Polymer-protein conjugates unify the benefits of both the synthetic and biological worlds.

Polymer-protein conjugates unify the benefits of both the synthetic and biological worlds.
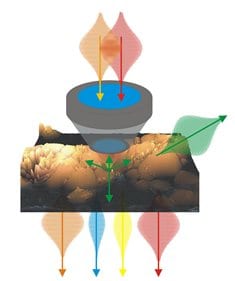
Multimodal nonlinear microscopy has matured to a key imaging modality in life science and biomedicine.
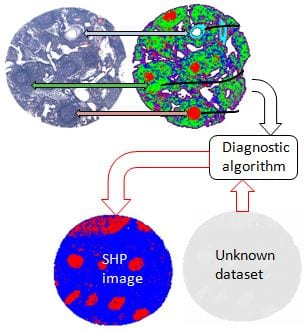
IR and Raman spectral imaging can distinguish between tissue types, disease types and stages, and even identify the primary tumors from spectral patterns observed in metastatic cells.
Researchs show that combining nanoparticles and DNA nanotechnology can amplify the signal obtained from imaging the extracellular matrix.
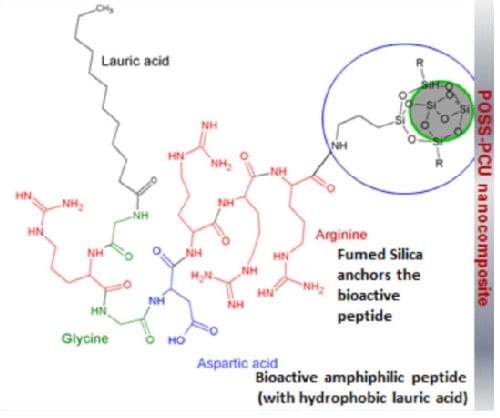
Fumed silica nanoparticles are functionalised to have ‘tethering’ proteins and link bioactive groups to induce biomimicry.
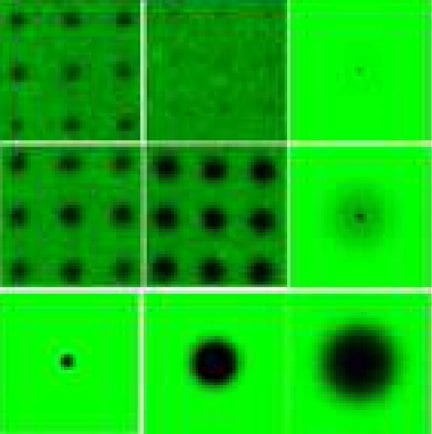
Technique finds new use in patterning polymers to control cells and proteins.
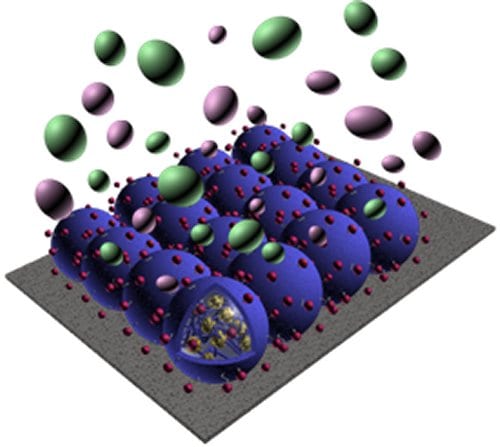
A novel approach is presented for making polymer nanoparticles that can release dual osteogenic growth factors while adhering to Ti surfaces.
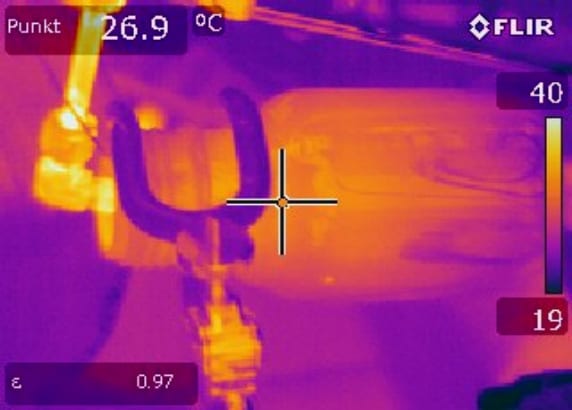

Research investigates the antimicrobial efficiency of microwave plasma processed air with manifold RNS against vegetative bacteria and bacterial endospores.
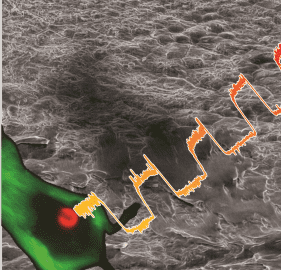
Oxygen-responsive hydrogels for non-invasive subcutaneous oxygen monitoring is reported by Prof. Jon Lovell and co-workers at the University of Buffalo.
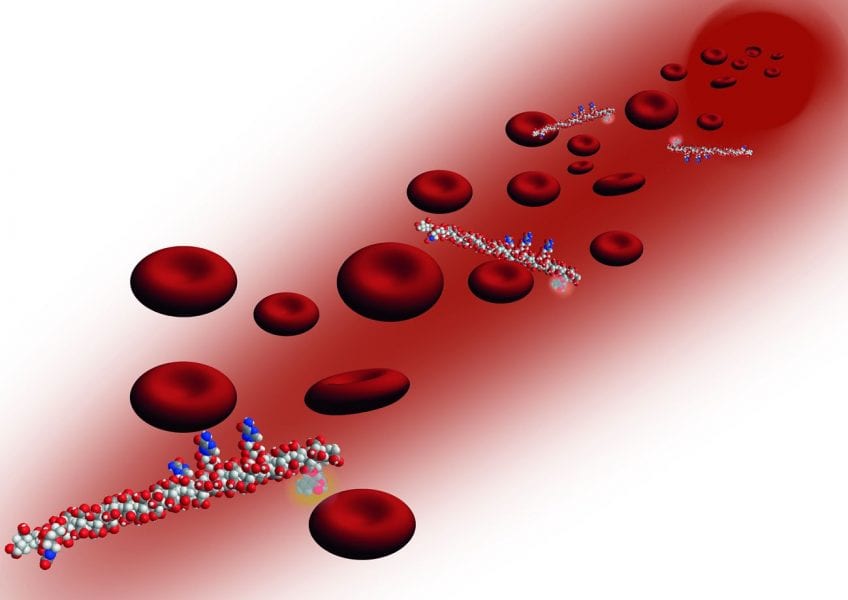
Conjugation of ribavirin to a carrier polymer prevents association of the drug with the red blood cells and thus overcomes the origin of the main side effect.