Predicting and managing resources in a changing climate requires an understanding of plant-accessible subsurface water storage.
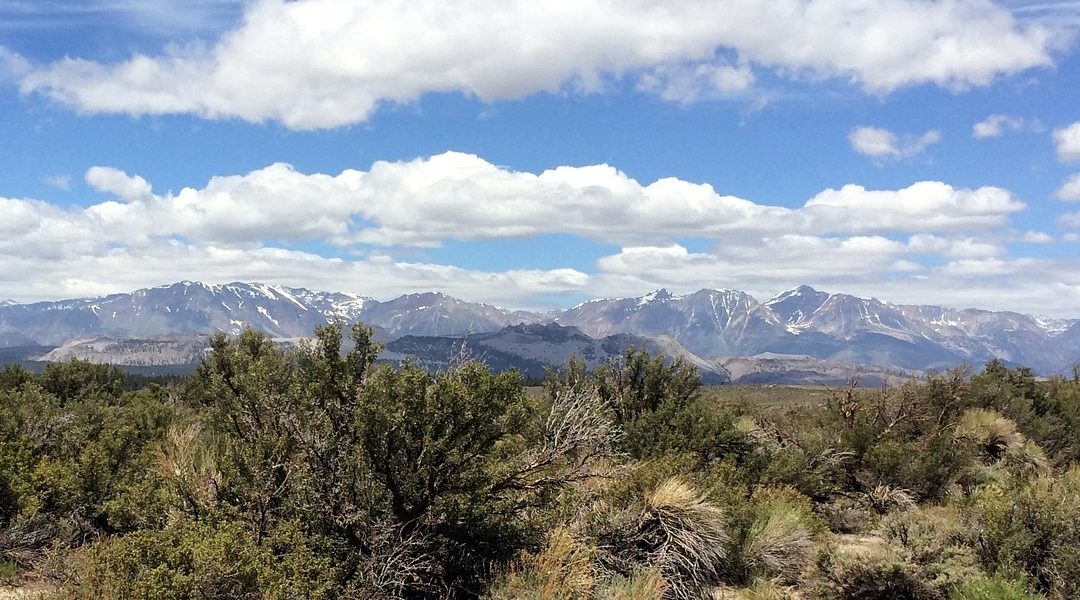


Predicting and managing resources in a changing climate requires an understanding of plant-accessible subsurface water storage.

Various approaches for converting CO2 and H2O to liquid hydrocarbons using solar energy involve electro/photo/thermochemical catalytic processes and combinations thereof exist.

Qantas used biofuel processed from a non-food, industrial type of mustard seed for a historic trans-Pacific 15 hour flight saving 18 000kg in carbon emissions.

Greener catalytic ammonia synthesis requires robust control experiments to eliminate artifacts.
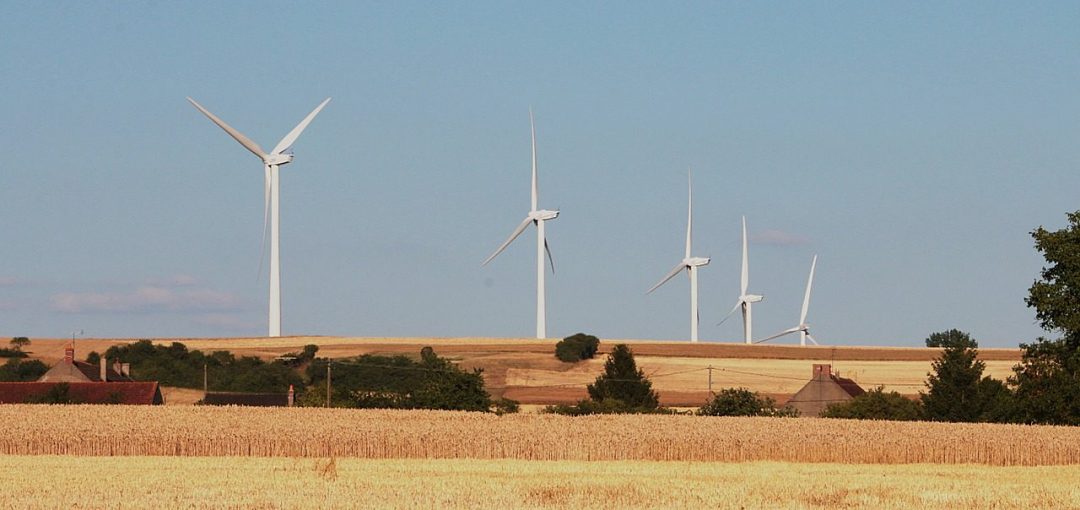

Today, wind power plant developers and wind turbine manufacturers increasingly face power system stability support requirements similar to conventional power stations. These new requirements intend to make wind power plant behavior more similar to conventional power stations.

Imagine a scenario where CO2 greenhouse gas emissions could be used to desalinate briny water. This would be a creative way of killing two birds with one stone, namely helping to ameliorate global-warming-induced climate change and producing high quality water for agriculture and drinking purposes.

Smart windows switch between transparent and opaque states based on environmental cues. Researchers reveal a prototype that exploits plasmons, converting incident sunlight into local thermal energy to trigger the switch.

Adding a layer of biodegradable paper over a photocatalyst is found to increase the activity of the catalyst significantly.
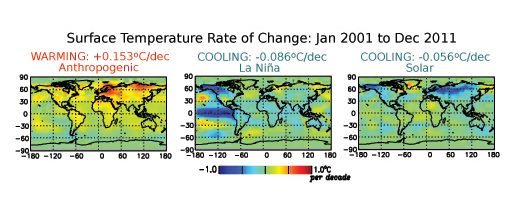
The divergence of physical model simulations from observations that precipitated the notion of a “global warming pause” does not signify a crisis in climate science or understanding but simply the limitations of current physical climate models.
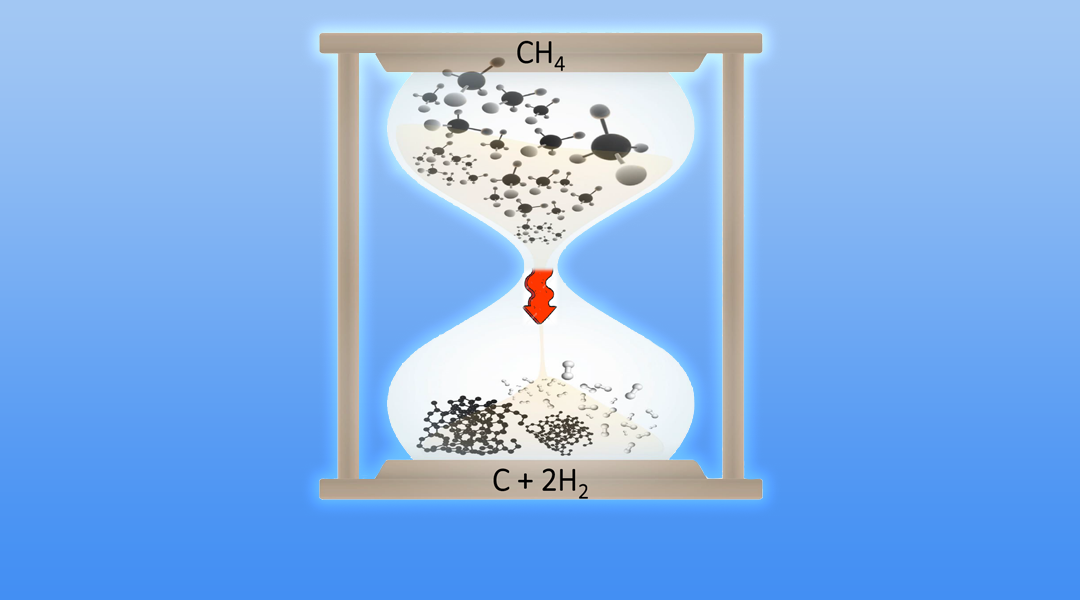
A fascinating approach for utilizing the chemical energy contained in the carbon–hydrogen bonds of methane without the co-production of carbon dioxide in the combustion process is discussed.