Supercritical carbon dioxide induced reverse micelles were used to create metallic 1T-phase molybdenum disulfide and tungsten disulfide nanosheets for hydrogen generation.
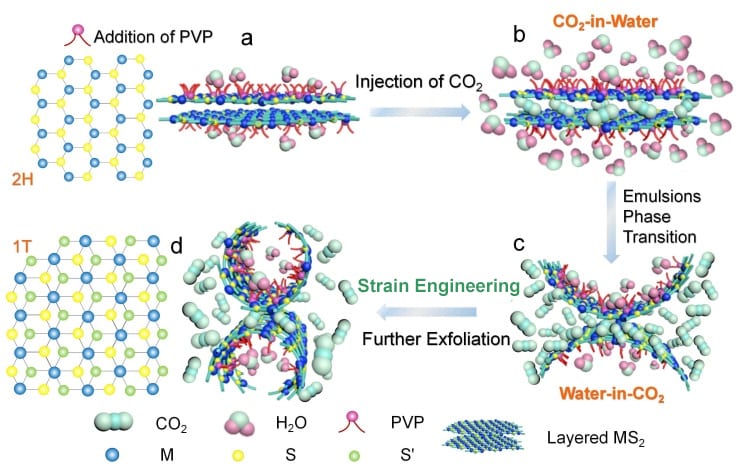

Supercritical carbon dioxide induced reverse micelles were used to create metallic 1T-phase molybdenum disulfide and tungsten disulfide nanosheets for hydrogen generation.
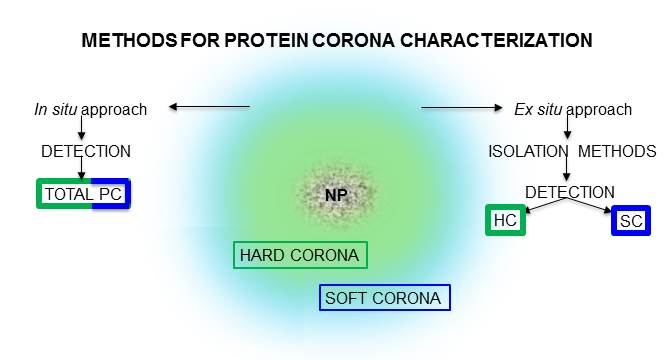
The application and the clinical development of nanomedicines strongly requires a deep study on the complex dynamics that happen after in vivo administration. Particularly, plasma proteins tend to associate to nanoparticles, forming a new surface named the “protein corona” that can have a strong impact on biodistribution, targeting efficacy, and toxicity.
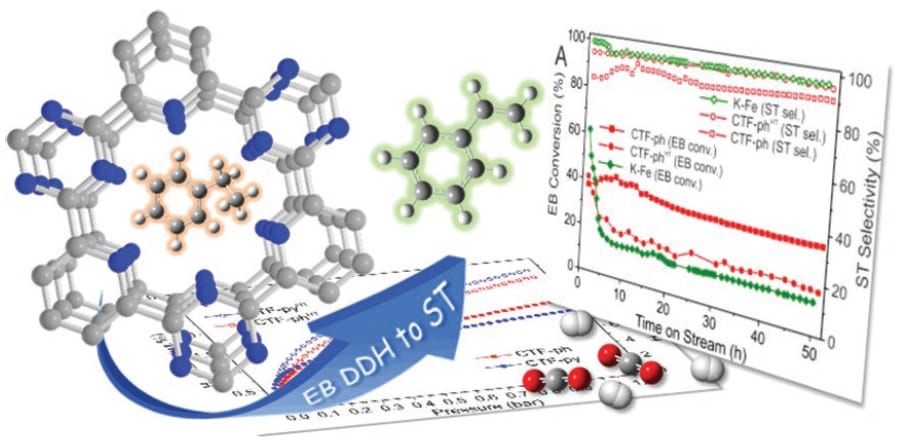
It reads like the plot of an action movie: against all odds, an unassuming catalyst avoids deactivation and captures its target with record effectiveness.
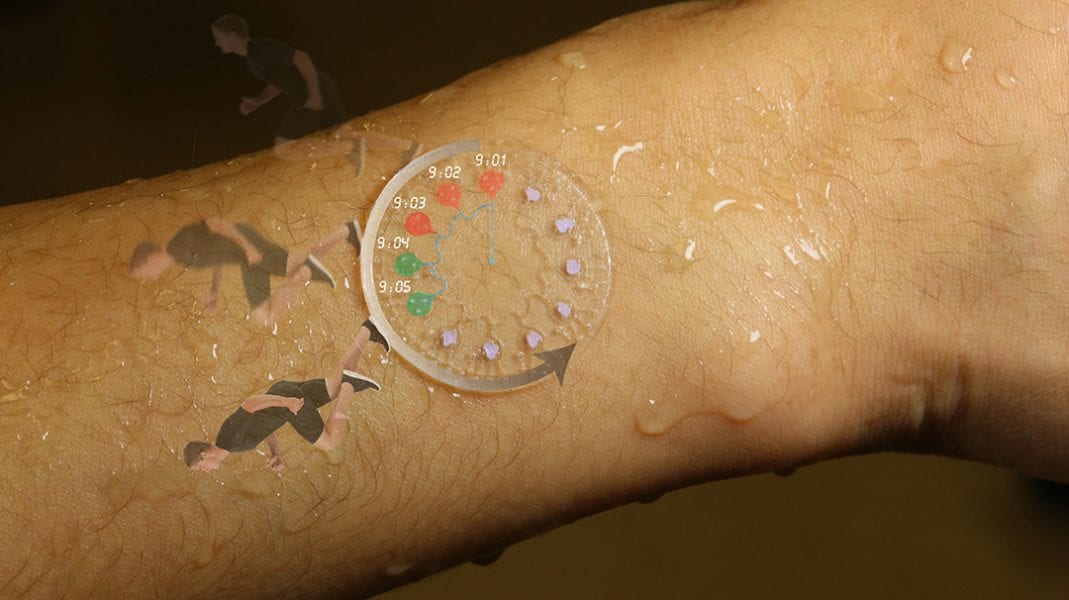
John Rogers and co-workers report a soft, skin-mounted microfluidic system for sweat collection and analysis directly from and on the surface of the skin.
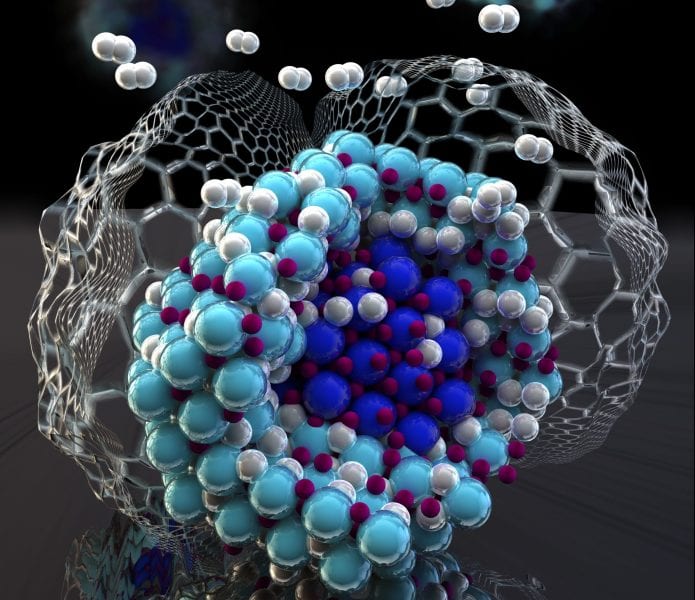
Internal interfaces in the Li3N/[LiNH2 + 2LiH] solid-state hydrogen storage system alter the hydrogenation and dehydrogenation reaction pathways upon nanosizing, suppressing undesirable intermediate phases to dramatically improve kinetics and reversibility.

Superamphiphobic and durable coatings on woven/non-woven surfaces for repelling many types of liquids.
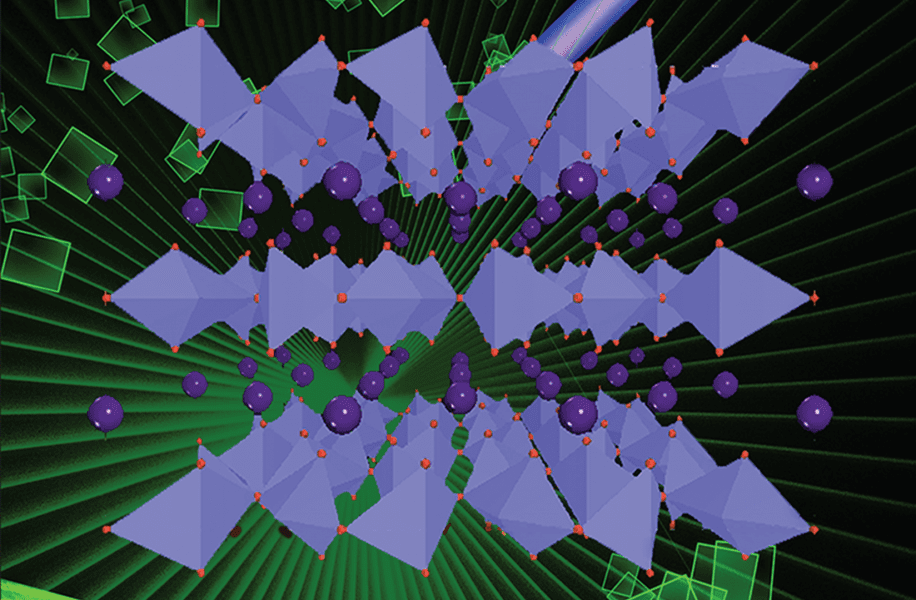
The month’s top articles from the field of nanooptics, optoelectronics, metamaterials, optical devices, detectors & sensors, micro/nano resonators and more.
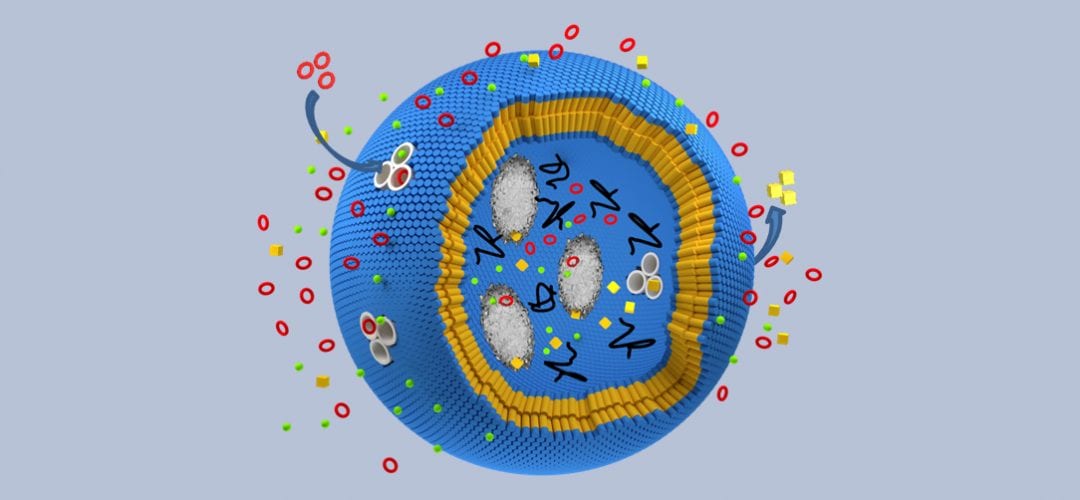
For the first time, the activity of an enzyme in a crowded environment vs a nonencapsulated enzyme is studied.
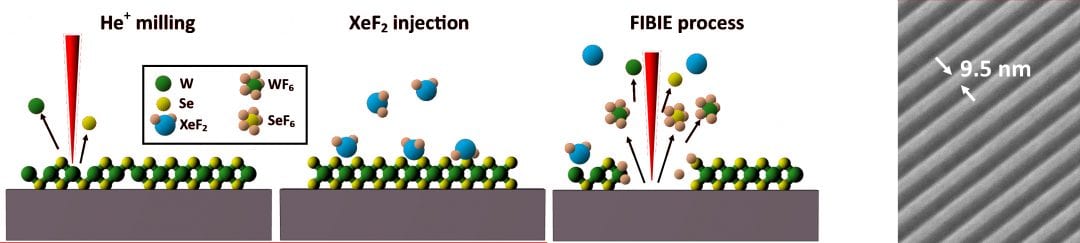
A chemically assisted focused-helium-ion-beam-induced etching process is introduced.
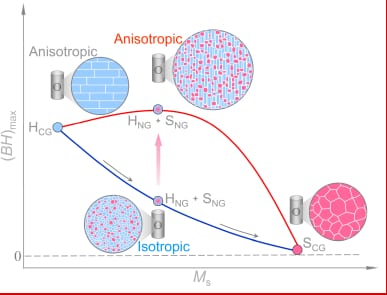
An exciting new strategy and direction in the quest for stronger permanent-magnet materials with fewer critical elements.