Latest

Constantly touching our faces linked to memory and facial hair density
People all over the world touch their faces up to 800 times per day—researchers wanted to know why.
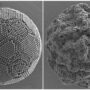
Tiny vesicles could help prevent amputations in diabetic patients
This safer, non-surgical treatment for diabetic limb ischemia could help patients with severe blood flow complications.
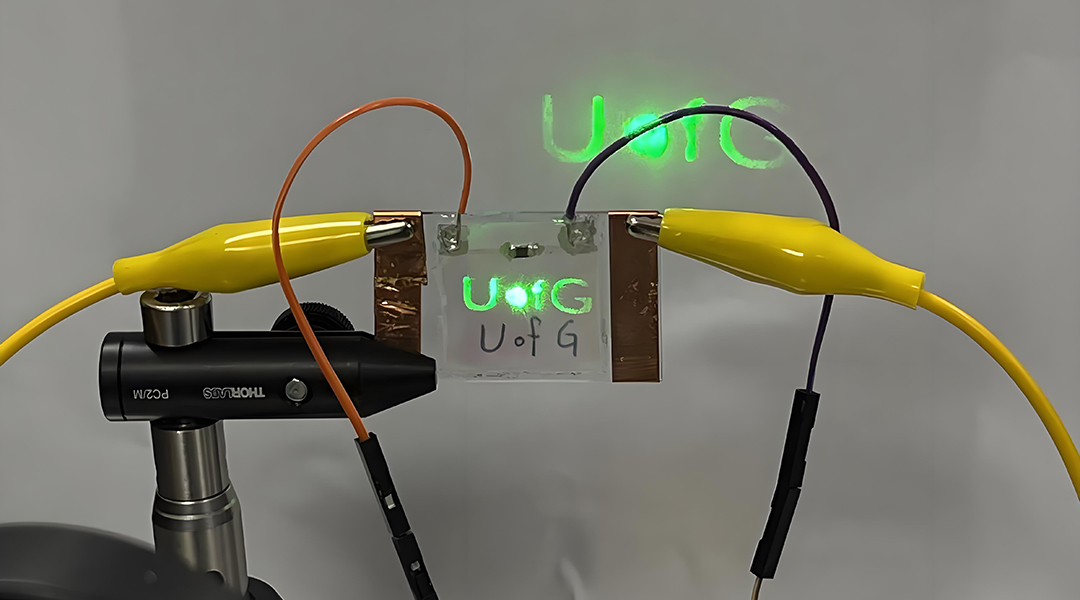
Liquid crystals bring a smoother switch between augmented and virtual reality
Temperature-sensitive materials seamlessly switch between VR and AR in headsets, paving the way for better extended reality experiences.
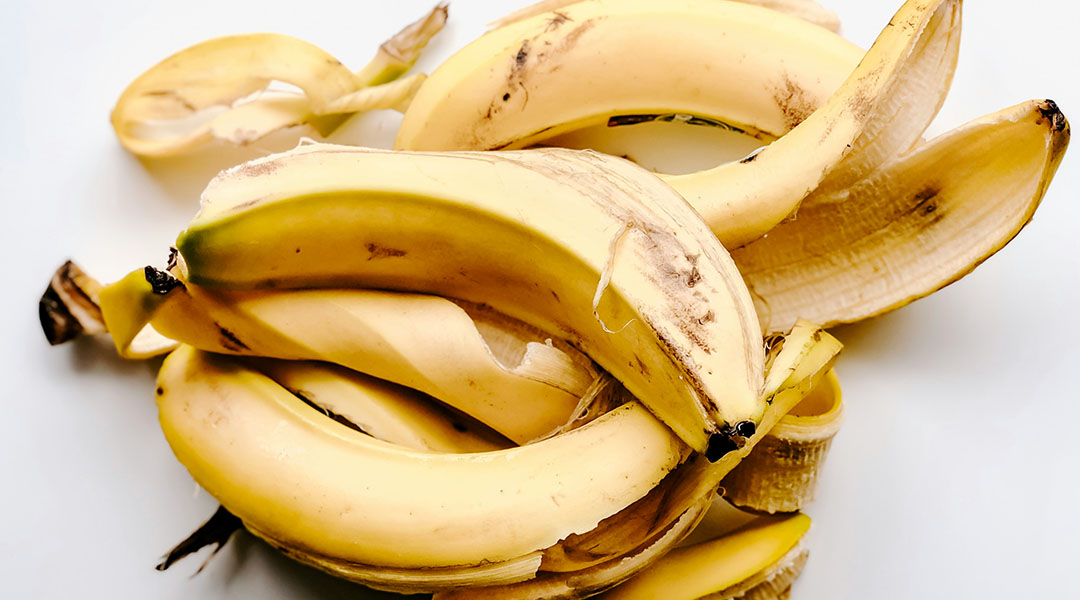

Turning banana peels and coconuts into clean energy
Researchers develop a device that generates clean energy from food waste, using banana peels and coconuts to power communities sustainably.
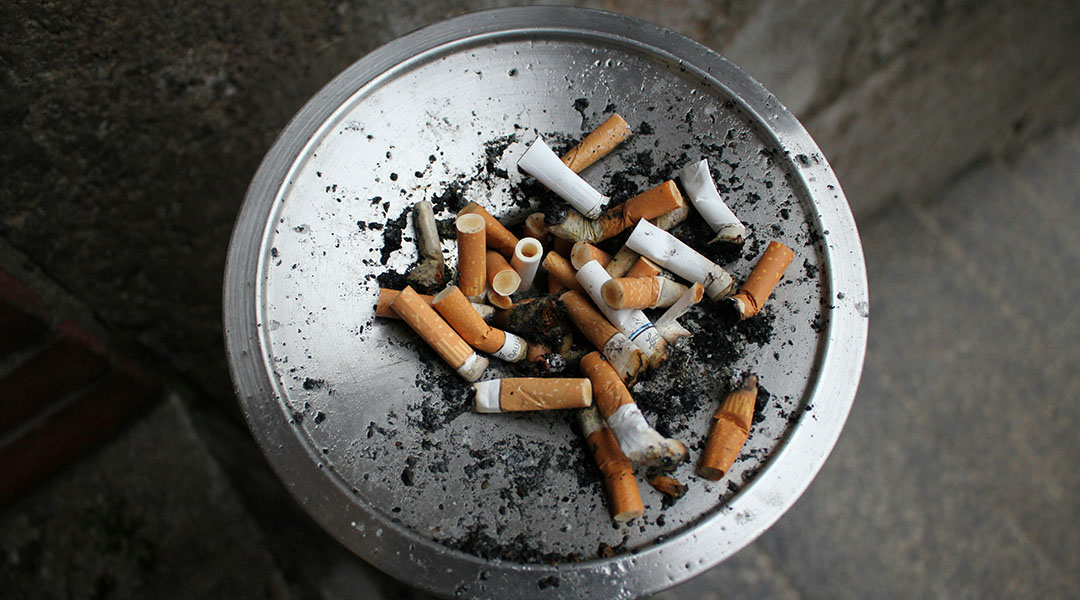

Parkinson’s drug helps alleviate nicotine withdrawal symptoms
Researchers discover that a Parkinson’s drug, procyclidine, can reduce physical nicotine withdrawal symptoms, such as tremors and immobility.
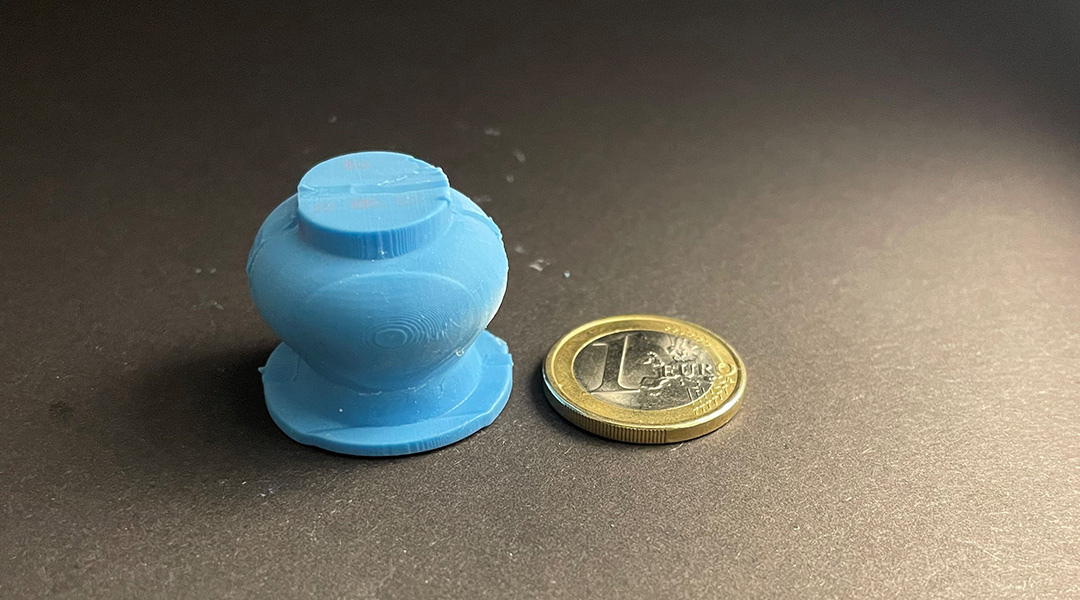

A blood sampling device inspired by leeches
Collecting blood in a painless and minimally-invasive way may soon be possible with this prototype suction cup device.

Magnetic fields from the beginning of time may resolve the Hubble tension
By adding primordial magnetic fields to the Standard Model, researchers may solve the mystery of the Universe’s expansion.
ASN Weekly
Sign up for our weekly newsletter and receive the latest science news directly to your inbox.
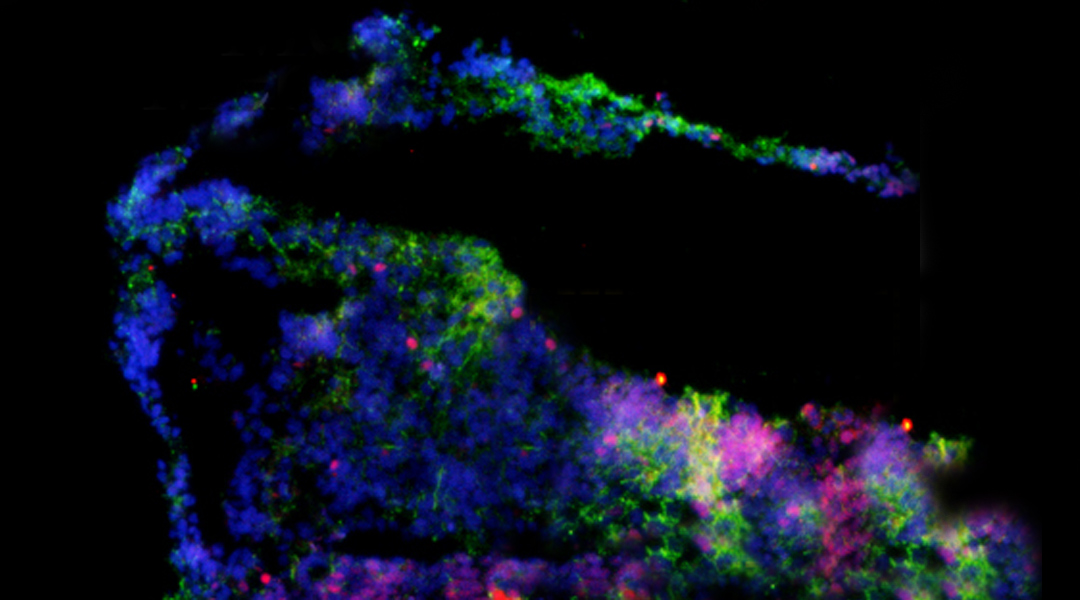
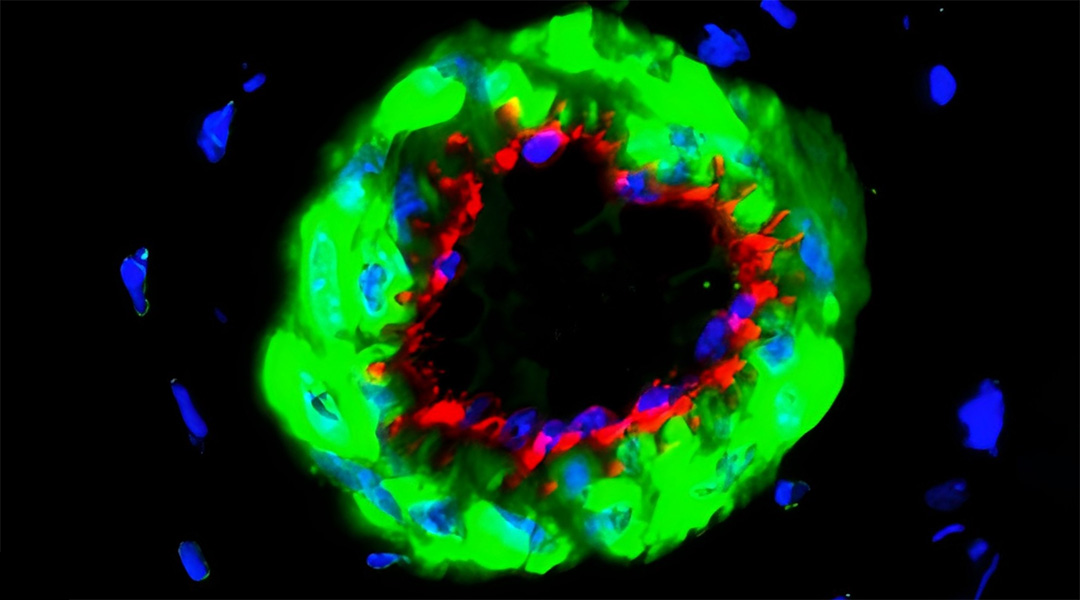
Building a model brain using microfluidics and brain organoids
To mimic the the interconnected structure of the brain, model organoids can be connected together into larger assemblies.
How does classical physics arise from quantum mechanics?
Emergence of classicality states that a quantum description of a large object must be the same as its classical description, but this isn’t always so…

Our brains use visual information to recognize a voice
A new study has shown that the facial recognition areas of the brain play a role in the recognition of famous voices.

Eliminating computer errors by combining computation and memory
A device brings memory and processing together, helping minimizing errors and avoiding increasing energy demands due to huge amounts of data.

Are sulfate-free shampoos really better?
The sulfate-free movement in beauty products has been gaining popularity, but this isn’t based in science, say experts.

Muons help explore physics beyond the Standard Model
Enhanced experimental precision has the potential to either confirm or dispel uncertainties surrounding the Standard Model of Physics.

Heat and cold tolerant sensors to help robots in extreme climates
Inspired by sea asparagus, scientists design a conductive hydrogel that is stronger than natural rubbers and adapted for extreme environments.

Radio emissions reveal unprecedented oscillations in black hole radiation
Previously unobserved frequency changes in radio signals detected in a black hole binary system could change our understanding of black hole physics.
How shape-shifting gratings and lenses are changing optical devices
Tuneable micro-structured surfaces could overcome the limitations of current unchangeable components that result in “static” optical devices.
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.

Antimicrobial resistance is an unwinnable arms race
Experts argue a new approach is needed so that we are less reliant on antimicrobial drugs, where less use means less resistance.
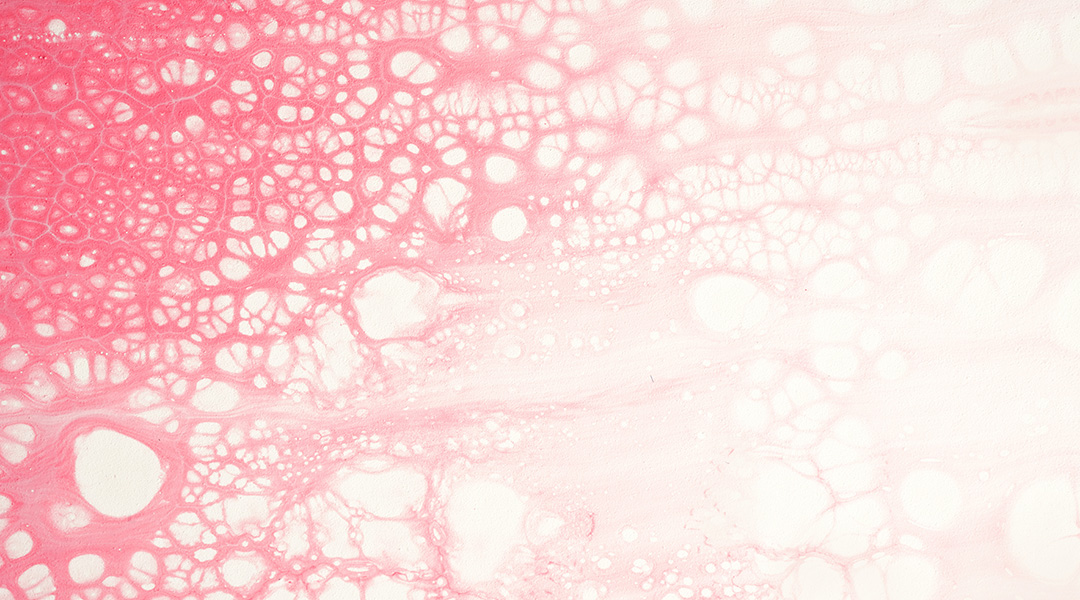
How high blood pressure turns healthy cells into “foam cells”
High blood pressure can rapidly transform healthy arterial cells into inflammation-prone “foam cells” that pose an increased risk of cardiovascular-related issues.
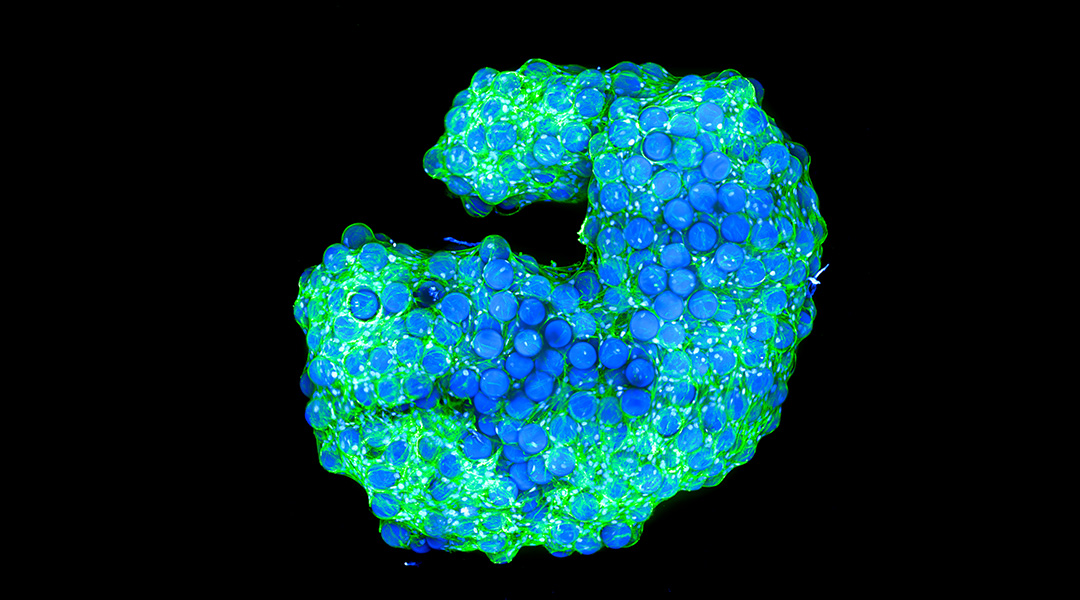
Cellular architects “build their own houses”
Scientists have created biological structures that when left alone, self-assemble into materials that resemble living tissue.
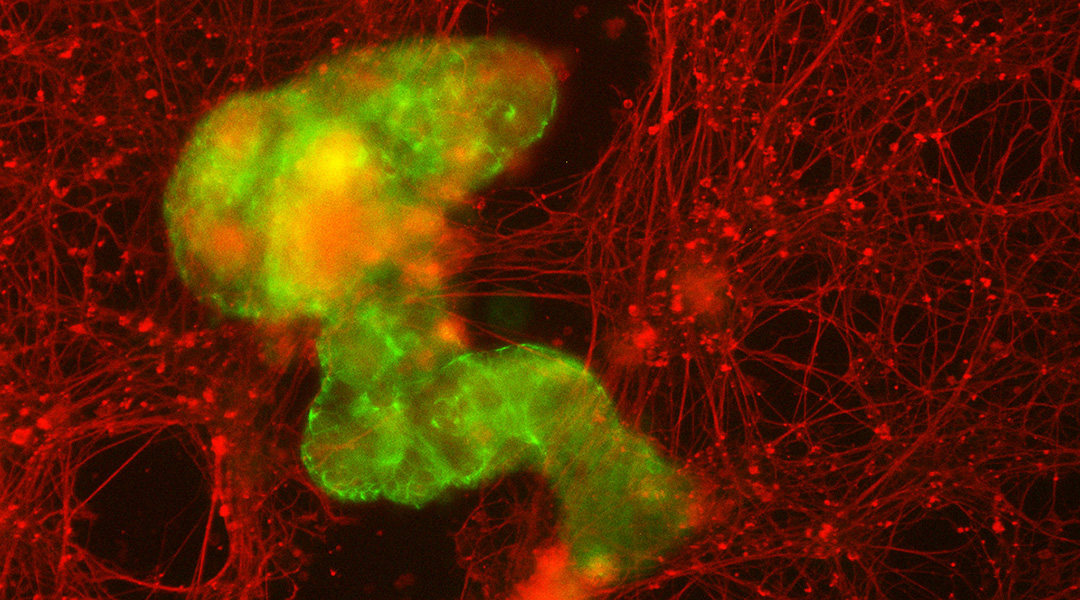
Living biobots come together to repair torn tissue
Microscopic robots made out of a patient’s own cells may be able to work inside the body to repair damage, scope out signs of disease, or fight off infections.

Bringing aqueous rechargeable zinc iodine batteries to the mainstream energy market
New research aims to improve the stability and safety of alternatives to rechargeable lithium-ion batteries using aqueous zinc and hydrogels.

What will it take to make sodium and potassium batteries viable alternatives to lithium?
Scientists explore the challenges facing alternatives to lithium-ion batteries and suggests a roadmap to overcome these obstacles.

A simple tweak supercharges microscopes and allows pathogen observation
A modification to conventional microscopes pushes the limits of their resolution and enables high-precision observation of difficult-to-observe pathogens.
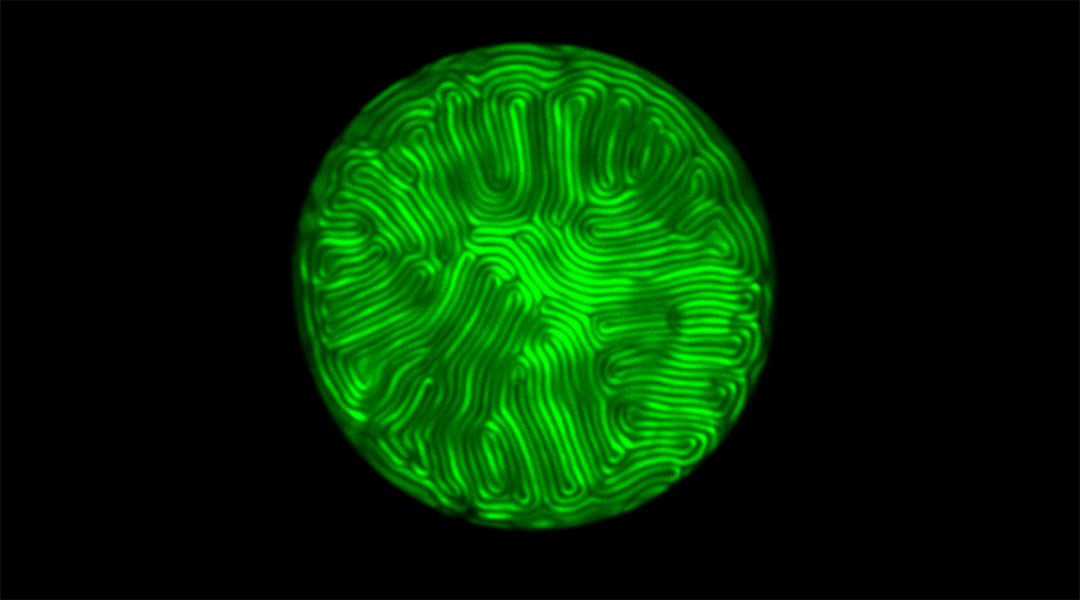
Artificial fingerprints could dramatically enhance biometric security
Liquid crystals that generate unclonable fingerprint-like patterns could make the sale of counterfeit goods and theft of personal data much more difficult.
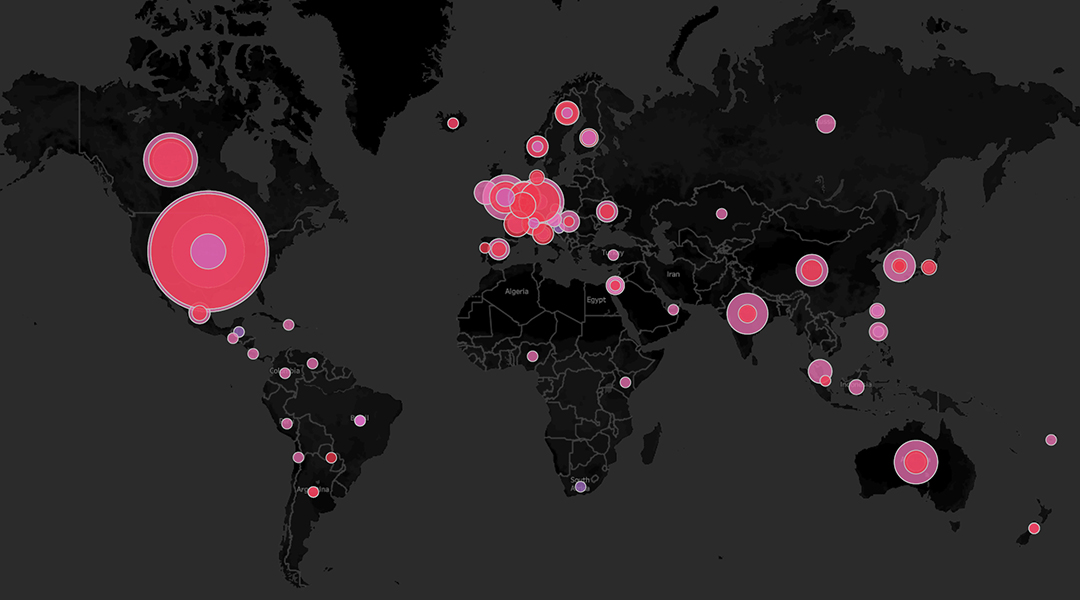
Circling a circular carbon economy
The circular carbon economy is still in its infancy, and realizing it will require innovative processes for capturing and utilizing carbon.

Artificial leaf sensor could revolutionize crop management
By accurately detecting moisture levels, this artificial leaf sensor could help increase crop yields while reducing the need for pesticides.
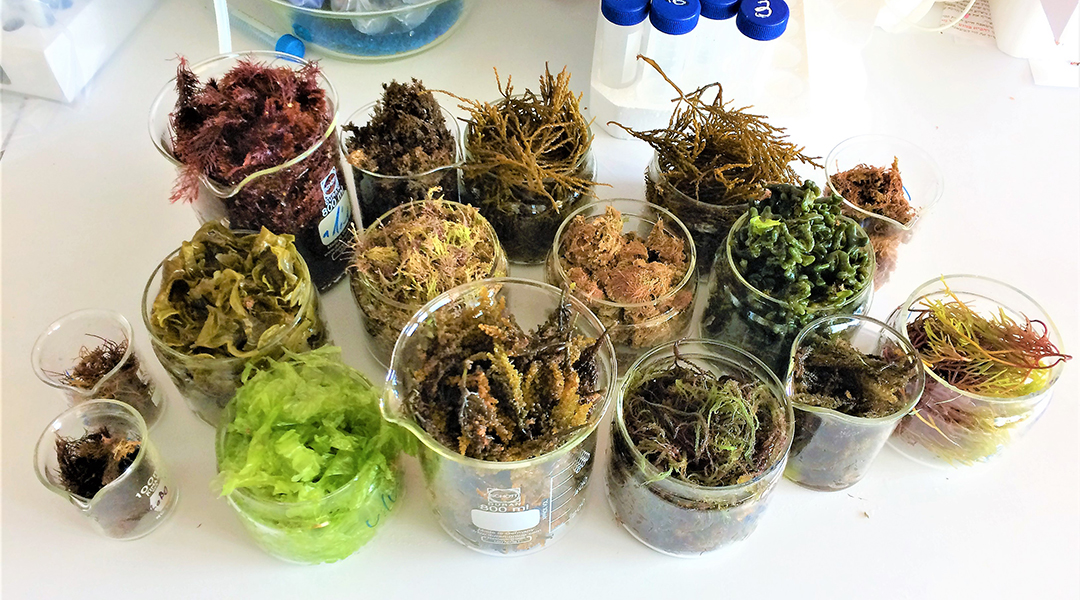

Super seaweed from sustainable aquaculture
A new cultivation method enhances the concentration of valuable compounds in seaweeds with substantial environmental benefits.
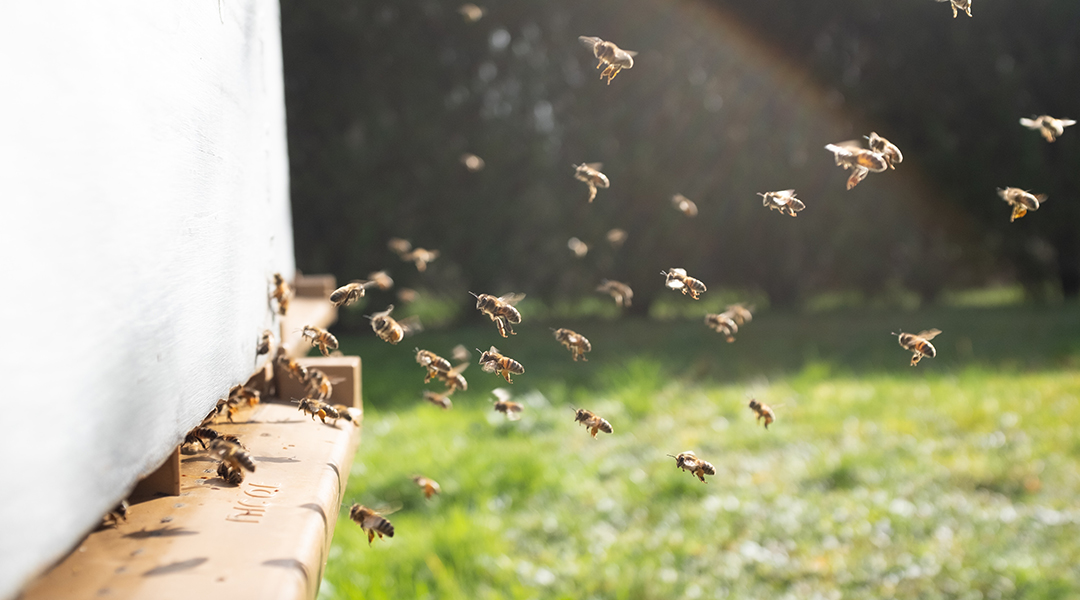

Beehive microbes hold the secrets to our cities’ health
The microbes in beehive debris vary widely between cities and neighborhoods, and could hold keys to assess the human populations’ health.

Are dark photons alternatives to dark matter?
Researchers investigate dark photons as alternatives to dark matter, aiming to detect these particles through experiments involving the conversion of light.

New theory of gravity rethinks the Big Bang
A new approach to understanding gravity helps eliminate some discrepancies inherent in general relativity.

Dark energy telescope reveals early look at almost two million cosmic objects
Galaxies, quasars, and stars… oh my! Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) first data is a small fraction of the huge cosmic survey it will conduct.

Atoms vs apples: How quantum effects challenge gravity’s rules
New research reveals that quantum effects defy the universality of free fall, providing a potential experimental pathway to test quantum gravity.