Shear-flow spinning used to produce poly(vinyl alcohol)/ single-wall carbon nanotubes composite fibers with high nanotube loadings and a unique combination of high-performance properties.
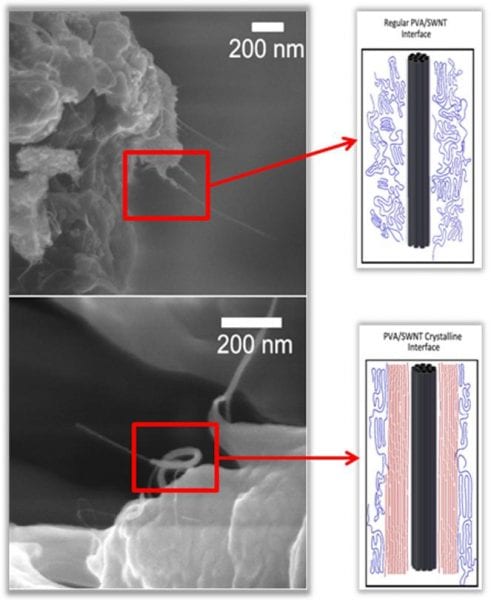


Shear-flow spinning used to produce poly(vinyl alcohol)/ single-wall carbon nanotubes composite fibers with high nanotube loadings and a unique combination of high-performance properties.
Microcapsules containing a brain cancer drug may simplify treatment and provide more tightly controlled therapy, according to Penn State researchers.
Nanjing University of Technology and Shanghai Jiao Tong University host ceremonies.
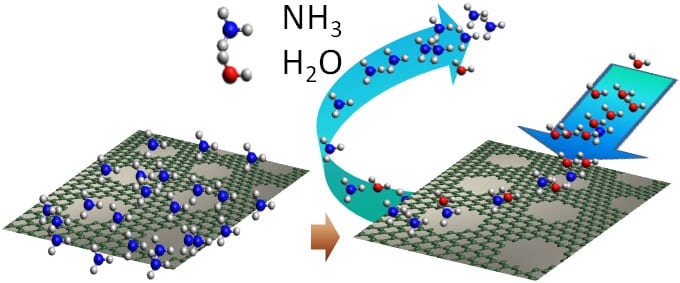
CSIRO scientists have developed new nanosensors capable of detecting very low concentrations of toxic gases such as ammonia and nitrogen dioxide, which can be reset using water molecules or ethanol.
Application of nanotechnology shown to substantially reduce necessary dose of anti-HIV antiretroviral efavirenz.
Scientists have found an efficient way to deliver nanoparticles containing a wide range of biomolecules without using endocytosis, for faster drug delivery.
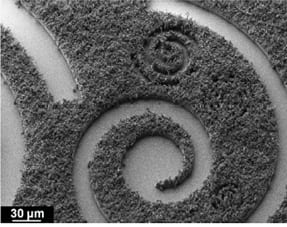
Researchers describe a generic patterning technique that combines UV-lithography with the hot-pressing of preformed metal-organic framwork crystals.
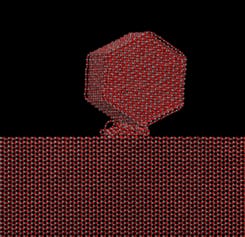
Researchers create a dense, thick, and organic-binder-free ceramic film consisting of stress-free nanoparticles at room temperature.
Team investigate the ability of the body to accept stretchable electronic devices for long-term use.
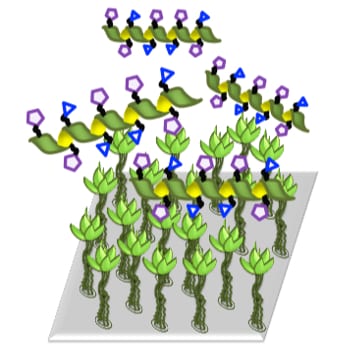
A precisely designed macromolecule that mimics the binding of HIV to immune system cells could be used to stop the virus from physically entering the body.