Developments in pathogen-detecting materials could provide an easy means of detecting viruses within public places.


Developments in pathogen-detecting materials could provide an easy means of detecting viruses within public places.
A sensitive blood test for the early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease could be possible with nanoparticle arrays.
Blood pooling in venous valves is a key risk factor in deep vein thrombosis. A new model is used to better understand how this occurs.
The FRESH-technique for 3D printing heart models could be a game changer for budding surgeons.
Stem cells found in the lungs can be redirected to the heart using a new inhaled antibody therapy to help boost healing following a heart attack.
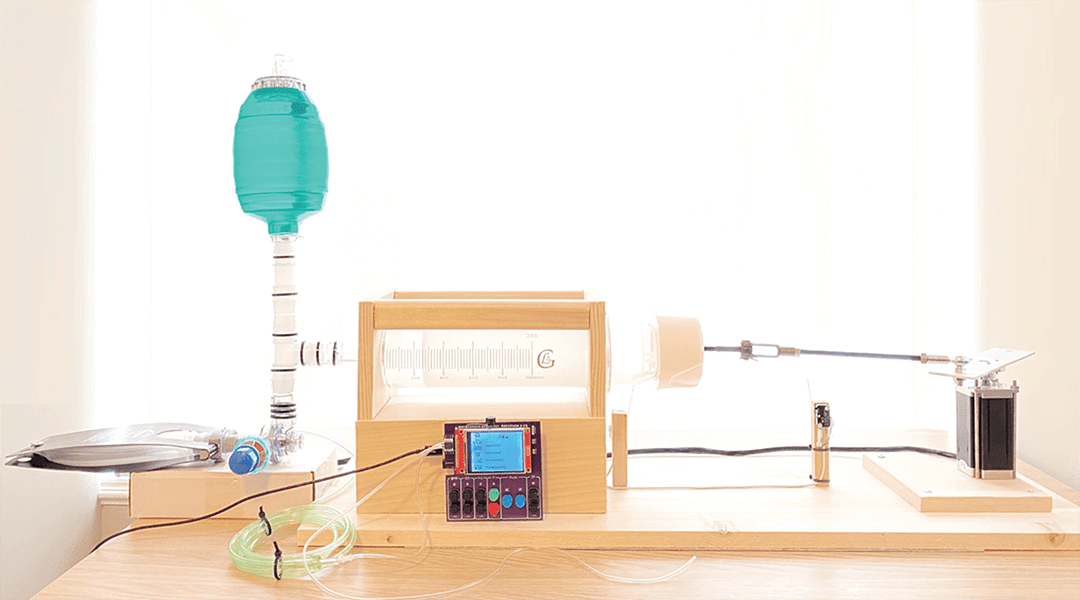
The procurement and maintenance of high‐end ventilators limits their use in emergency situations. By removing the “frills”, researchers create a viable alternative.

In a survey of biomaterials articles that included cell culture experiments, only 3.7% of studies reported the sex of the cells.

Recent advanced in nanoparticle-based SERS imaging has led to better diagnoses of diseases like cancer, and improvements in image-guided tumor surgeries.

A new blood-derived embolic material with regenerative properties stops bleeding instantly, even in cases of impaired coagulation.

Understanding how gluten affects the gut is a key to understanding whether gluten-free diets are merely a fad or based in solid science.