Patchy particles, and Janus particles in particular, already have such broad application potential that it’s hard to believe they are a relatively young concept to nanoscience.
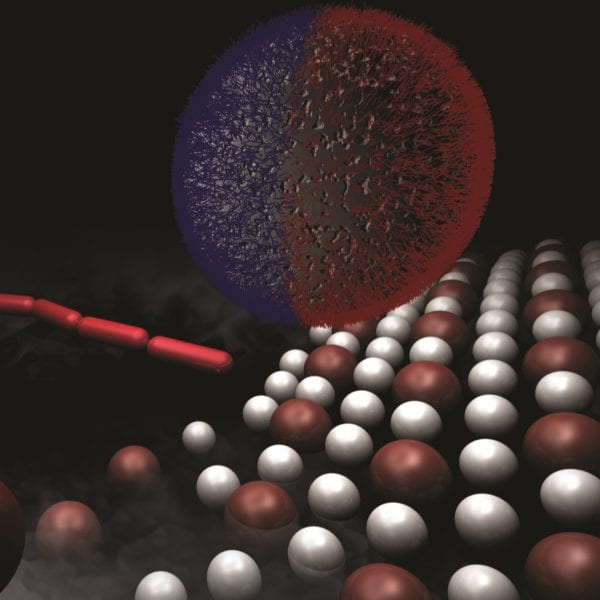

Patchy particles, and Janus particles in particular, already have such broad application potential that it’s hard to believe they are a relatively young concept to nanoscience.
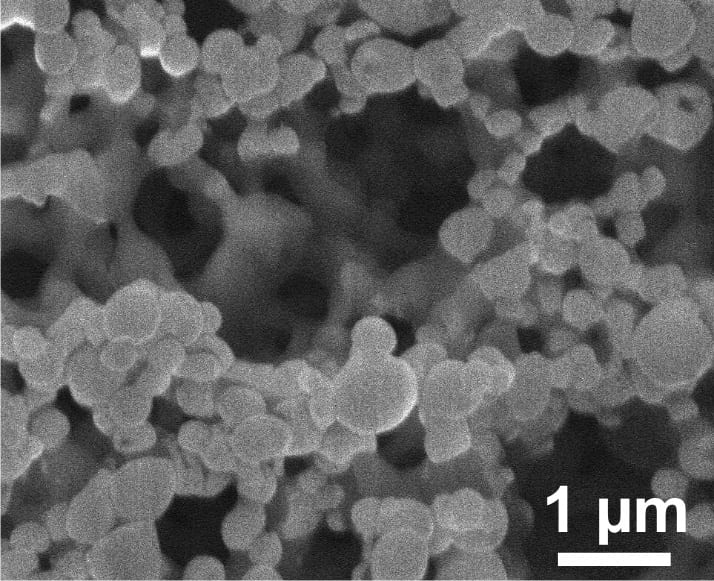

Researchers have developed a network of nanoscale particles that can be injected into the body and release insulin when blood-sugar levels rise.
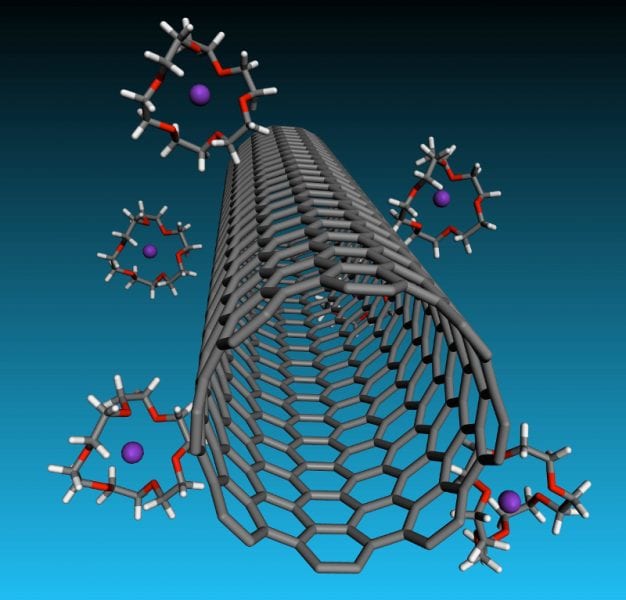
Rice University strategy turns negatively charged carbon nanotubes into liquid crystals that could enhance the creation of fibers and films.
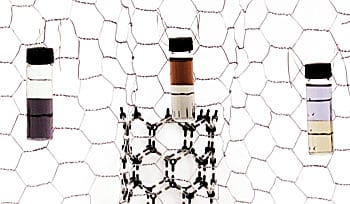
An old, somewhat passé, trick used to purify protein samples based on their affinity for water has found new fans at NIST.
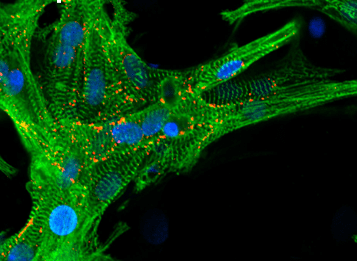
A new biomaterial for heart tissue regeneration, resembling live cardiac tissue in key characteristics, has been reported.
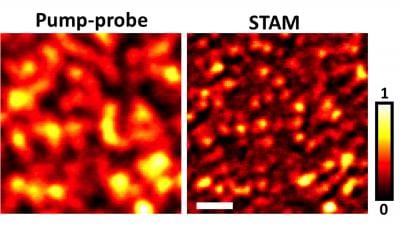
Researchers have found a way to see synthetic nanostructures and molecules using a new type of optical microscopy that does not require fluorescent dyes.
100-nanometer-long “meta-atom” of gold and silicon oxide is capable of straightening and speeding up light waves.
Researchers succeed in generating flashes of extreme ultraviolet radiation via the reflection from a mirror that moves close to the speed of light.
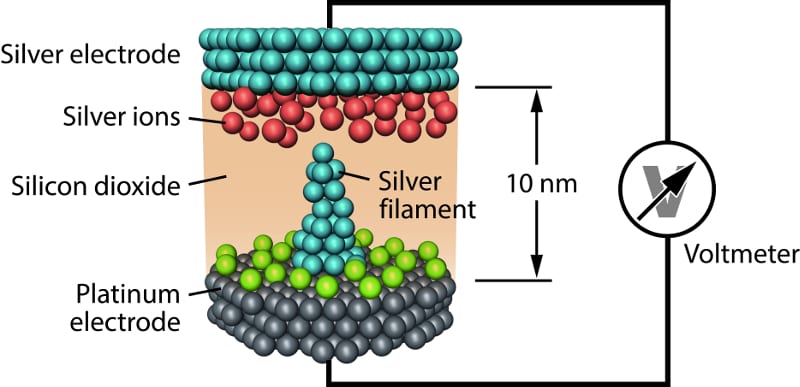
Resistive memory cells open up new possibilities in nanoelectronics.
Researchers develop technique for imaging nanoparticle dynamics with atomic resolution as these dynamics occur in a liquid environment.