A new biomimetic strategy provides a platform for the synthesis of ligand-targeted nanovesicles that can mediate selective drug delivery to specific tissues.

A new biomimetic strategy provides a platform for the synthesis of ligand-targeted nanovesicles that can mediate selective drug delivery to specific tissues.
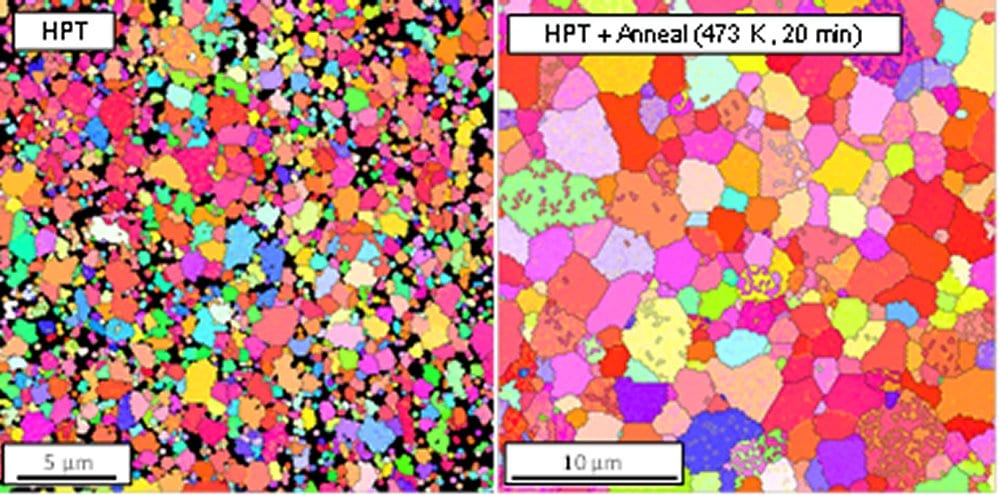
A new concept to solve the ductility problem of SPD-processed magnesium alloys was examined by using a ZK60 magnesium alloy processed by high-pressure torsion to obtain an HSHD material.
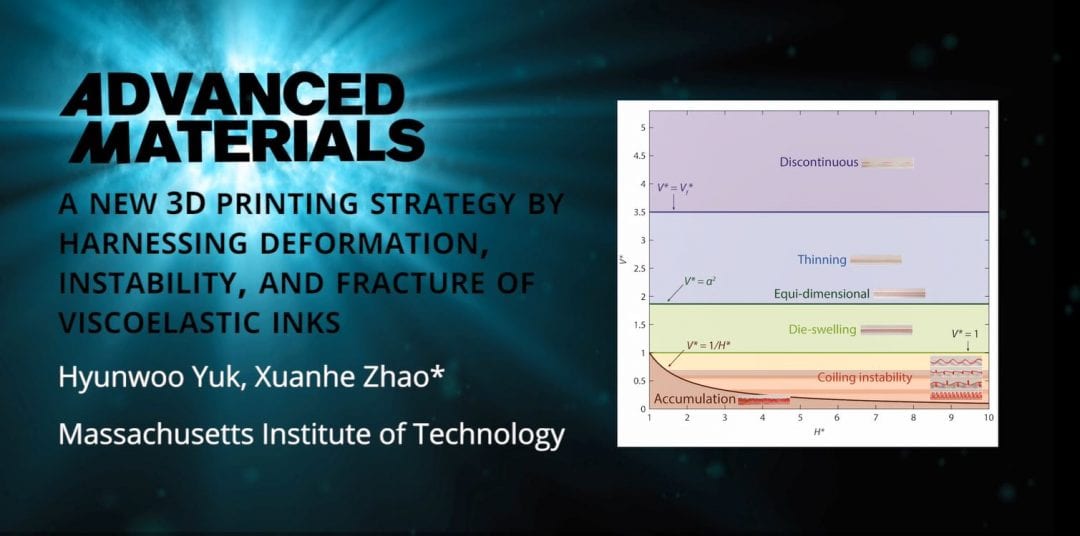
Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) researchers introduce a new 3D printing strategy that overcomes the limitations of direct ink writing. Structures can be printed in six different modes, and can even be printed to have different kinetic properties.
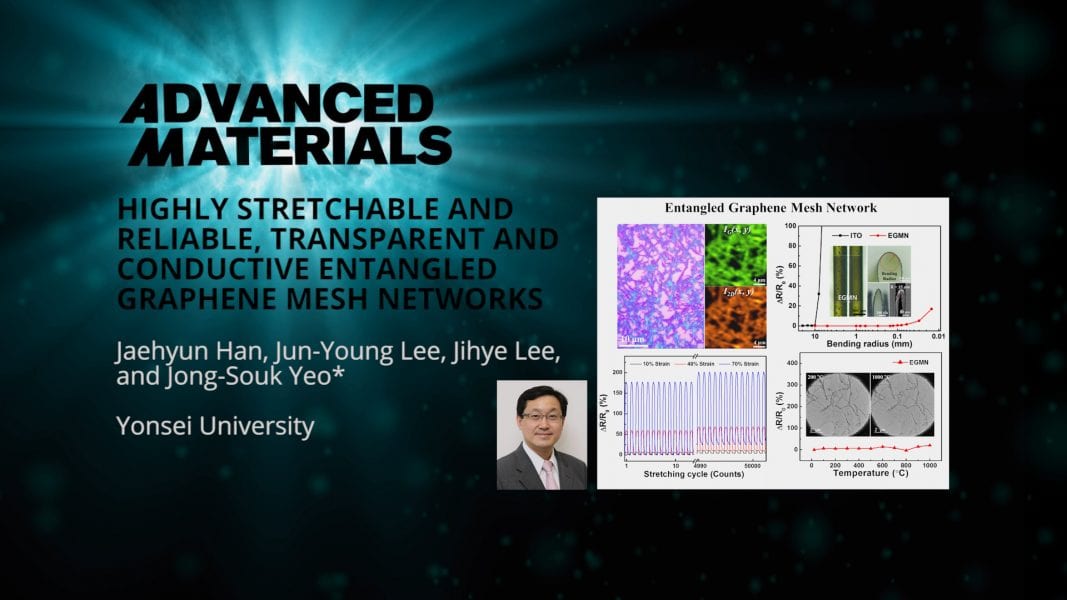
A highly stretchable, transparent, conductive entangled graphene mesh network (EGMN) is developed by a team researchers at Yonsei University, South Korea. The device is mechanically durable, and electrically and thermally stable, even in harsh environmental conditions.
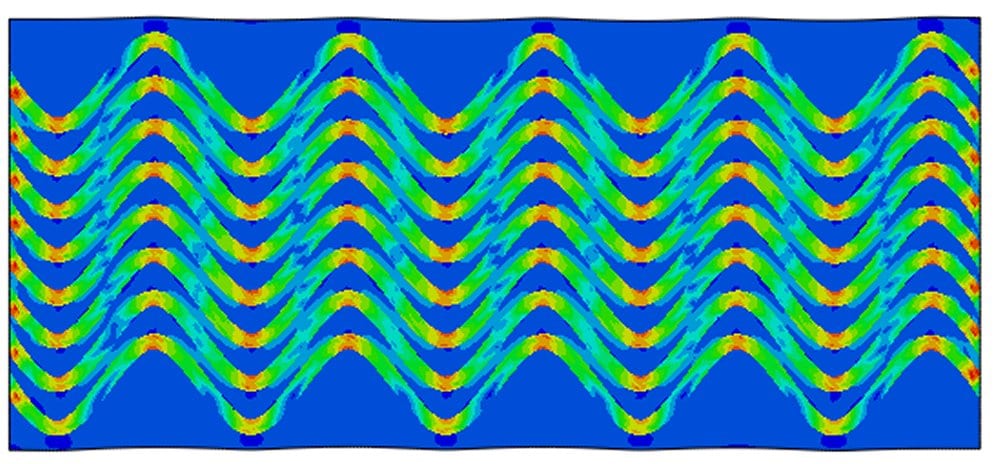
This work illustrates the importance and utility of considering the geometry and arrangement of the components of a composite material in addition to the properties of the component materials and shows how simply the design of the architecture can lead to accessing new desirable combinations of properties.
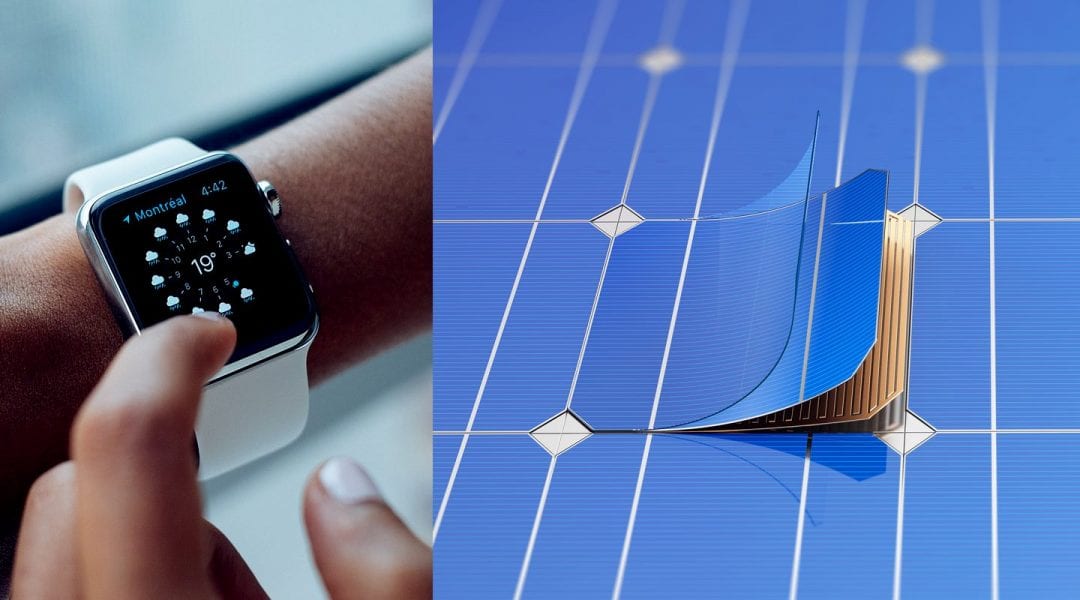
Significant implications of and recent progress made in iCVD-based technologies in three fields: electronic devices, surface engineering, and biomedical applications are discussed.
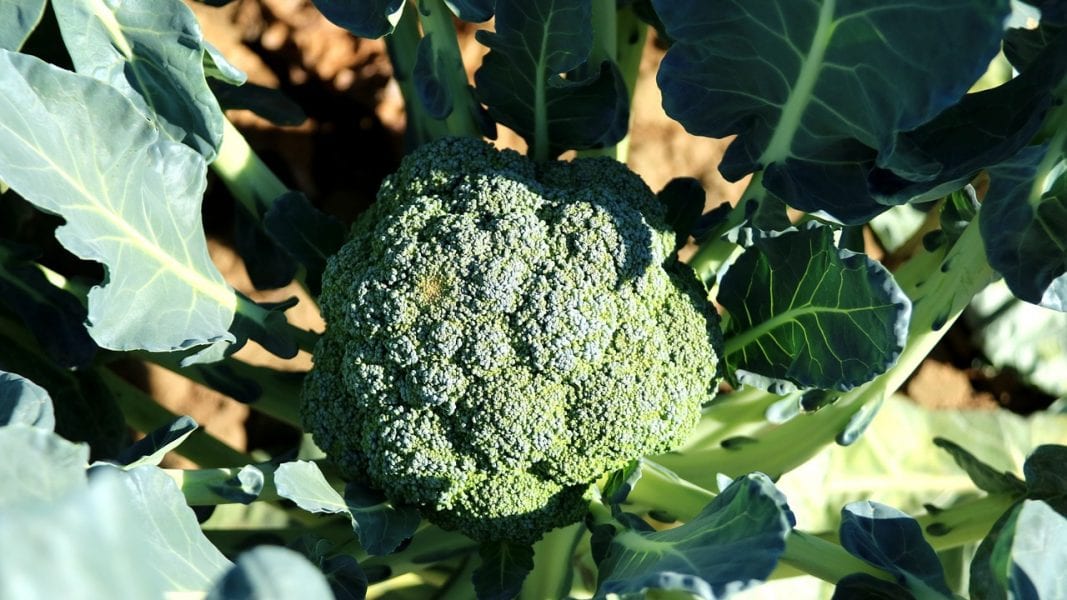

Researchers from France develop a new UV responsive polymer from broccoli seed oil.

Researchers from the King Abdullah University of Science and Technology, Saudi Arabia, have developed a wavy architecture for thin-film transistors using amorphous oxide zinc oxide (ZnO) as the active channel material. The device achieves both high resolution and fast frame rate display technology.
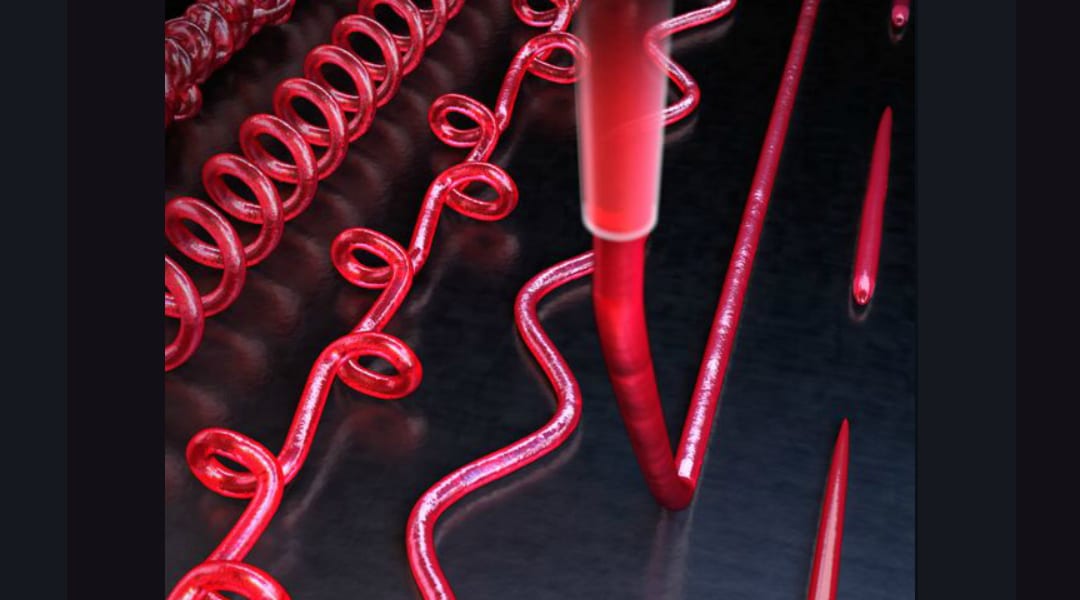

Researchers from MIT present a strategy to increase printing resolution beyond the nozzle size, while drawing diverse complex patterns with a linear nozzle path.
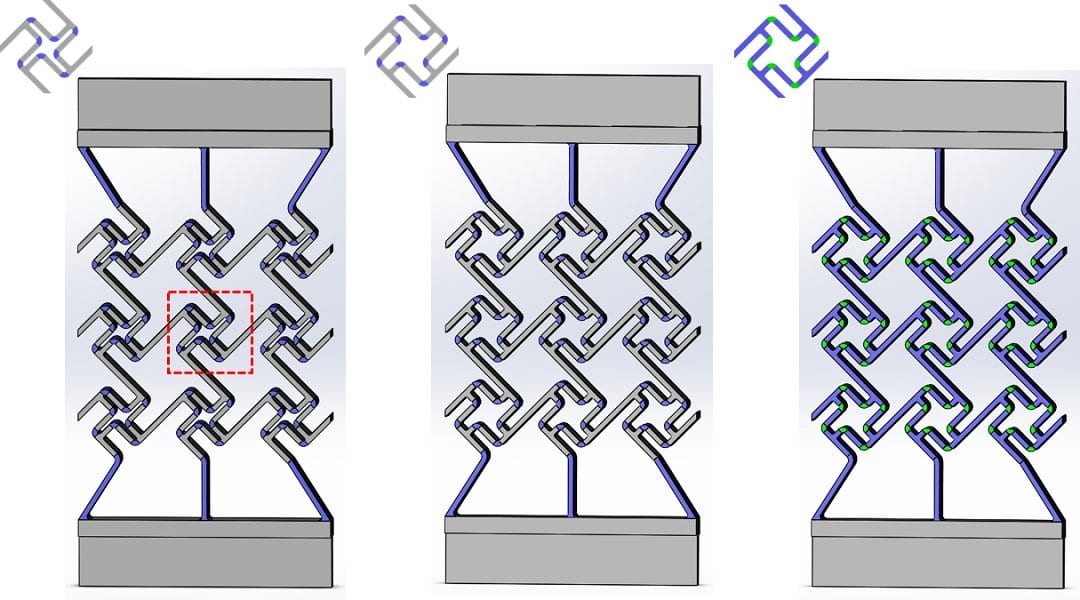
New designs were fabricated via multimaterial 3D printing and potential applications of sequential particle release mechanisms were systematically explored.