Swedish researchers have pioneering a polymerization process that converts the pulp and fragments released from many wood processing operations into value-added products such as refined chemicals and materials.
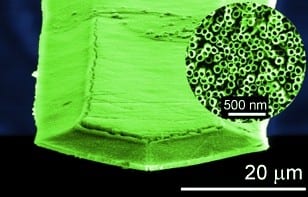
Synthetic Scent Hounds: Nanotechnology to Detect Explosives
Nanostructured sensor for the detection of very low concentrations of explosive.

New Carbon Materials for Faster Computers and Better Mobile Phones
Graphene and carbon nanotubes could improve the electronics used in computers and mobile phones, reveals new research from the University of Gothenburg, Sweden.

Advanced Healthcare Materials Offering Free Subscription
Get free access to the best biomedical materials papers, including work on tissue engineering, drug delivery, bioimaging, and more.
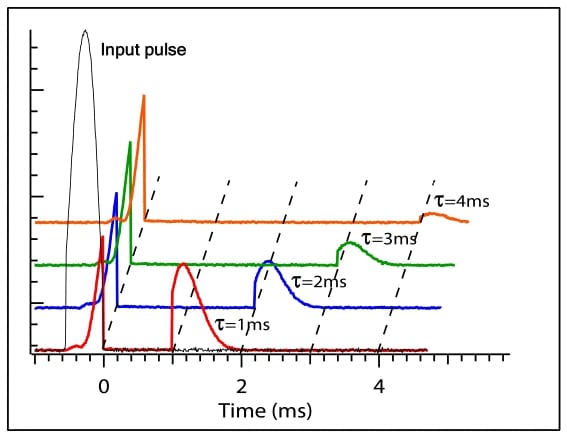
Warm atoms for a long memory: Implementing quantum computing
One of the exciting potential applications of electromagnetically induced transparency and slow and stored light is for practical realization of quantum memory, and, ultimately, quantum computing. Recent advances using ensembles of warm atoms in vapor cells have been made.
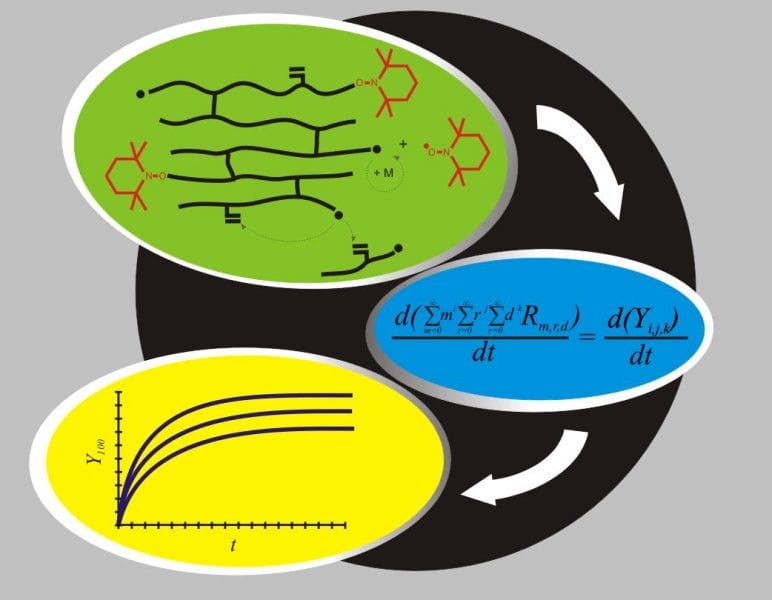
Copolymerization Understood: Modeling Network Formation
New research demonstrates a unique mathematical model for the kinetics of the nitroxide-mediated free radical copolymerization of vinyl/divinyl monomers.
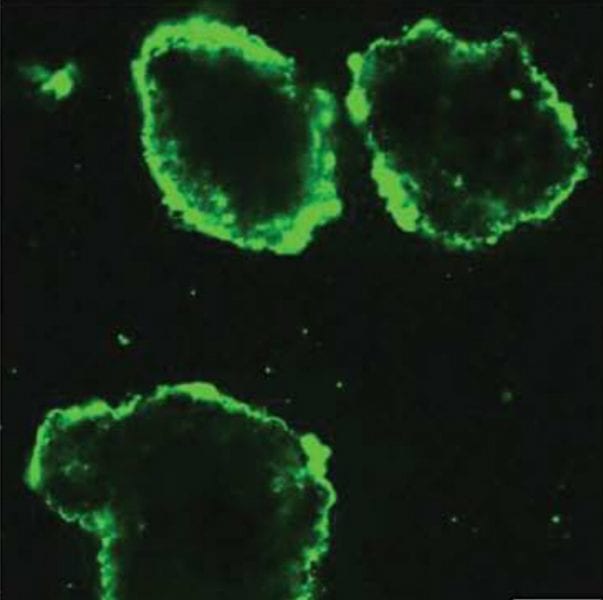
Curing diabetes, with a little help from polymer science: coating could make widespread treatment a reality
American researchers report new coating to improve promising treatment for Type 1 diabetes.
The need for speed: Developing coherent Raman scattering
Coherent Raman scattering methods have one key advantage over spontaneous Raman microscopy: speed. The (sub-)microsecond pixel dwell times offered by narrowband CRS imaging methods have initiated a new era of chemical imaging applications in biology and biomedicine.
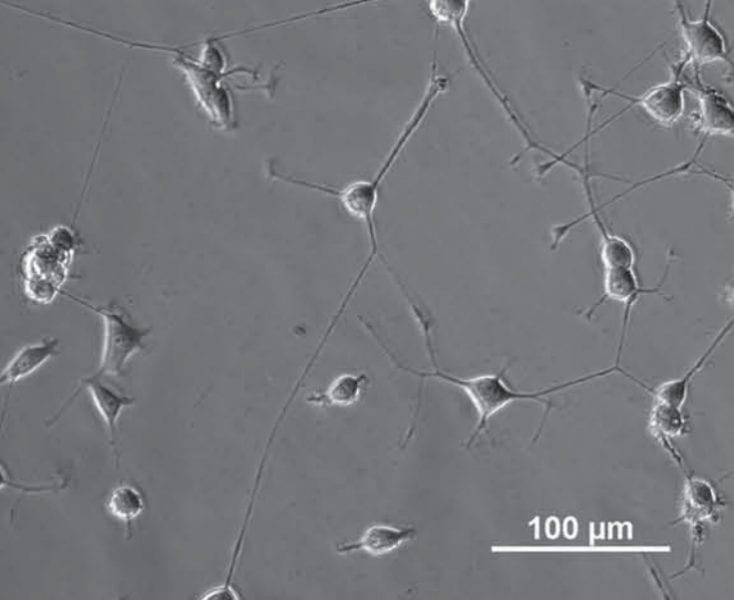

Pitt Researchers Develop Synthetic Platform to Produce Materials for Specific Biomedical Applications
New platform shows promise in the advancement of tissue engineering and drug delivery
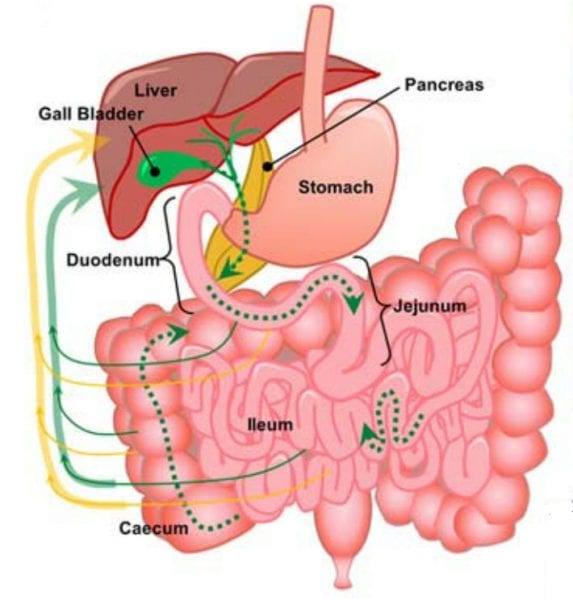
Nanoparticles on their way through the body – Medicine in miniature
Which pathways do nanomedicines take after they have been swallowed? Scientists find a recirculation pathway of polymeric micelles using multimodal nonlinear optical microscopy.










