Cell printing using this new electro-hydrodynamic technique allows the creation of cell structures with multiple layers and a high cell viability.
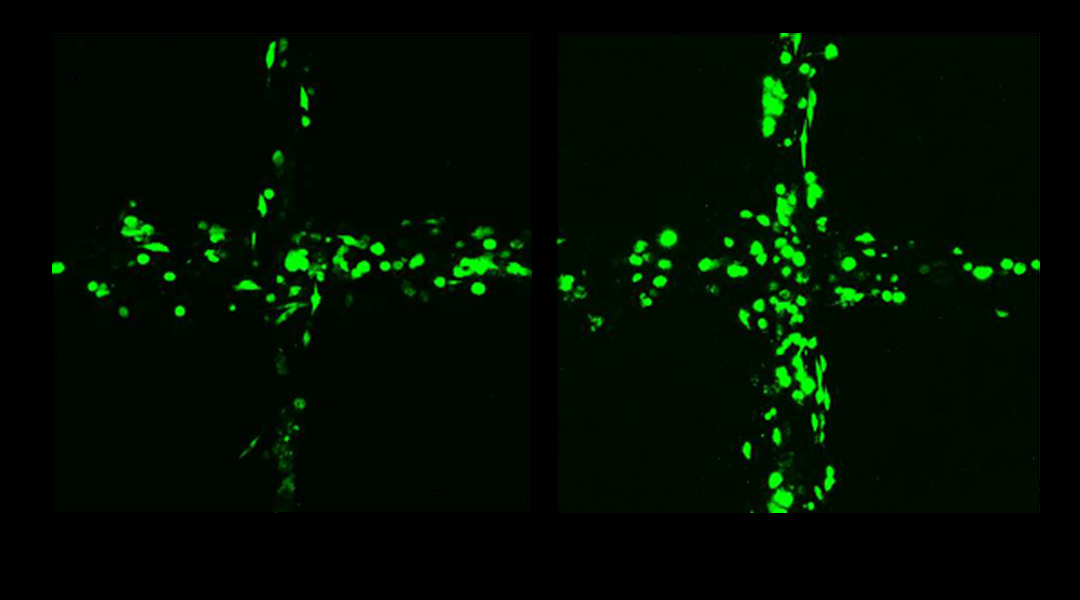

Cell printing using this new electro-hydrodynamic technique allows the creation of cell structures with multiple layers and a high cell viability.
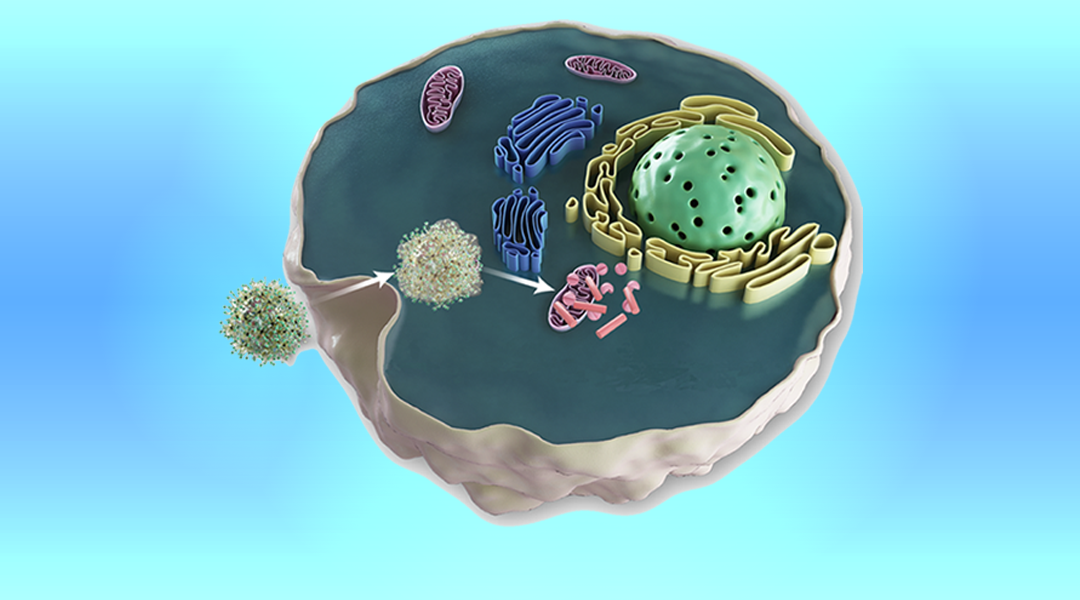
A novel reactive oxygen species (ROS)-promoted nanomedicine platform can effectively inhibit tumor growth, reduce side effects experienced in common anticancer drugs, while promote on-target uptake.
Researchers from the University of Tokyo shed light on the formation of the crystallographic structure of organometal halide perovskites.
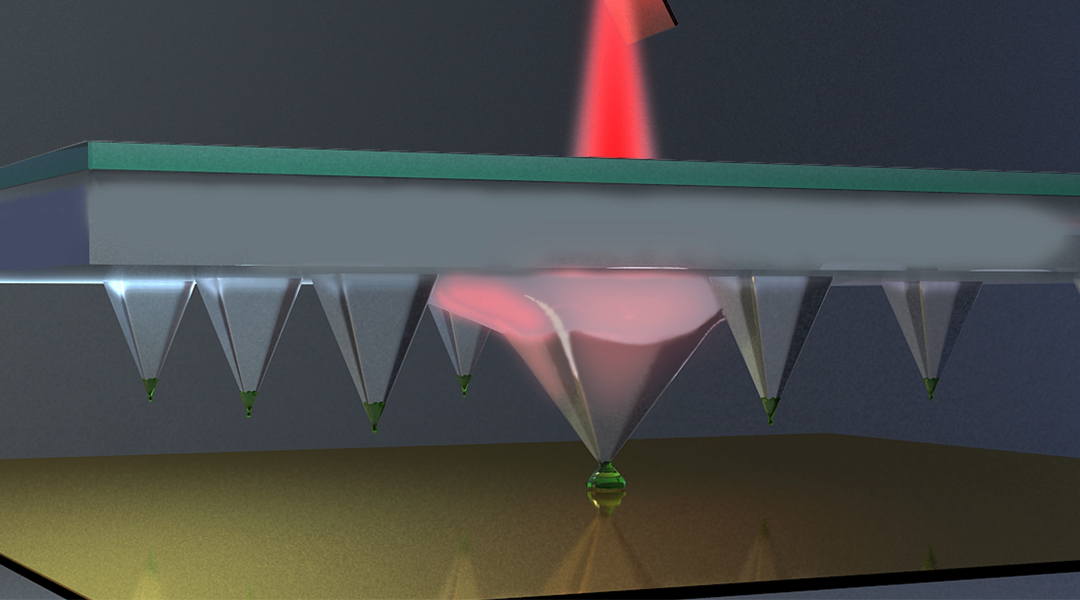
Local control of pens in a large-scale pen array can be achieved by using a nanotube composite that is photo-responsive to fabricate each individual pen.
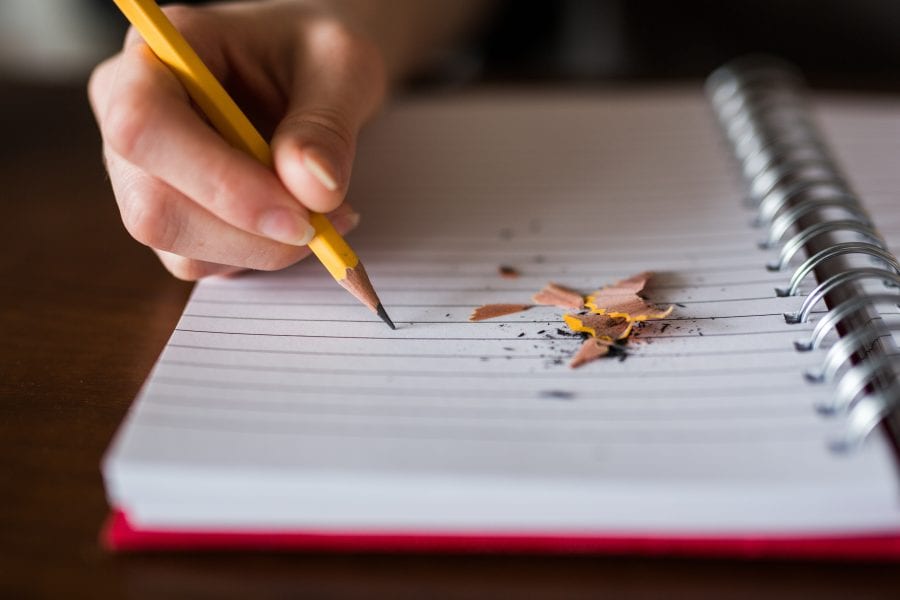

Researchers from INST present various functional materials that have recently emerged as candidates for rewritable paper.
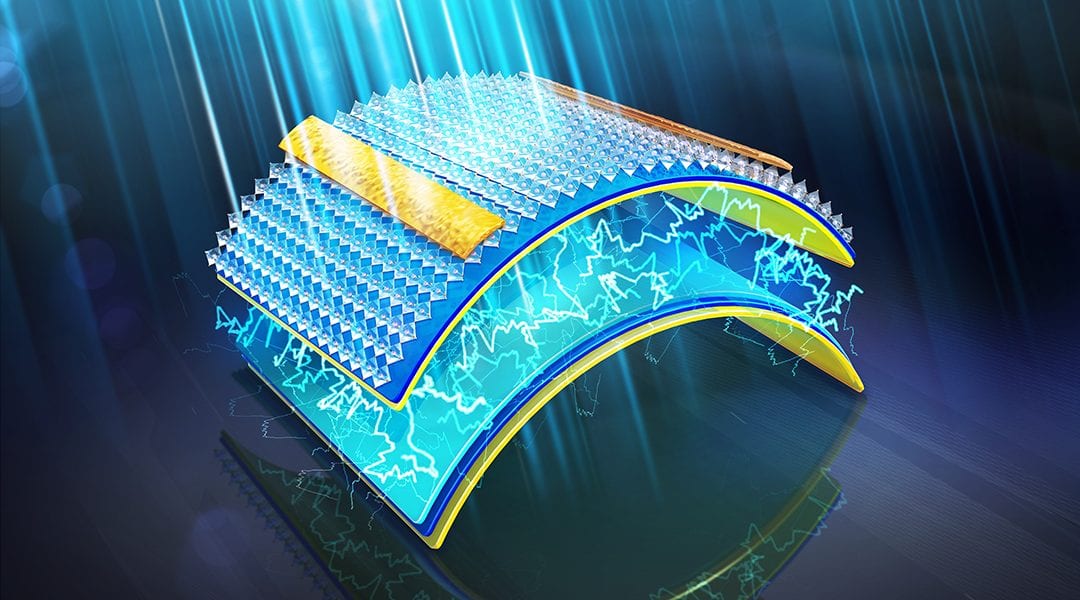
Next-generation electronics should be wearable, versatile, and energy-efficient. A new sensor systems combined with a triboelectric nanogenerator provides an excellent solution.

Self-healing of a phase change memory device with a metallic surfactant layer opens up new pathways in storage class memory.

Researchers in Barcelona have proposed a new mechanism for bone repair. They hope that the work might pave the way for advances in self-healing prostheses.

A hybrid thermochromic window coating with excellent visible transmittance and thermochromic performance at room temperature, opens new directions in plasmonic coatings.

Complex micro and nanodevices are fabricated using a simple strategy that enables sophisticated architectures to be produced.