Synergistic developments in advanced fluorescent imaging and labeling techniques enable direct visualization of the chromatin structure and dynamics at the nanoscale level and in live cells.


Synergistic developments in advanced fluorescent imaging and labeling techniques enable direct visualization of the chromatin structure and dynamics at the nanoscale level and in live cells.
An atypical, low‐power, atmospheric pressure plasma source for application in plasma medicine.
Physical, chemical, and synthetic virology work together to reprogram viruses as controllable nanodevices.
Poxviruses are an unusual family of large double‐stranded (ds) DNA viruses that exhibit an incredible degree of self‐sufficiency and complexity in their replication and immune evasion strategies.

Low-cost, wearable sensor that use the metabolic response of yeast to measure ionizing radiation doses are developed.
Single stranded RNAs with a free 5′ monophosphate end are susceptible to rapid degradation. Transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs) are stabilized by hairpin structures and by “hiding” their 5′ ends within complex protein structures.
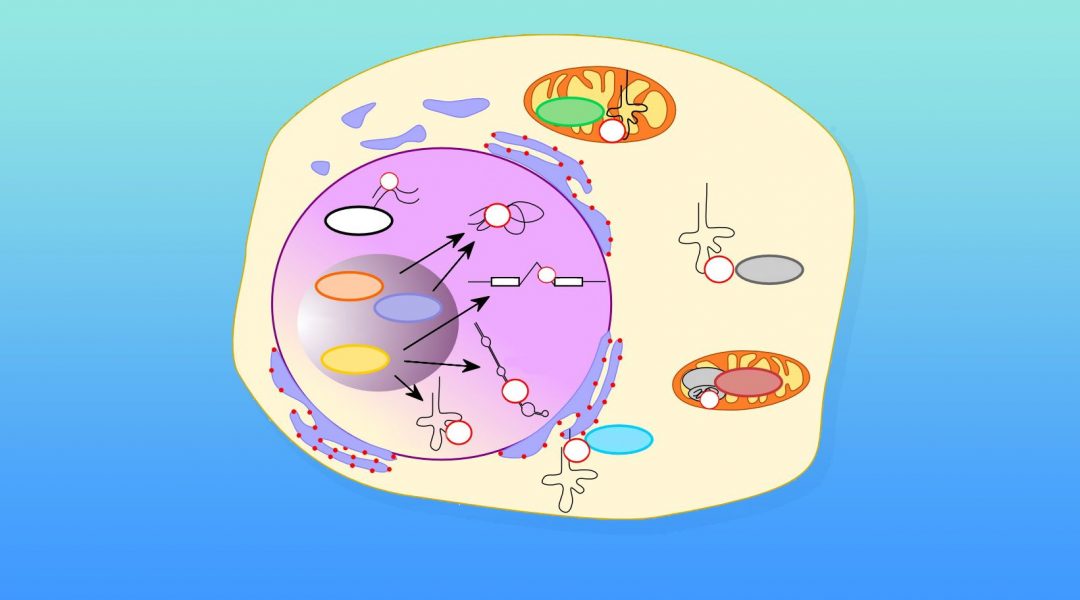
It is a well‐known fact that RNA is the target of a plethora of modifications which currently amount to over a hundred. The vast majority of these modifications was observed in the two most abundant classes of RNA, rRNA and tRNA. With the recent advance in mapping technologies, modifications have been discovered also in mRNA and in less abundant non‐coding RNA species.
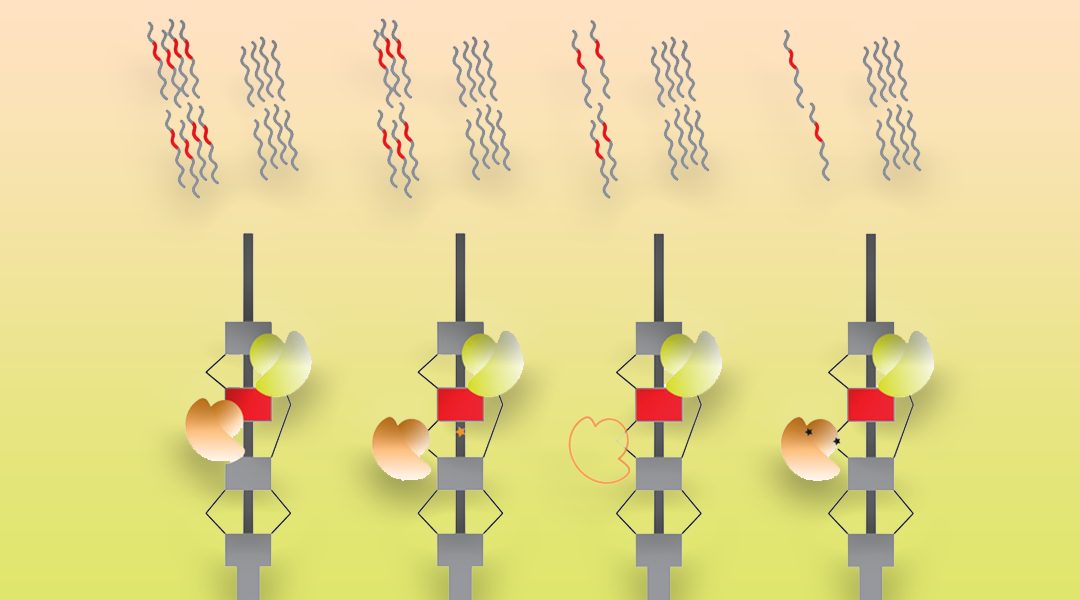
RNA processing has emerged as a key mechanistic step in the regulation of the cellular response to environmental perturbation.

New research from India shows that vitamin E may prove beneficial to alleviate chemotherapy associated side effects in cancer patients.

The Editors of Small Methods are pleased to publish this special biomedical virtual issue. This collection highlights outstanding research in Small Methods from the very first issue to now, in the areas of biosensing, biomedical engineering, nanomaterials,...