Anna Musyanovych of the Max Plank Institute for Polymer Research reviews Biodegradable Polymers in Clinical Use and Clinical Development.


Anna Musyanovych of the Max Plank Institute for Polymer Research reviews Biodegradable Polymers in Clinical Use and Clinical Development.
Can organic matter behave like a fridge magnet? Scientists from The University of Manchester have now shown that it can.

Glass-ceramics that combine strength with good optical characteristics may lead to improved dentures.
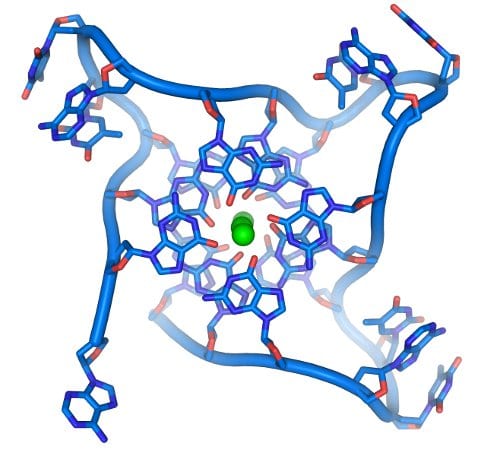
Tim Long and co-workers provide a broad overview of established and ongoing work in the area of DNA nucleobase-modified polymer synthesis.
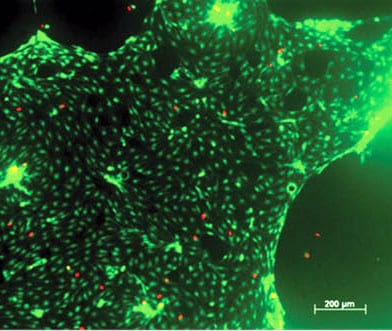
A biocompatible polyacrylate network for the build-up of artificial tissues is created by a 3D printing process.
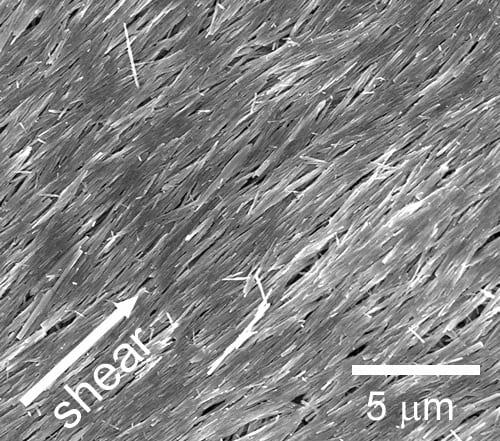
A new hybrid structure of ZnO nanowires and polythiophenes with nanometer-scale ordering and a high crystallinity could be used for hybrid photovoltaics.

Bioinspired surface patterning and a landmark review on graphene are among the most-downloaded Advanced Materials papers in December 2011.

The International Center for Materials Nanoarchitectonics (WPI-MANA) features in a new special issue from Advanced Materials.
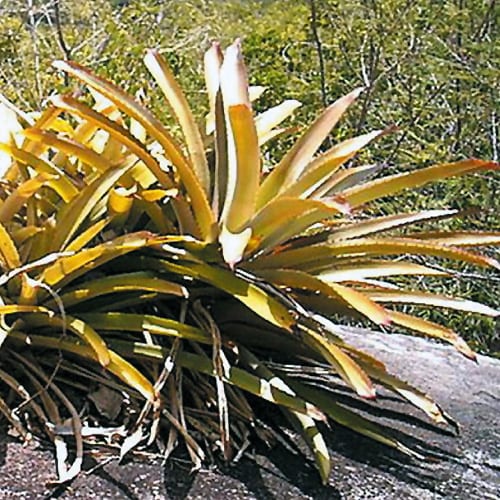

Brazilian scientists have studied the water absorption in unsaturated polyester composites reinforced with macambira fiber.

A hemostatic material for field dressings in emergency wound treatment is made by layer-by-layer deposition of thrombin and tannic acid.