Unusual compound is the first metallic oxygen ion conductor of its kind, as well as the first that is active at room temperature.
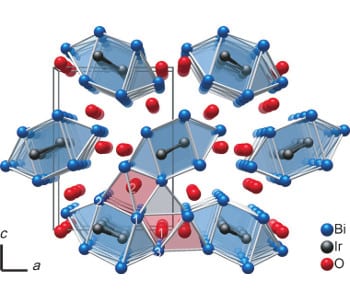

Unusual compound is the first metallic oxygen ion conductor of its kind, as well as the first that is active at room temperature.
New magnetic phase could have significant implications for our understanding of unconventional superconductivity.

Development of cobalt and boron alloyed steel with more resistance at high temperatures avoids CO2 emission and increases the efficiency of power plants.
Ultrathin layers made of tungsten and selenium may be used as flexible, semi-transparent solar cells.

Check out the articles highlighted on the covers of the latest issue of Advanced Optical Materials.

The Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems ISE in Freiburg, Germany has developed a new solar cell structure for crystalline silicon.
A research group has uncovered the unique structural, electronic, optical, and defect properties of halide peroveskites.

A special issue of chemsuschem dedicated to the chemistry of energy conversion and storage.
Post-combustion CO2 capture presents a great opportunity to reduce emissions, but some hurdles still exist before widespread deployment can be considered.

New Humboldt Professorships have been awarded, among them three prominent international physicists working on electronic, magnetic and superconducting materials.