Interfaces to capture, detect, and analyze circulating tumor cells are reviewed, which give a valuable insight into tumor progression and metastasis.


Interfaces to capture, detect, and analyze circulating tumor cells are reviewed, which give a valuable insight into tumor progression and metastasis.
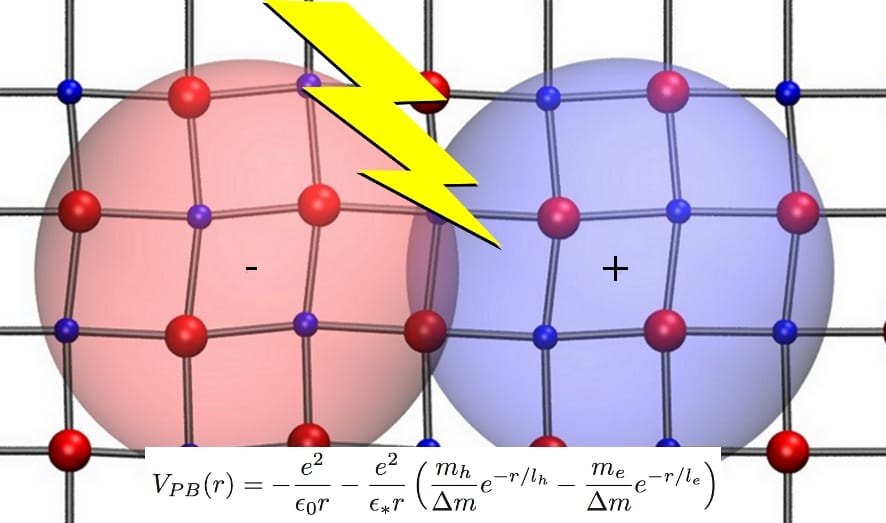
Menendez-Proupin et al. study excitons in metal-halide perovskites using the effective mass approximation providing better agreement with the experiment.

The month’s top articles from the field of nanooptics, optoelectronics, optical devices, detectors & sensors, micro/nano resonators and more.
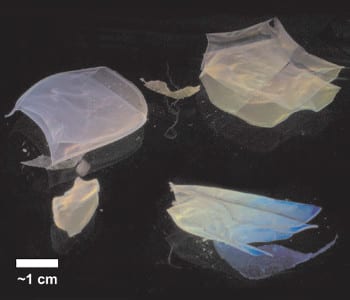
Cross-linked hydrogel-particle films with tunable size, shape, porosity and optical transmission are obtained with a simple evaporation method.
Topography of plant virus nanoparticles has been shown to influence osteogenesis of bone derived mesenchymal stem cells.

In this comprehensive review, the main research routes and technologies that are being followed to deliver high-performance electronic skin are discussed.
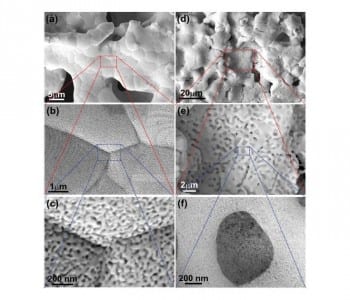
An innovative and cheap method to produce bi- and trimodal Au–Ag and a hierarchical nanoporous Ni–Mn with excellent electrochemical properties is developed.

Researchers demonstrate that phenazine compounds can bioaccumulate and self-assemble in macrophages and epithelial cells.
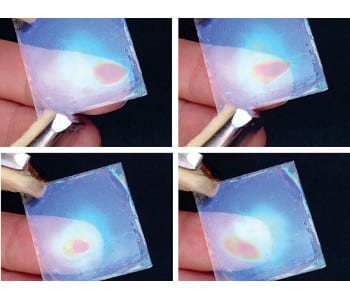
A new sensor technology could enable touchless displays that respond to moisture emitted by the human body.

A unique 3D reduced graphene oxide–cobalt oxide composite material presents promising properties as an anode for lithium-ion batteries.