A recent study provides a new platform for investigating light trapping, higher pseudospin states, vortex generation, and other interesting phenomena.
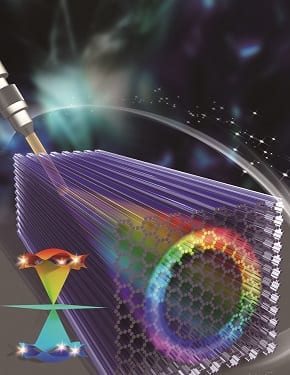

A recent study provides a new platform for investigating light trapping, higher pseudospin states, vortex generation, and other interesting phenomena.
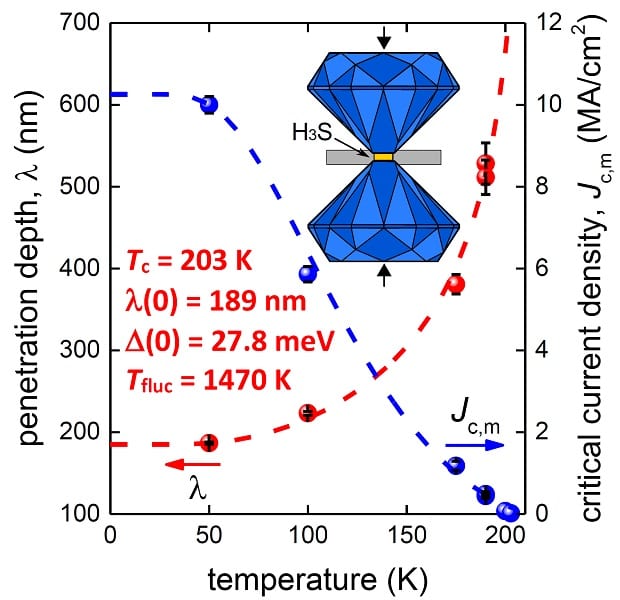
Superconductivity has been discovered in highly compressed hydrogen sulphide at an amazing 203 degrees kelvin.

A historic article by Max Planck, first published (in print) in 1901 has reached the top 5% of scores in Altmetrics.
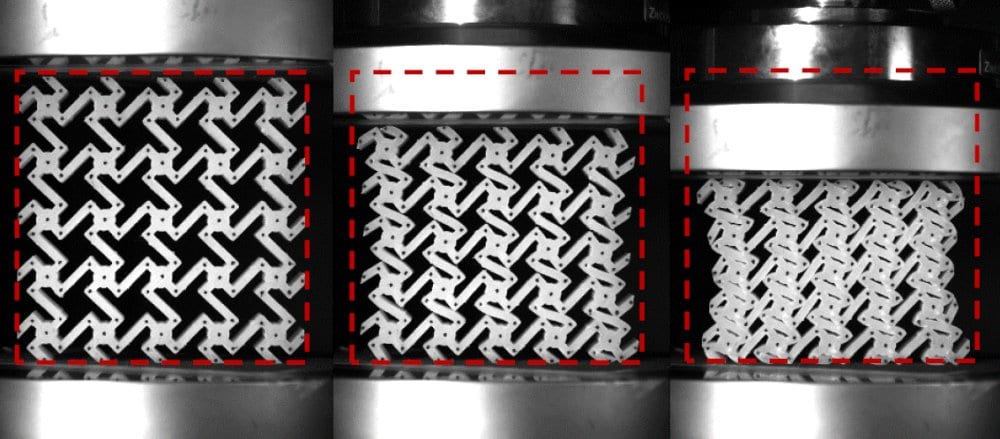
The concept of amplifying chirality-induced auxetic effect via elevating internal rotation efficiency was proposed and proved via multi-material 3D printing, mechanical experiments, and FE simulations.
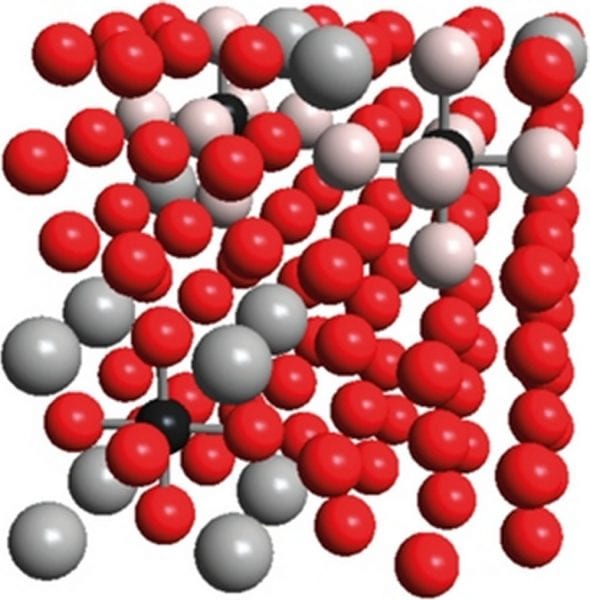
The energetic consequences of having iron, manganese or aluminum atoms sit at certain positions close to carbon are studied by performing first-principles quantum-chemical calculations.
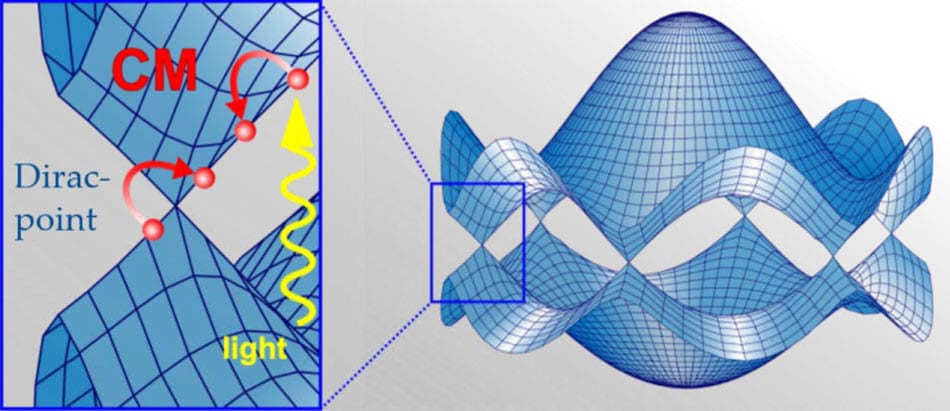
The remarkable electronic properties of graphene open up new carrier relaxation channels that can result in a significant multiplication of optically excited carriers.
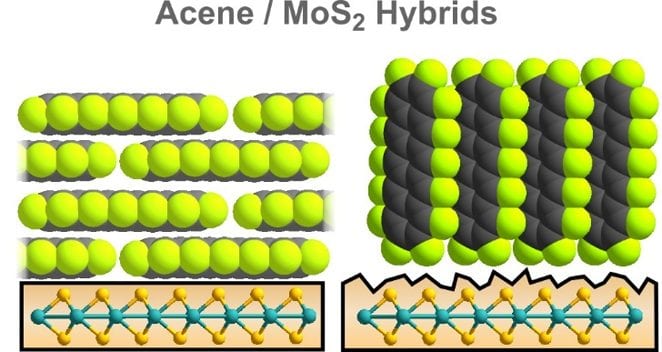
A group of scientists from Philipps-Universität Marburg have performed a careful and systematic study of organic film formation on molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) crystals.
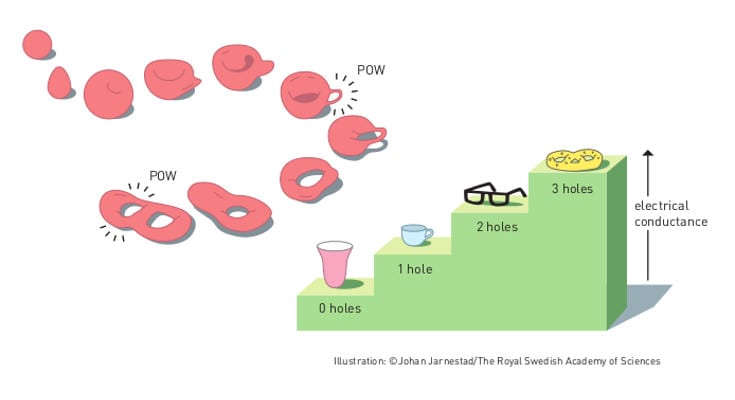
The Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences has decided to award the Nobel Prize in Physics 2016 with one half to David J. Thouless and the other half to F. Duncan M. Haldane and J. Michael Kosterlitz for theoretical discoveries of topological phase transitions and topological phases of matter.

Andreas Müller from the Technische Universität München and part of the Excellence Cluster Universe asks “Do we need fundamental research?” in the newest issue of the Journal of Unsolved Questions (JUnQ).

Researchers describe a methodology for coupling diffraction contrast tomography and the finite element method.