Procedure produces near-net-shape titanium components with superior mechanical properties and significantly reduced energy consumption and processing costs.
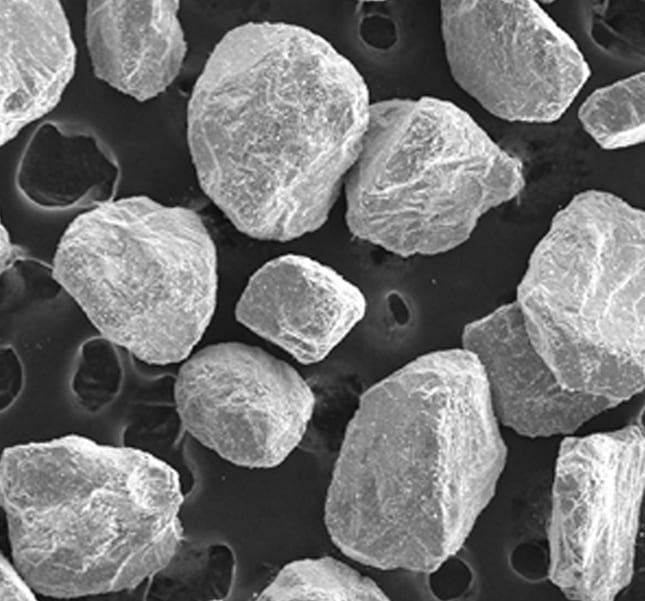


Procedure produces near-net-shape titanium components with superior mechanical properties and significantly reduced energy consumption and processing costs.
Researchers develop method to design synthetic materials and quickly turn the design into reality using computer optimization and 3-D printing.

Developments in electrospinning core–shell nanofibres improve toughening and facilitate self-healing in nanofibre-reinforced polymer matrix composites.
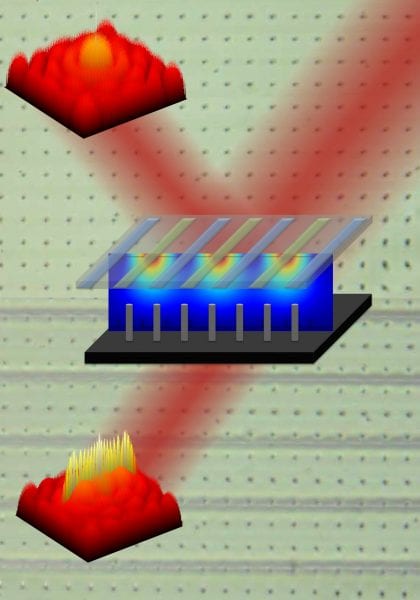
Voltage-dependent diffraction switching makes a hybrid liquid crystal–carbon nanotube device a good candidate for high-resolution displays.
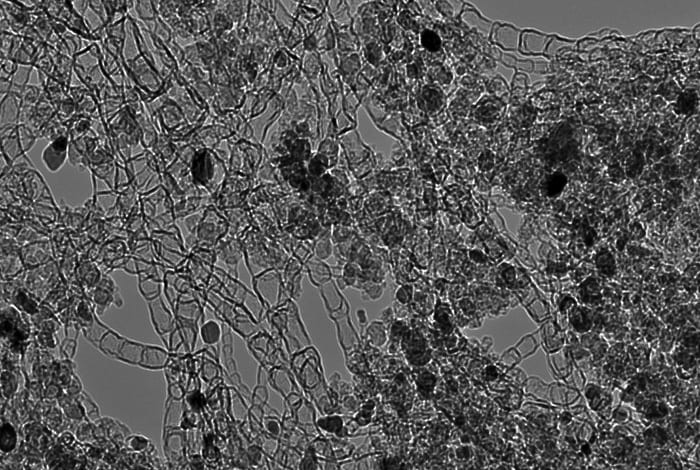
Economical non-precious-metal catalyst capitalizes on carbon nanotubes.
New thin, planar, lightweight, and broadband polarimetric photonic devices and optics could result from recent research by a team of Los Alamos scientists.
Researchers at the University of Illinois have developed a new flow-based method for manipulating and confining single particles in free solution.
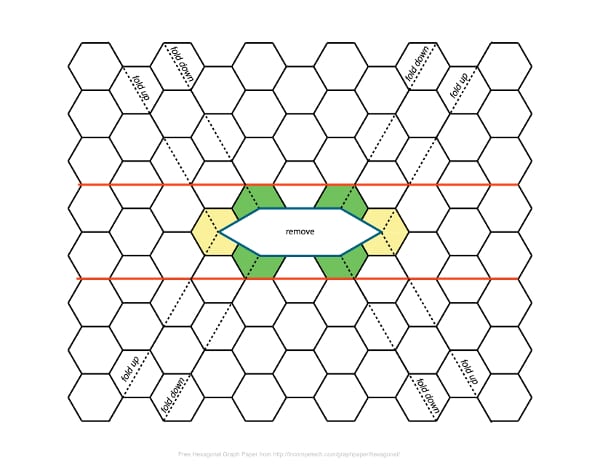
Research could ultimately lead to a drug-delivery device, an emergency shelter, or even a space station.
Catalysts can stop working when atoms on the surface start moving – new work means this dance of the atoms could now be observed and explained.
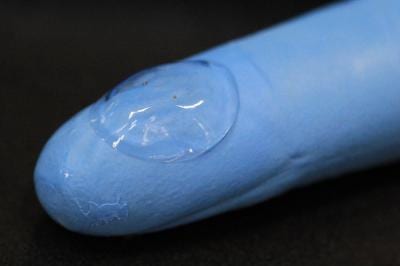
A transparent and stretchable electrode could open the new way for flexible displays, solar cells, and electronic devices fitted on a curvature substrate.