Internal ribosome entry sites (IRES) are used by some viruses to hijack the host cellular translation machinery for their own translation.
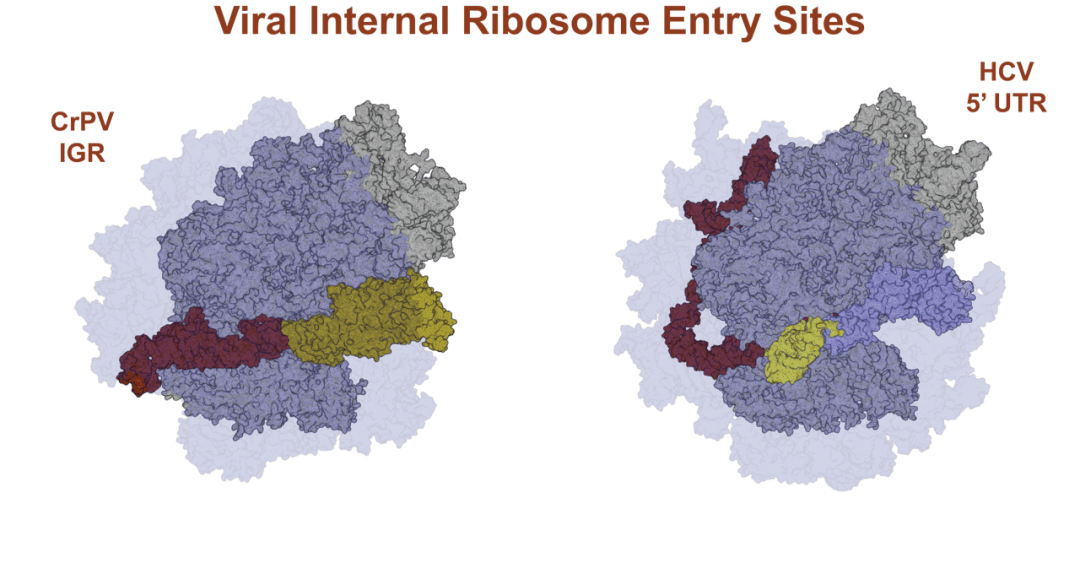

Internal ribosome entry sites (IRES) are used by some viruses to hijack the host cellular translation machinery for their own translation.
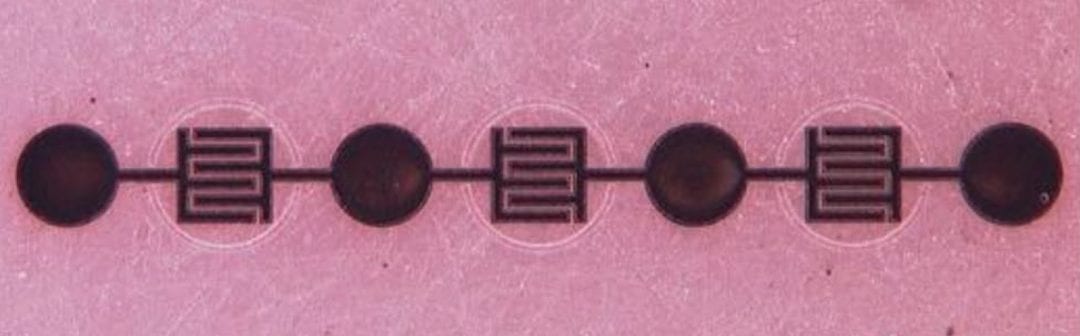
A new printing method produces flexible graphene microsupercapacitors with a planar architecture, suitable for integration in portable electronic devices.
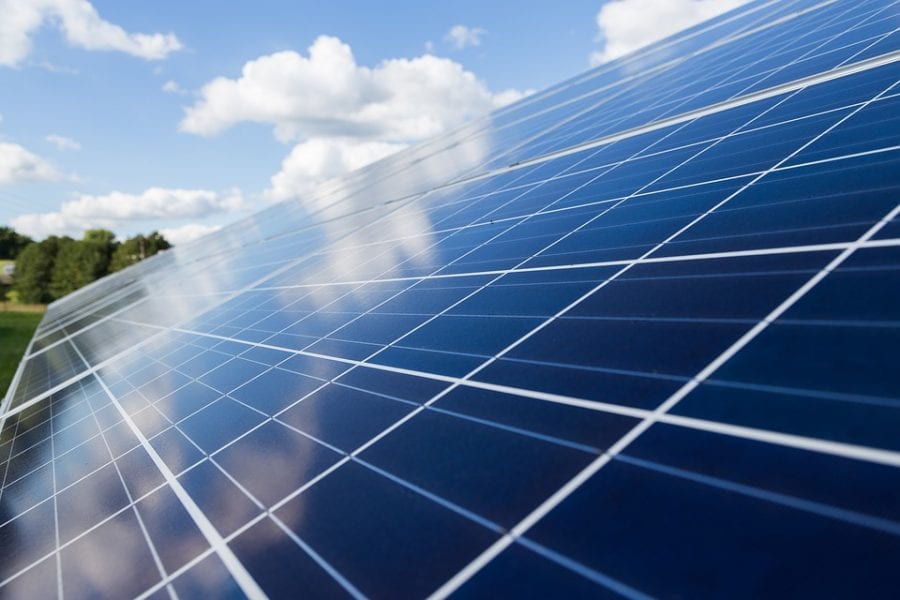

A new technique renders the low-cost process of sputtering a highly competitive fabrication method for photovoltaics.

Australian researchers have developed a promising new plasma treatment method to decontaminate and increase the shelf life of milk.
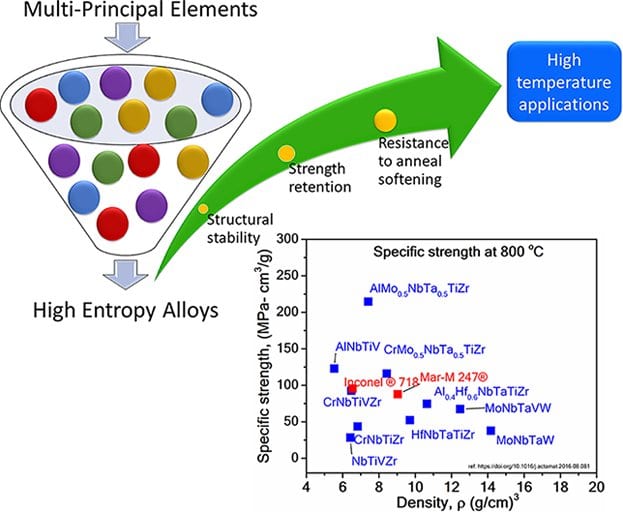
New work reviews advancements in the field of HEAs as a potential emerging material for high-temperature applications.

Dr. Marta Mas-Torrent and her team are developing high-performance electrolyte-gated field-effect transistors (EGOFETs), electronic devices capable of working in an aqueous environment.

Wood could potentially replace petrol in chemistry and concrete in construction, according to studies conducted under the Swiss Research Programme “Resource Wood”.

University of Houston and Pennsylvania State University researchers fabricate conducting polymer microcups from polylactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) for neural applications and drug delivery. These microcups are tunable in terms of size, surface roughness, electrical properties, and drug release.

Ting Zhang and co-workers from the Suzhou Institute of Nano-Tech and Nano-Bionics at the Chinese Academy of Sciences develop a novel superhydrophobic and piezoresistive coating for wearable sensing devices. The coating is durable in harsh conditions and can be used to detect real-time human movement when fabricated as a wearable strain sensor.
Serotonin neurons are highly plastic; their development, maturation and regeneration is controlled by a complex gene regulatory network in constant interaction with the environment. An overview article recently published in WIREs Developmental Biology offers an updated view of these fundamental developmental mechanisms, pointing to the many ways by which developmental dysfunction of serotonin systems might occur at different periods in life. This opens new possibilities for therapeutic intervention, which can range from prevention of risk to stem cell therapies.