Researchers from Uppsala University highlight a polymer synthesis strategy for biomaterials that could provide a boost for tissue regeneration research.
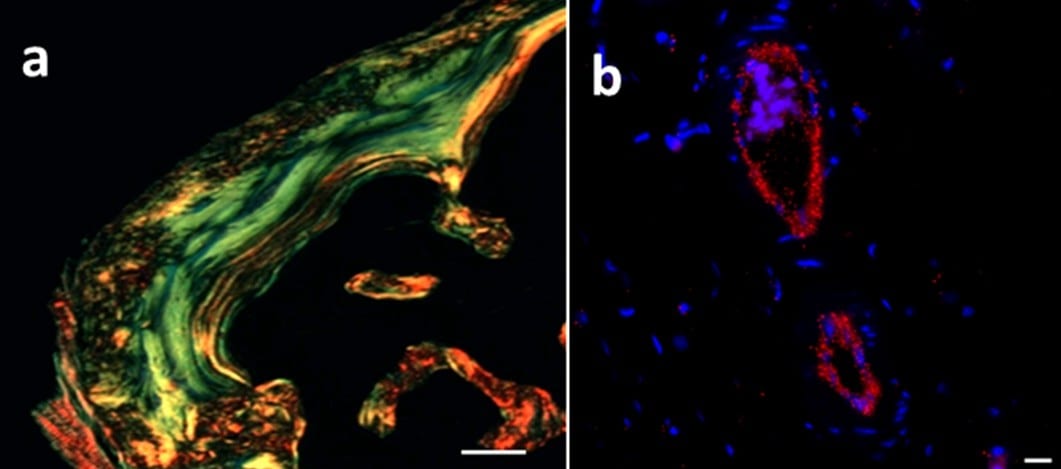

Researchers from Uppsala University highlight a polymer synthesis strategy for biomaterials that could provide a boost for tissue regeneration research.
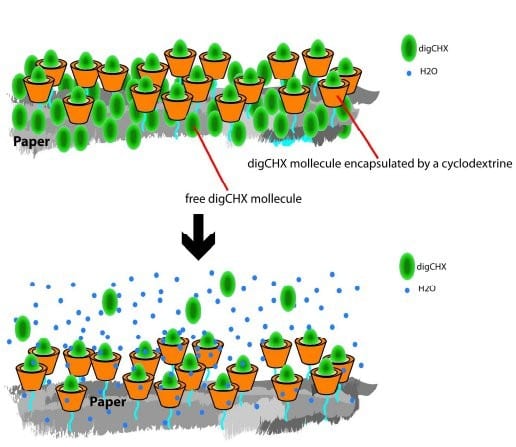
Scientists use functionalization of cellulose through cyclodextrin for long release of antibacterial drugs and production of antibacterial paper.
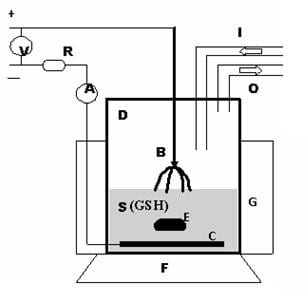
The action of plasma at the gas-solution interface in argon on reduced glutathione has been investigated through Raman spectroscopy.
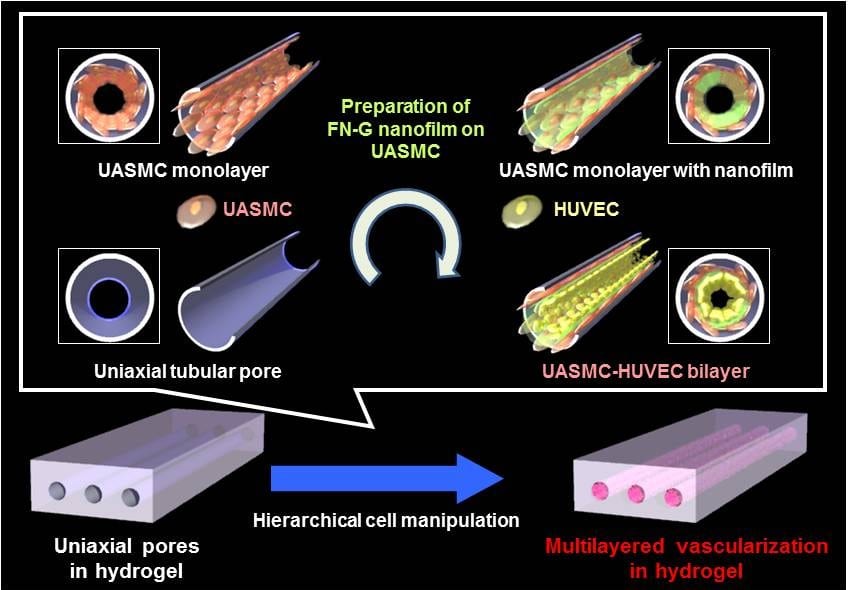
Blood capillary analogues have been developed in a biodegradable hydrogel as a promising platform for in vitro drug testing.
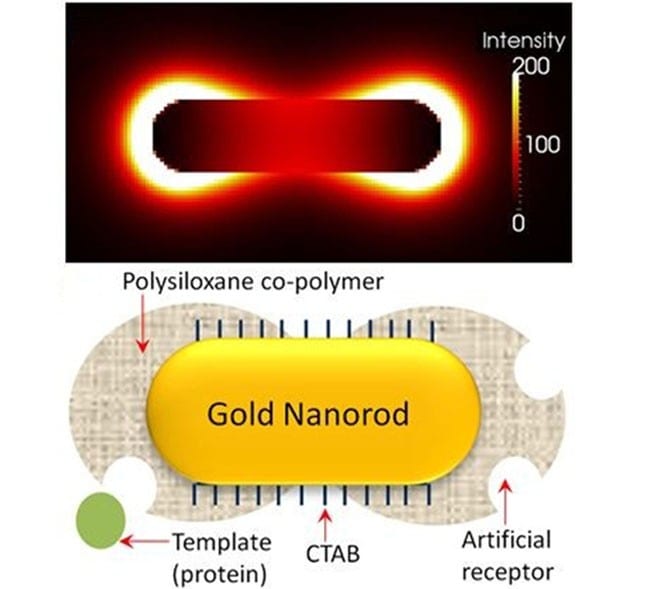
Researchers use molecular imprinting to develop a highly sensitive and selective nanorod biosensor with artificial antibodies.
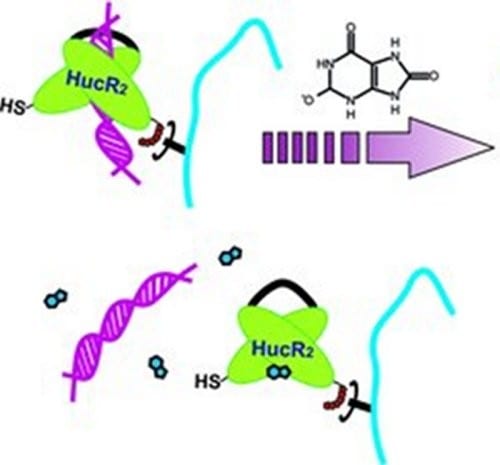
A hydrogel that can tell good from bad: this material can distinguish between normal and pathological levels of urate, a salt related to gout arthritis.
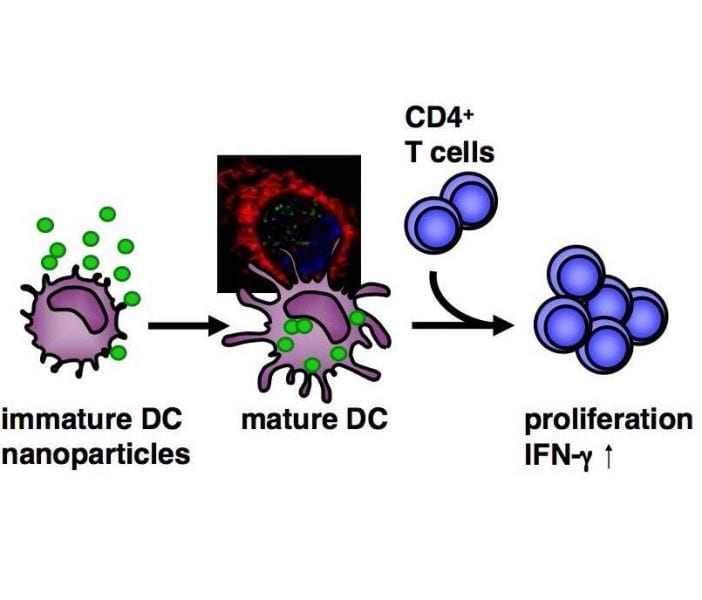
Functionalized polystyrene nanoparticles are analyzed for their interaction with human monocyte-derived dendritic cells.
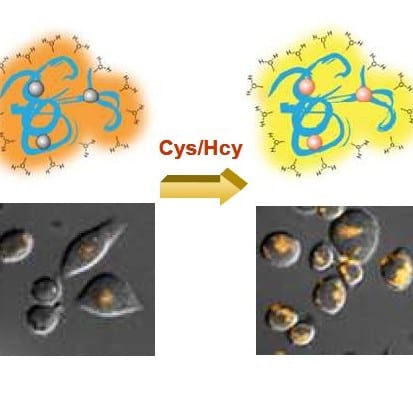
A phosphorescent iridium(III) complex-functionalized poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) is a promising probe for bioimaging applications.
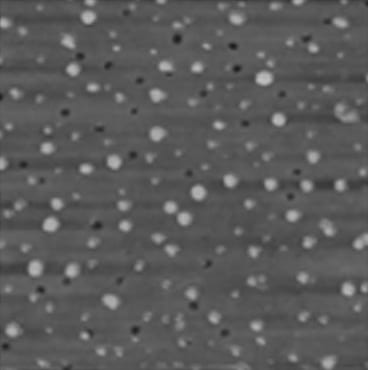
Hyperbranched polymers help nanoparticles migrate to the surface of composite materials to improve their antimicrobial properties.
Scientists at Columbia University show how a corneal collagen crosslinking agent works, a possible cure for keratoconus and other sight problems.