A new fabrication method allows researchers to create ultra-thin OLED materials that can be applied to the skin using temporary tattoo paper.
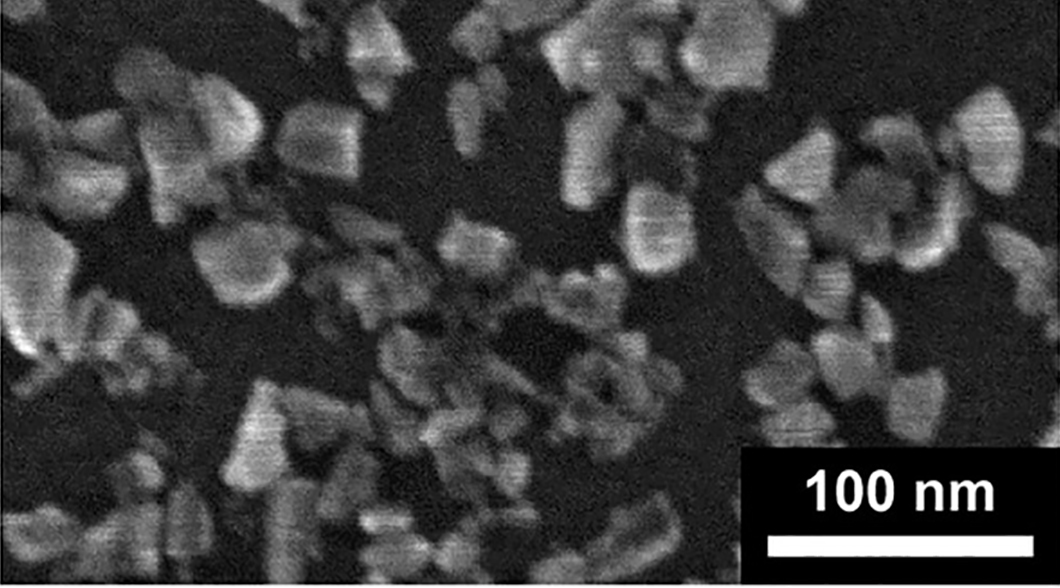
Fluorescent nano-sized diamonds give a better glimpse inside cells.
Minimally invasive delivery of capsaicin into adipose tissues under the skin shows promise for countering obesity.