Cold ytterbium atoms were used to test a fundamental theory which describes phenomena in solids such as magnetism and superconductivity.

Cold ytterbium atoms were used to test a fundamental theory which describes phenomena in solids such as magnetism and superconductivity.
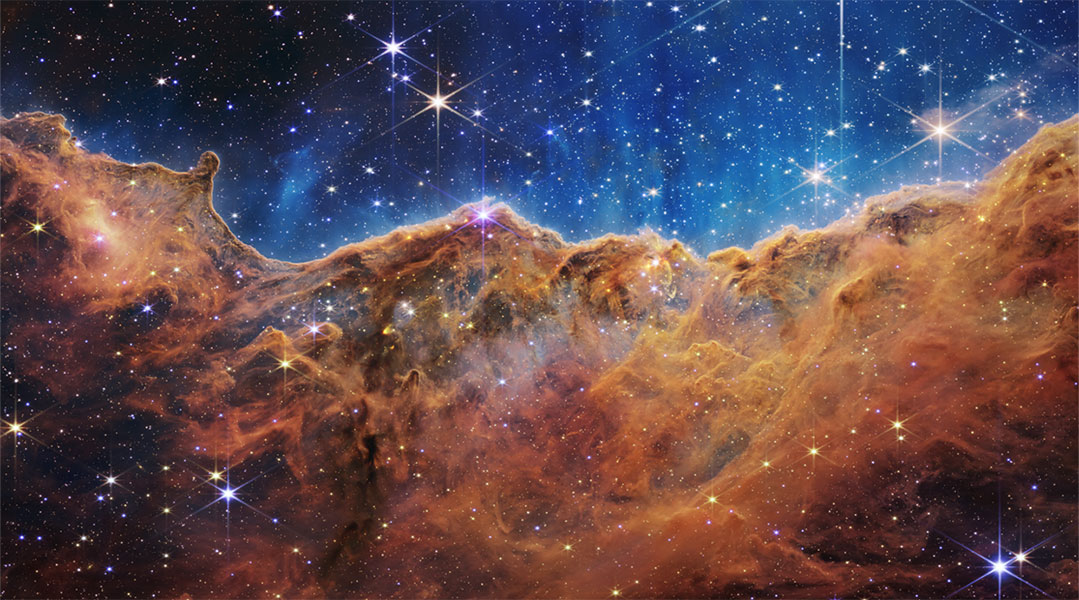

Astronomers are discovering that the rate of star formation in the universe is dropping, and they want to know why.
To address unknown quantum gravitational effects in the early universe, physicists have recruited string theory to help solve the problem.

Paleontologist, historian, evolutionary biologist, writer; Stephen Jay Gould sparked a revolution in how scientists view evolution.
Using bilayered graphene, physicists explore the possibility that our reality is only one half of a pair of interacting worlds.

A new theory for the origin and nature of dark matter resolves some inconsistencies between cosmological predictions and astronomical data.
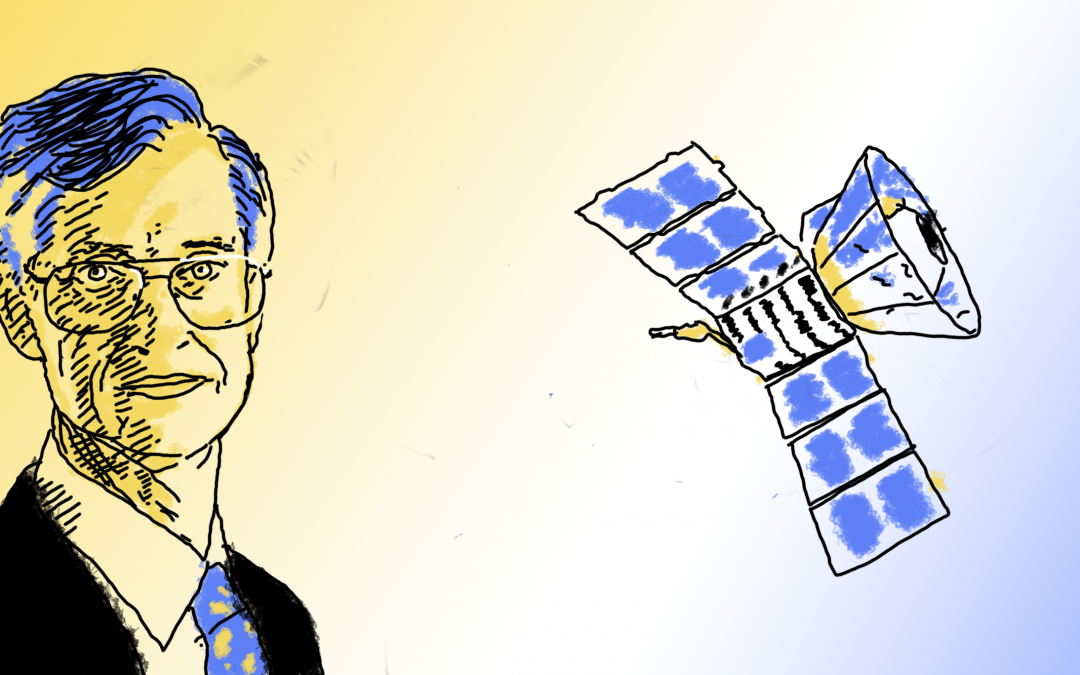
With the launch of the James Webb Telescope, this edition of Pioneers in Science honors an integral member of its mission: John Mather.
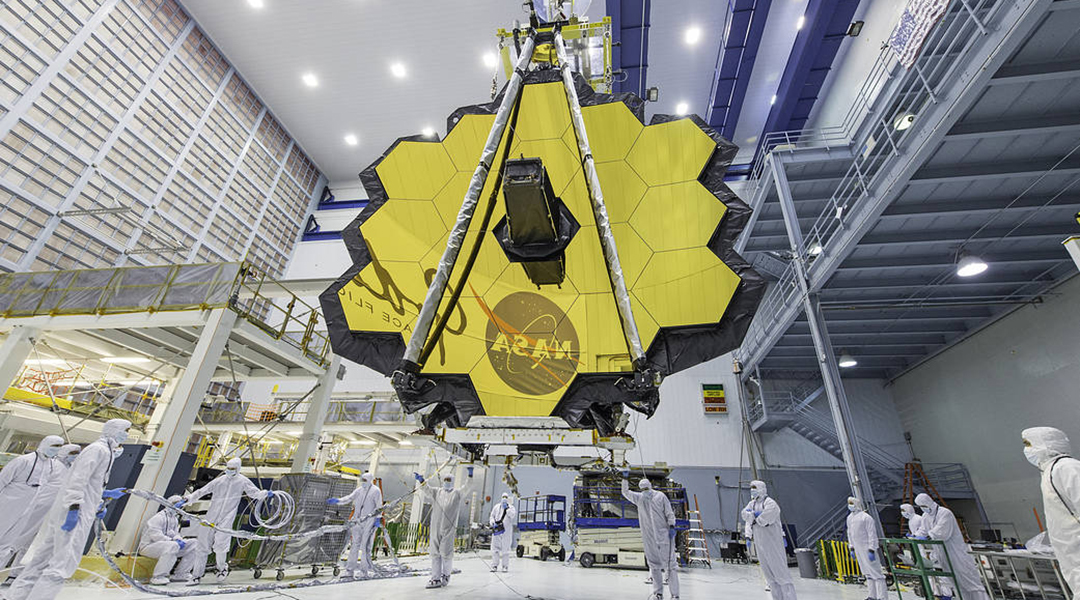

The new James Webb Space Telescope will collect infrared light from distant corners of the cosmos, enabling scientists to see further than ever before.
By cooling antimatter to absolute zero, physicists may finally be able to answer questions that could fundamentally alter our understanding of the universe.

Bright bursts of radio waves help astronomers locate a type of matter that researchers have been searching for for the past 30 years.