A hydrogel that can tell good from bad: this material can distinguish between normal and pathological levels of urate, a salt related to gout arthritis.
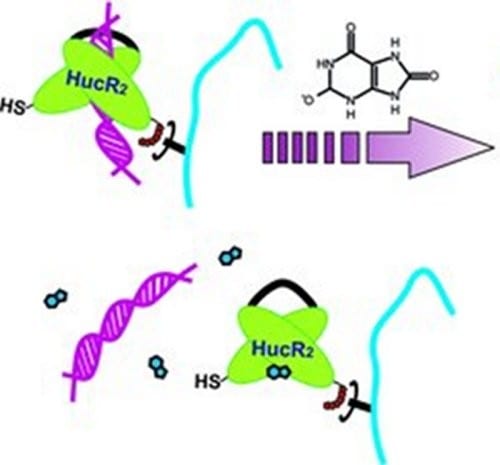

A hydrogel that can tell good from bad: this material can distinguish between normal and pathological levels of urate, a salt related to gout arthritis.
The mechanical holdfast of mussels, the byssus, is used as inspiration in the development of pH-repsonsive mechanical properties in hydrogels.
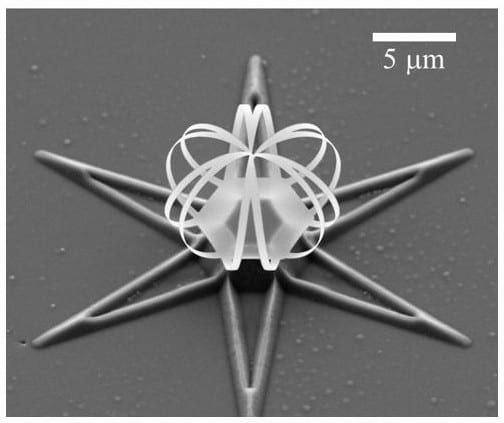
Researchers develop complex 3D nanometer-sized structures using ion-induced plastic strain.

Researchers investigate formation of polymer networks produced by mixing Fe(III) and polymers, mimicking the reaction that mussels use to bind to rocks.
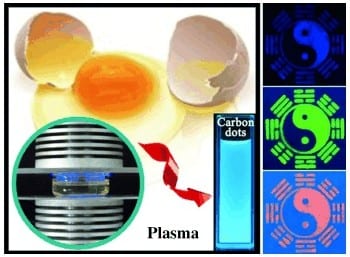
Fluorescent carbon dots can be made by plasma pyrolysis and used as printer ink.
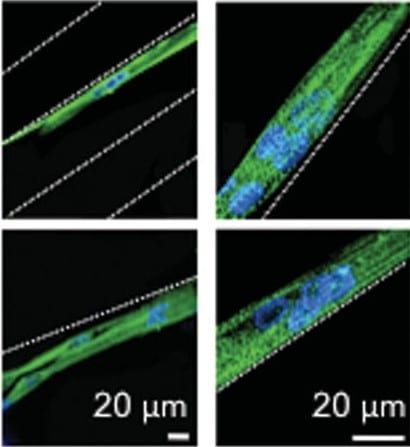
Researchers have engineered a protein biomaterial to generate mimics of human skeletal muscle to study the effect of injury and disease on this tissue.
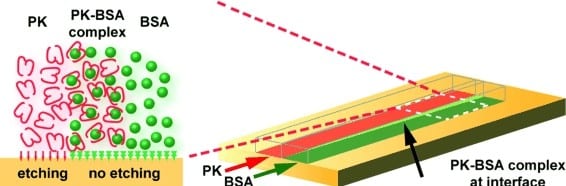
Enzymatic etching used to build nano- and microscale surface topologies.
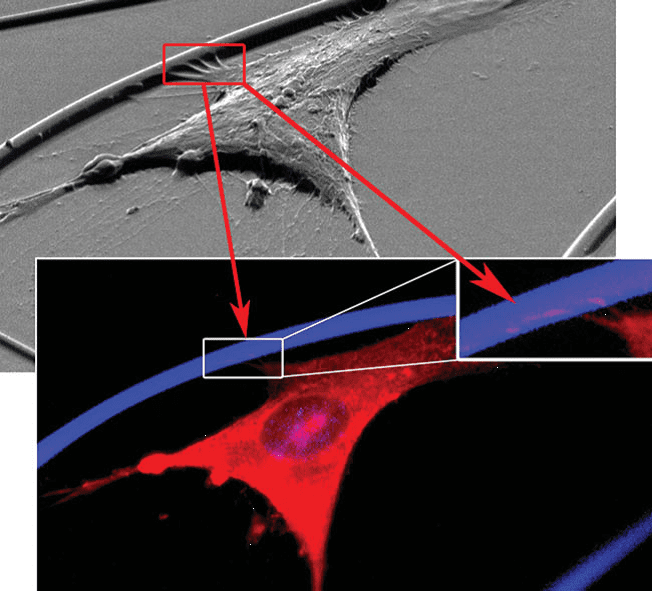
Researchers from Imperial College, London, have now developed a series of modified g-PGA polyester scaffolds for tissue engineering applications.

Interview with Joachim Kohn, director of the New Jersey Center for Biomaterials, on the center’s innovative model and research outsourcing.
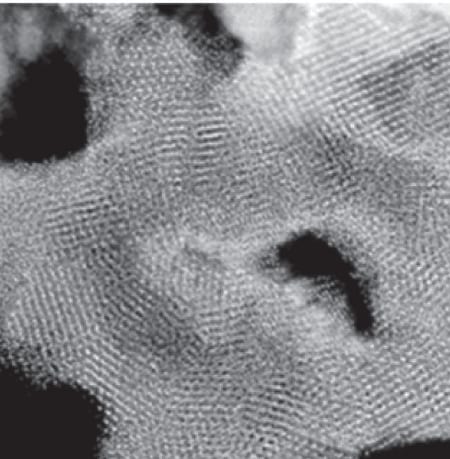
Researchers develop a new, more stable method for synthesising nanoparticle lattices using DNA.