In their review in BioEssays, Mariano Bizzarri et al. discuss how commitment of cell specification is constrained by physical cues.
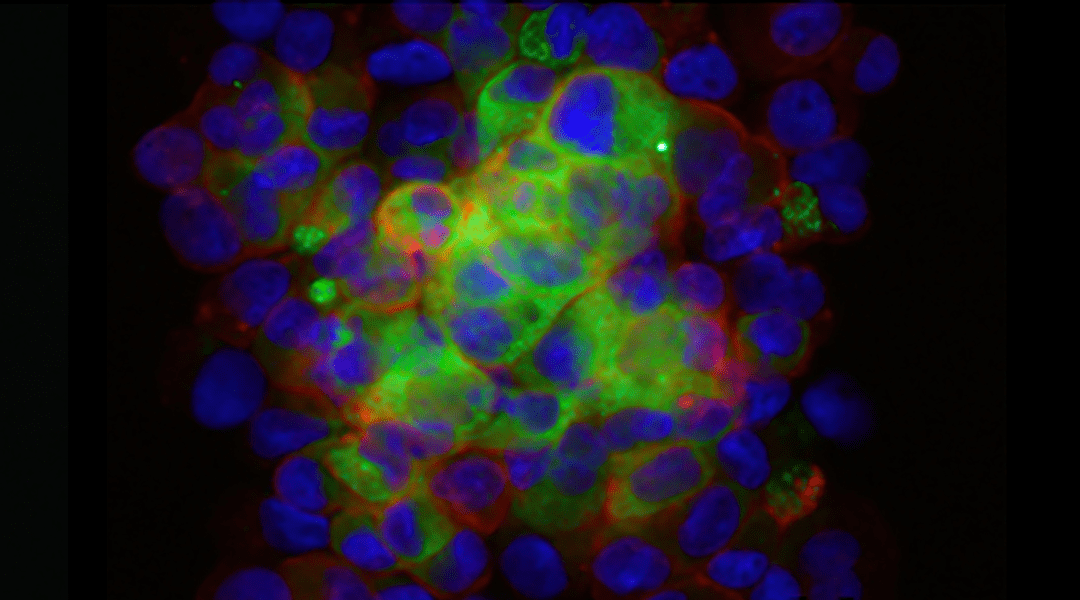

In their review in BioEssays, Mariano Bizzarri et al. discuss how commitment of cell specification is constrained by physical cues.
Increasing consumption of western and low fiber diets, smoking or just exposure to tobacco smoke, harmful use of alcohol, physical inactivity, and environmental pollutants may have programed the human epigenome for higher NCCDs risk.

Latest Advanced Healthcare Materials covers.
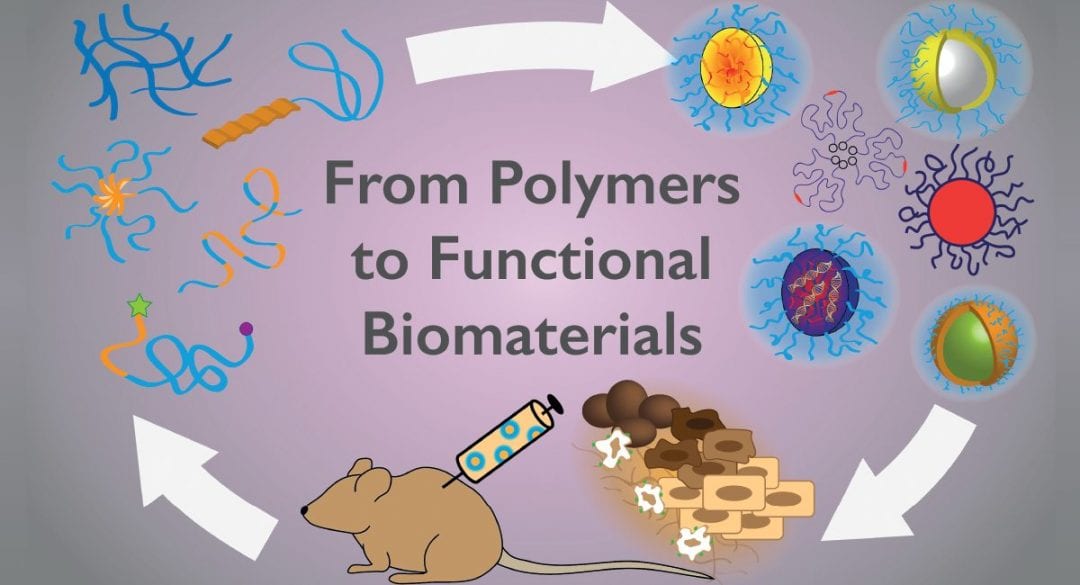
A new special issue in Macromolecular Bioscience highlights emerging applications of polymers for the synthesis of functional biomaterials.

Taiwanese scientists create a new atmospheric-pressure plasma jet tooth bleaching method that is safe, cost effective and portable.
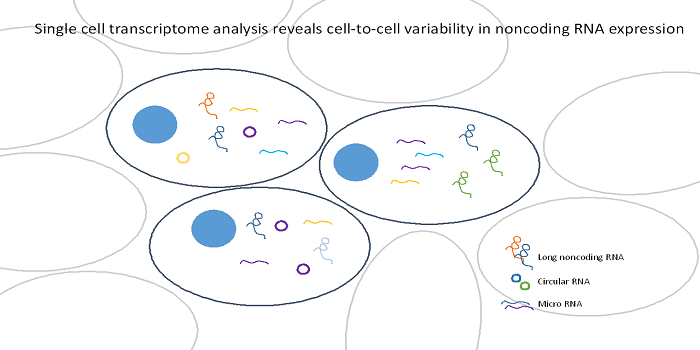
Non-coding RNA expression varies at the single cell level, at least as much variability as protein-coding RNA, and some classes of non-coding RNA may display more single cell variability.
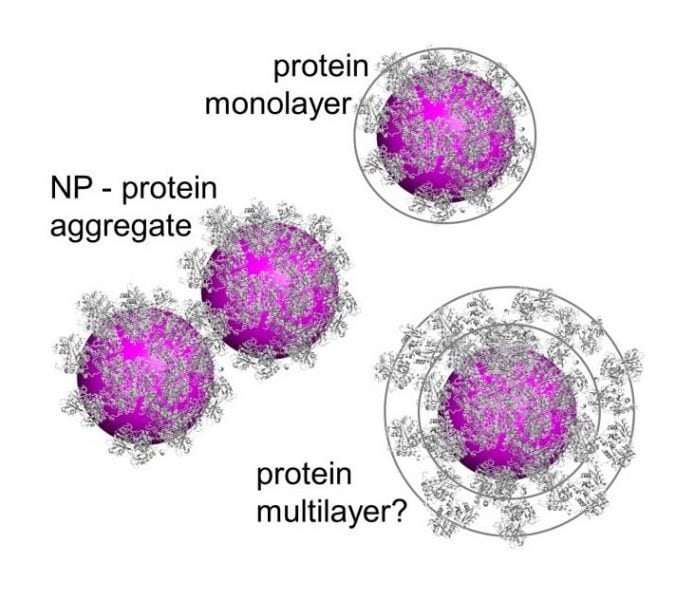
A biomolecular adsorption layer (corona) forms on essentially all nanoparticles immersed in biological fluids, and governs their interactions with the biological environment. Key aspects of protein corona formation and its structure and dynamics have yet remained elusive and call for further investigations.

The Phospholipid Research Center Heidelberg, organised already its “5th International Symposium on Phospholipids in Pharmaceutical Research” from 18th – 19th September 2017 at the University of Heidelberg, Germany.
This special issue of Macromolecular Bioscience was dedicated to the 65th birthday of Prof. Kazunori Kataoka.

Guest editors Yugang Sun and Zhiyong Tang outline current research directions in the field of plasmonic particles.