Recent advances in chromosome conformation capture technologies have led to the discovery of previously unappreciated structural features of chromatin.
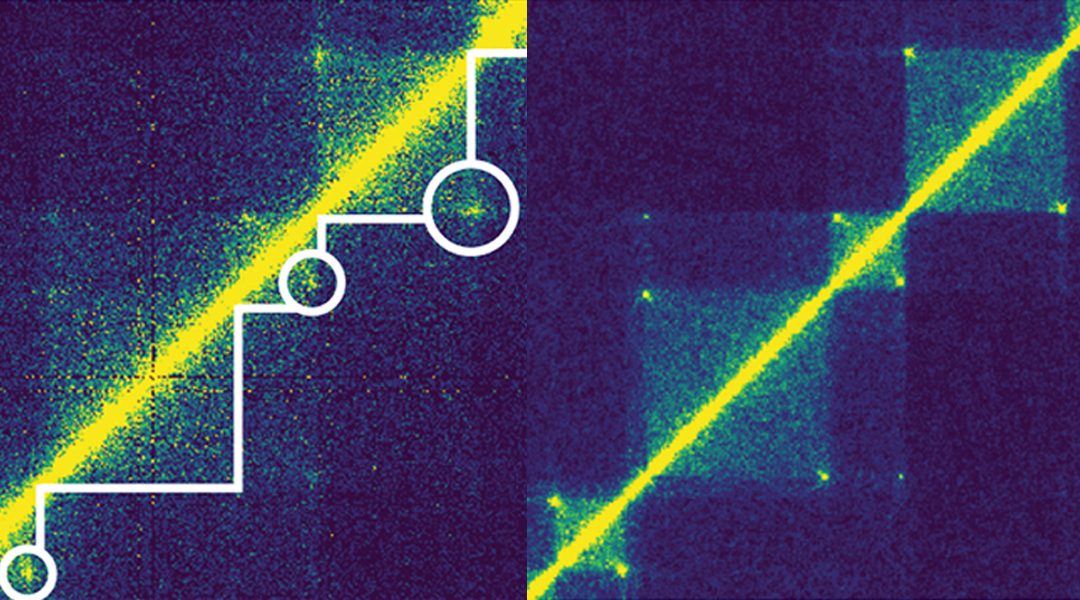

Recent advances in chromosome conformation capture technologies have led to the discovery of previously unappreciated structural features of chromatin.

Quantitative systems modeling aims to integrate knowledge in different research areas with models describing biological mechanisms and dynamics to gain a better understanding of complex clinical syndromes.

An investigation into how pioneer factors interact with closed chromatin to influence chromatin landscapes and generate differentiated cells.
Throughout development and into adulthood, Wnt proteins ensure embryonic patterning, cellular proliferation, cellular identity, and organization of tissues.

From individual neuron models to cutting-edge control approaches, the evolution of computer methods for deep brain simulation (DBS) can lead to personalized DBS therapy.

PharmGKB is one of the preeminent worldwide resources for pharmacogenomic information. It is freely available to all users, and provides an interface that is easy to use for researchers, clinicians, and everyday citizens.
Research into how to better visualize tumor cells during surgery is underway, with a hope of limiting the occurrence of positive surgical margins.
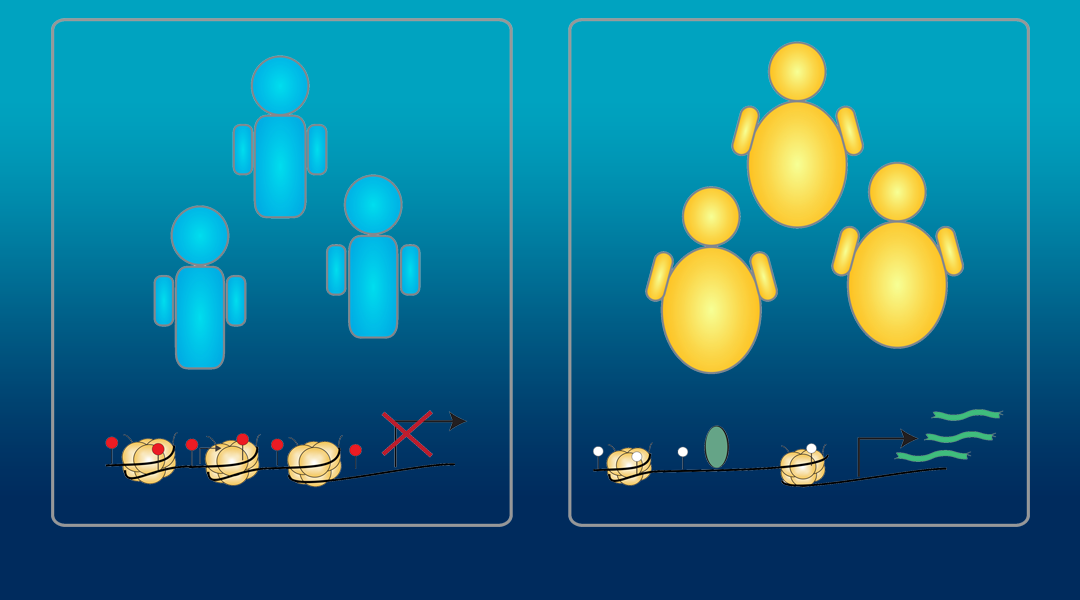
Modifications to chromatin are associated with the development of metabolic diseases, including Type 2 diabetes and obesity. There is evidence that these chromatin modifications can lead to long-term disease risk and increased disease risk for offspring.
Human microbiota, blood group antigens, and disease, a look at the ways that microbiota interact with the human body.
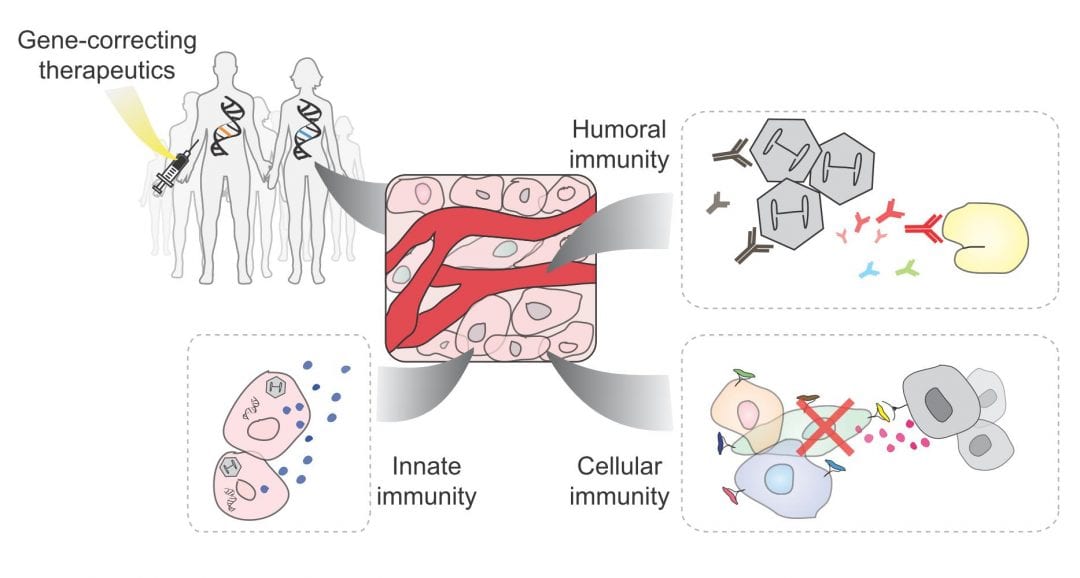
Genome-editing therapeutics introduce foreign nucleic acids and proteins into the circulation and cells, which can activate the innate, cellular, and humoral immunity in human patients. The key obstacle in translating CRISPR therapeutics to the clinic is hence to identify, diminish, and monitor these immunological risks before adverse immune reactions.