Aluminum clusters move along graphene tracks, controlled by applied electric currents, in work by Spanish and Dutch researchers.
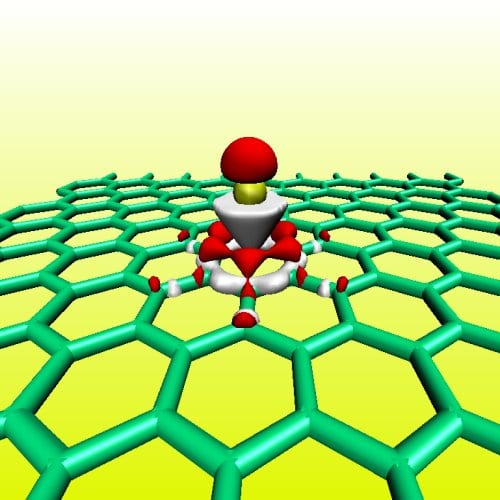

Aluminum clusters move along graphene tracks, controlled by applied electric currents, in work by Spanish and Dutch researchers.

Systematic insights into well-defined platinum-alloy nanoparticles promise cheaper and more-efficient fuel cells.
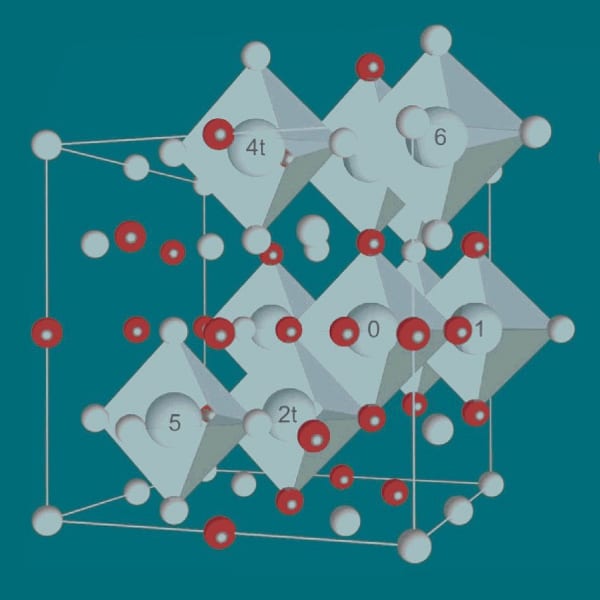
A new and important development in complex steels is reported in the current issue of Steel Research International, dedicated to “Steel ab initio”.
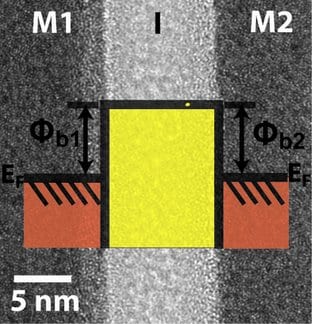
Researchers at Oregon State University develop cutting edge metal-insulator-metal diodes, harnessing quantum tunneling of electrons to increase performance of electronics.
The sample size of nanomaterials with functional properties has been limited to just a few millimeters. This fact has limited their commercial use, so far.
Tapered nano-sized ribbons have been made by tearing sheets of graphene from a sticky surface.
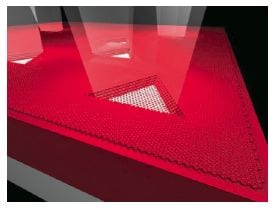
Graphene films grown over epitaxial metal films deposited on single-crystalline substrates give unique micropits with rectangular and triangular shapes, reflecting the crystallographic orientation of the substrate.
Metals encapsulated within carbon nanotubes by capillary action are prevented from crystallizing by the confined space of the nanotubes.
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are considered to be the next-generation reinforcement material to potentially replace conventional carbon fibers for producing superhigh-performance lightweight composites.
The human brain is one of the most complicated machines that Nature has ever invented. Can we ever hope to artificially replicate its incredible complexity?