Scientists based in the Netherlands and Spain have recently developed a two-step printed scaffold-removal method to fabricate intricate microfluidic devices.
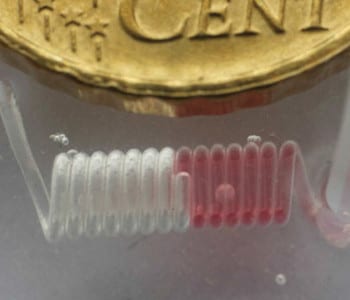

Scientists based in the Netherlands and Spain have recently developed a two-step printed scaffold-removal method to fabricate intricate microfluidic devices.
A new review in Advanced Science summarizes new nanotechnology-based potential diagnosis and treatment methods for triple negative breast cancer.
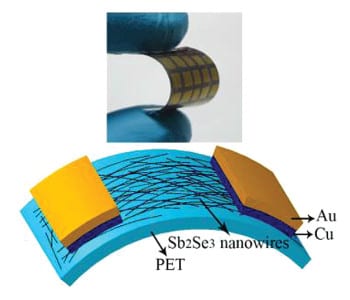
A new solvothermal approach to synthesize ultrathin nanowires, with applications in flexile photodetectors, is demonstrated.
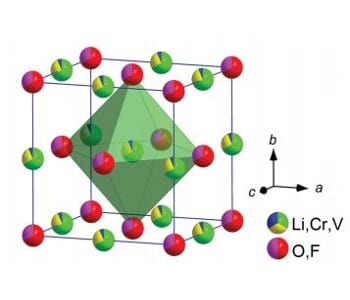
An oxyfluoride-based cathode material for Li-ion batteries with high practical specific capacity beyond that of classical systems has been developed.

Interfaces to capture, detect, and analyze circulating tumor cells are reviewed, which give a valuable insight into tumor progression and metastasis.
Topography of plant virus nanoparticles has been shown to influence osteogenesis of bone derived mesenchymal stem cells.

In this comprehensive review, the main research routes and technologies that are being followed to deliver high-performance electronic skin are discussed.

Researchers demonstrate that phenazine compounds can bioaccumulate and self-assemble in macrophages and epithelial cells.

Getting a PhD is the first big step towards a career in academia. Hints and tips for grad school are presented in Advanced Science.
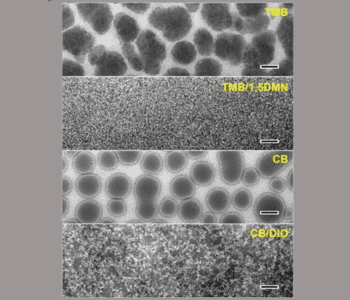
A team of US and Chinese scientists has demonstrated a new, nonhalogenated solvent system to produce high performance polymer solar cells.