A team of researchers at Stanford University has developed shape-controlled, self-wrapping electronics based on carbon nanotubes.


A team of researchers at Stanford University has developed shape-controlled, self-wrapping electronics based on carbon nanotubes.
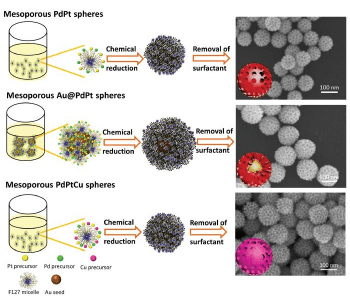
A facile, green, and tunable synthesis for mesoporous spheres consisting of noble metals is developed. The spheres are potential catalysts in fuel cells.
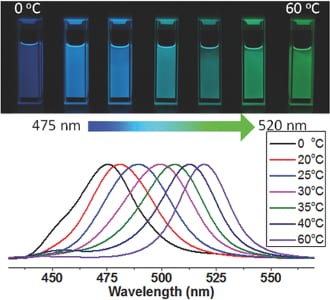
New research published in Advanced Science by a team of Chinese researchers presents the control of the emission color of CH3NH3PbBr3 perovskite quantum dots using precipitation temperature.
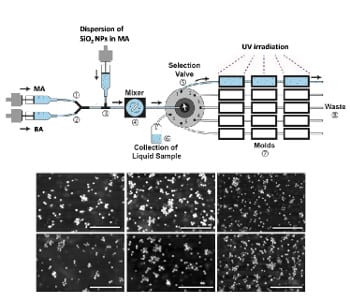
Researchers have developed a microfludic platform for high-throughput preparation of multicomponent photopolymerized nanocomposite films.
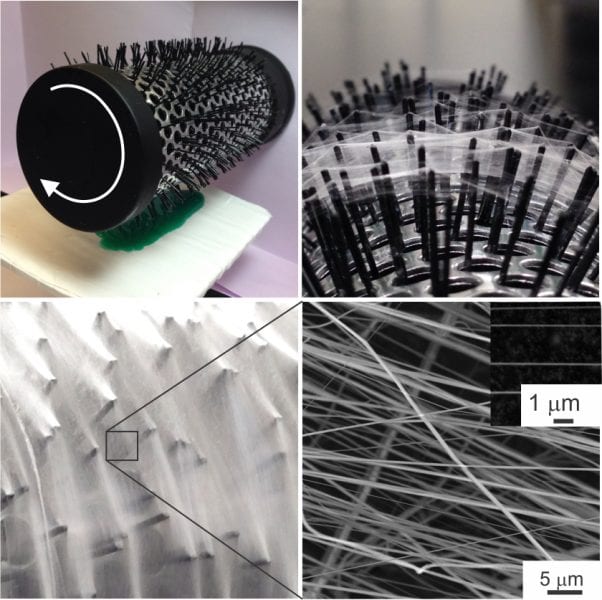
Touch- and brush-spinning methods for drawing of nanofibers, core–shell nanofibers, and their aligned 2D and 3D meshes have been developed.
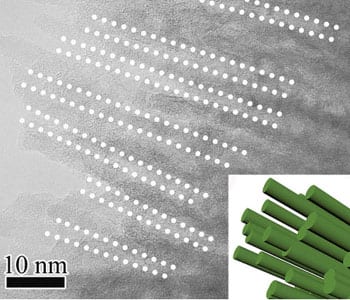
Hierarchical structuring in hybrid amorphous/crystalline nanowire bundles provides a promising anode material for lithium-ion batteries.

A new study in Advanced Science presents the development of a new nanocomposite material electrocatalyst for more efficient hydrogen production.
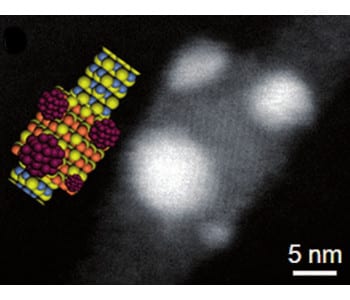
A Chinese research team has demonstrated the synthesis of unique one-dimensional heteronanostructures for photo-induced applications.

Different types of photodetectors realized with carbon nanotubes are presented in this comprehensive review article.
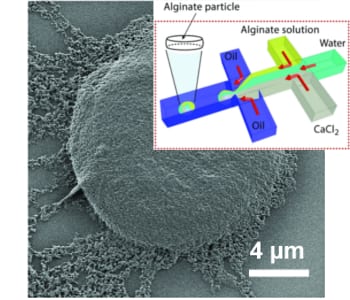
L. Mazutis and co-workers have developed a microfluidic approach for production of alginate hydrogels having a unique biconcave shape and the size of a mammalian cell (~10 µm).