A shape-shifting polymer allows scientists to create a safer implantable device that results in less trauma upon insertion.
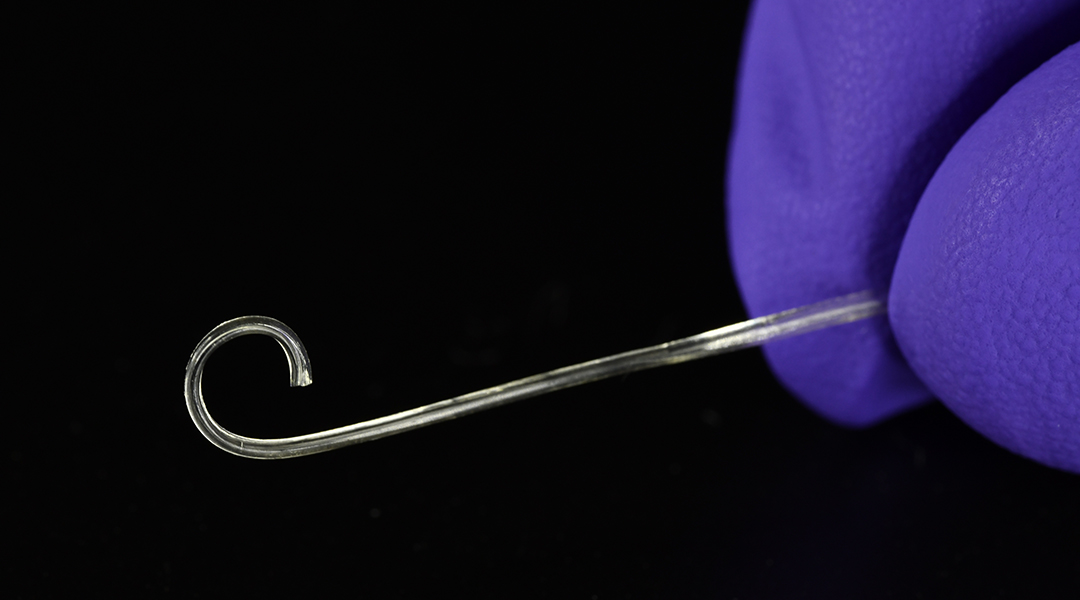

A shape-shifting polymer allows scientists to create a safer implantable device that results in less trauma upon insertion.
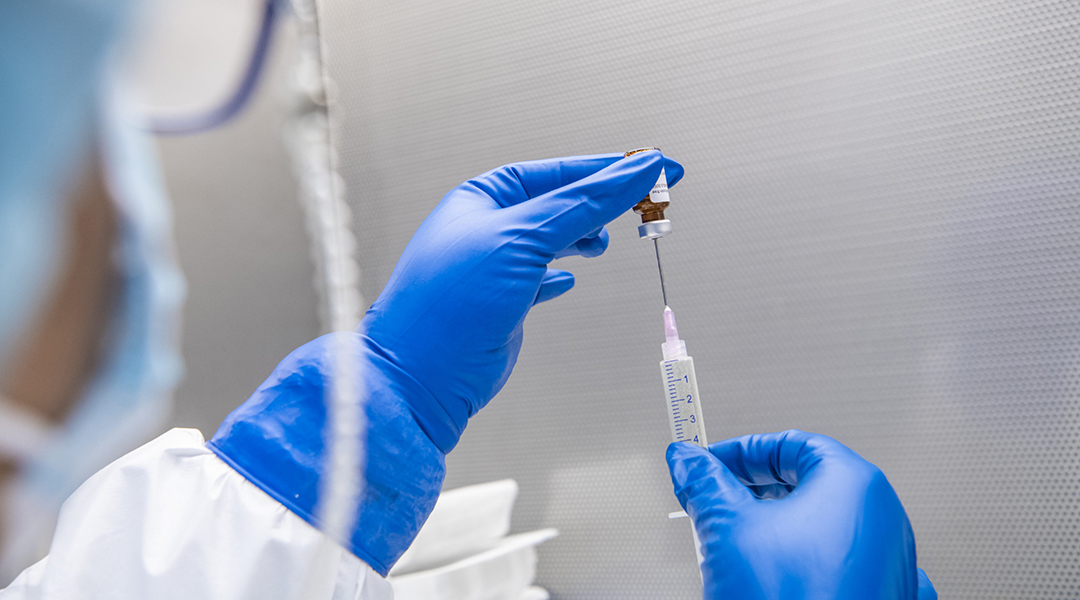
A new vaccine aims to prevent one of the most aggressive forms of breast cancer.
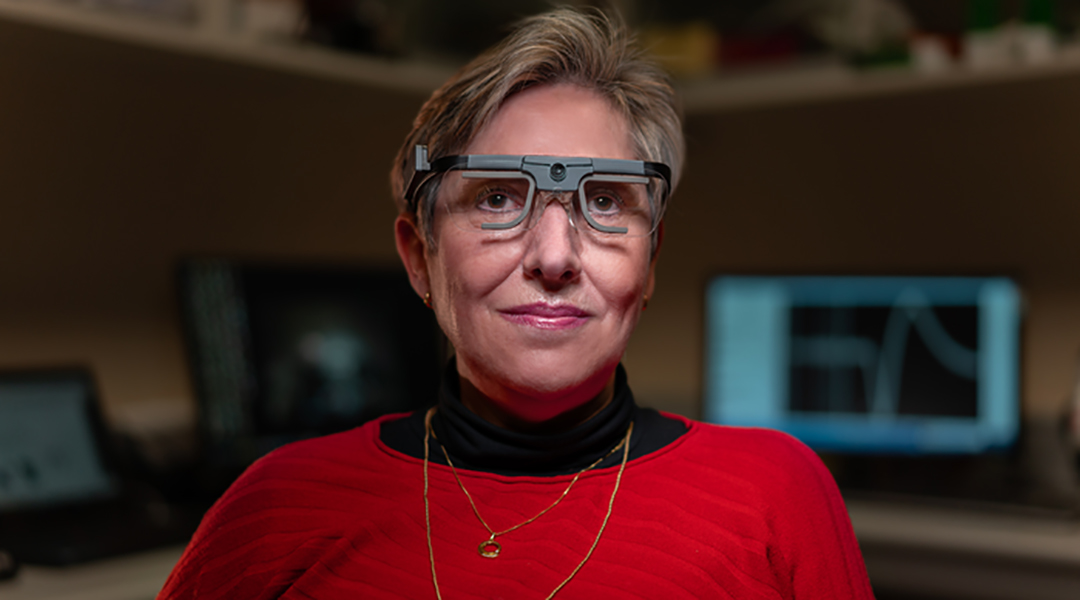

A microelectrode array no bigger than a penny gives hope to restoring sight in blind people.
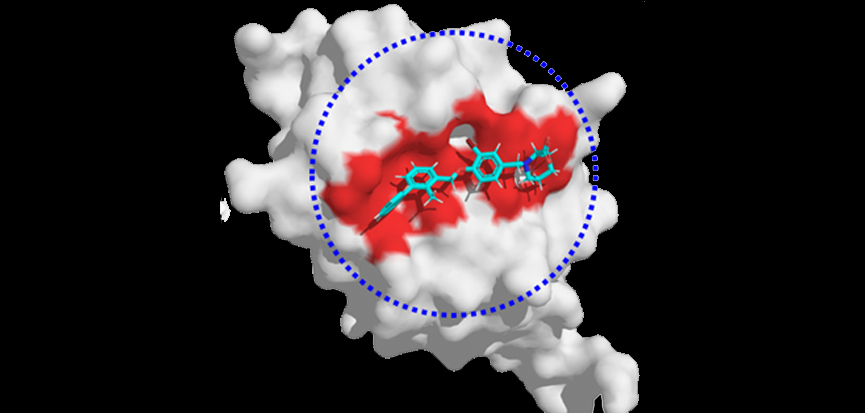
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are playing increasing roles in drug discovery, potentially saving significant time and money.
By using the advantage of hybrid nanomaterials, researchers may have unlocked a new pharmacological route for treating degenerative diseases.
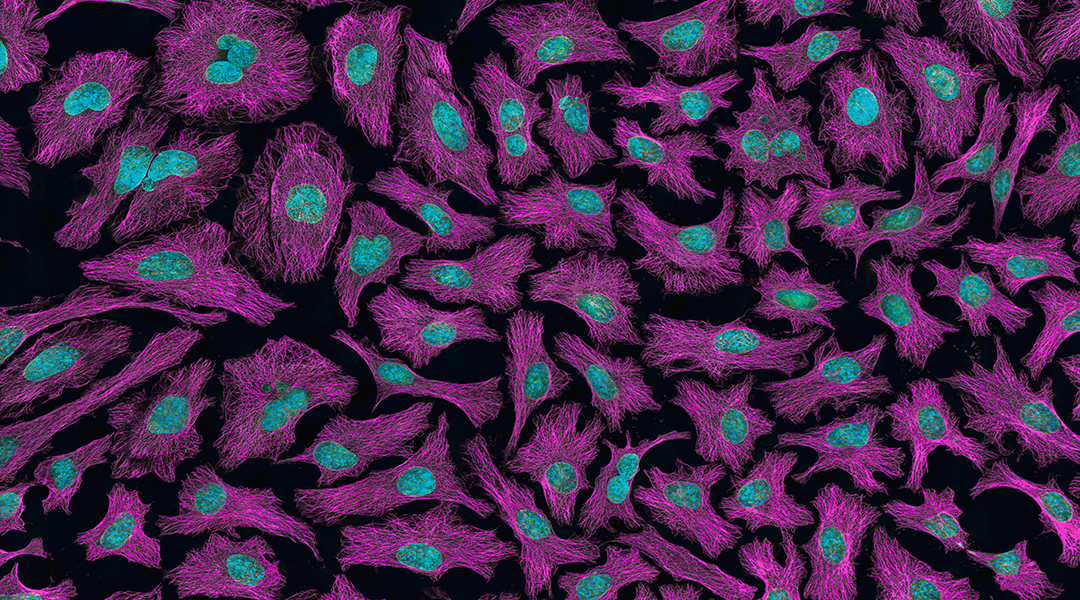
DNA robots built to transverse fluidic cell membranes and control cell function for future regenerative and cell-based therapies.
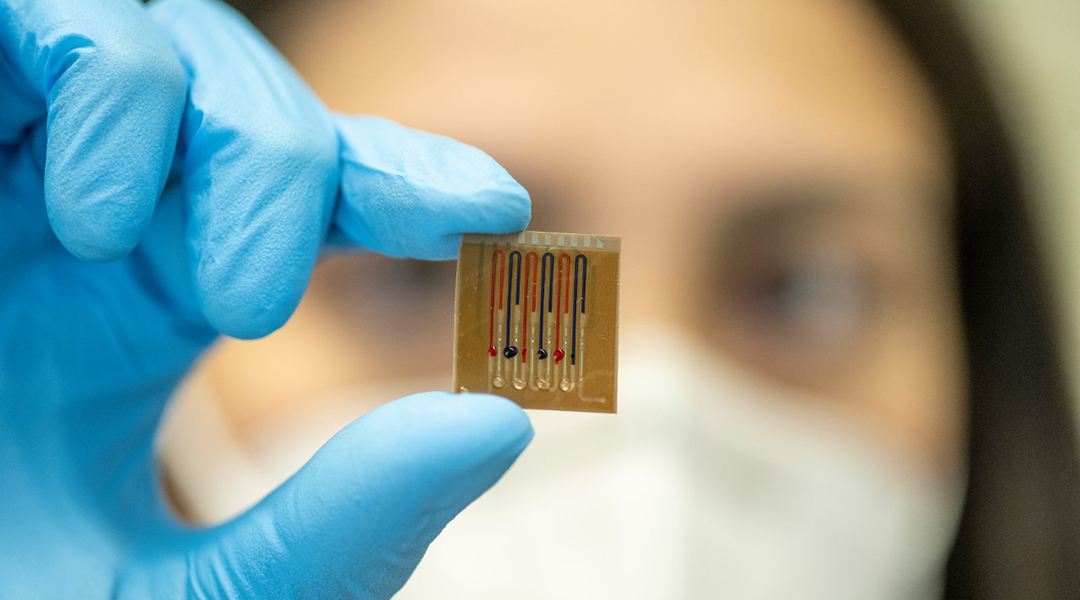
To help combat antibiotic resistance, scientists have developed a biosensor for more efficient and controlled administration of antibiotics.
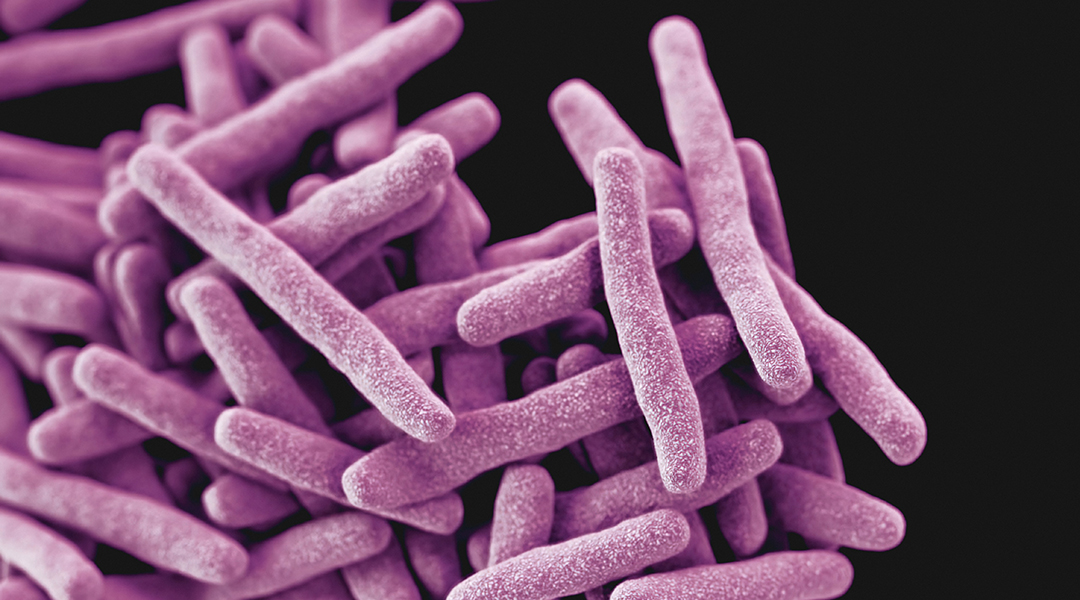
Researchers are devising a quicker and cheaper way to diagnose tuberculosis — and it’s based on how your skin smells.
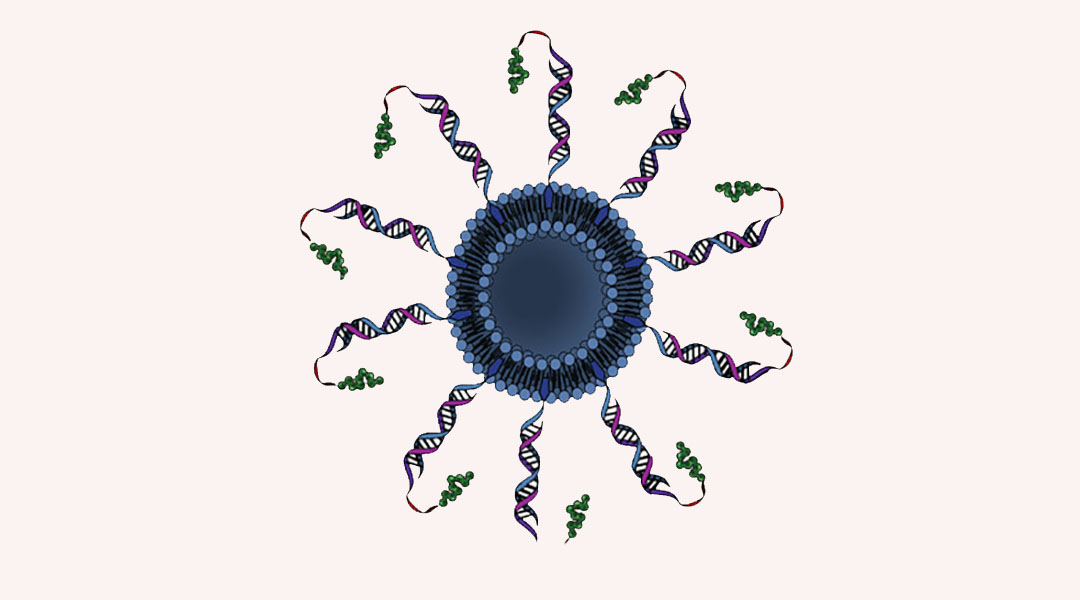
Spherical nucleic acids show promise as a targeted and effective immunotherapy for patients with metastatic prostate cancer.

Plant virus nanoparticles home in on the lungs to help prevent the spread of cancer.