Device developed at the University of Exeter is both flexible and transparent.
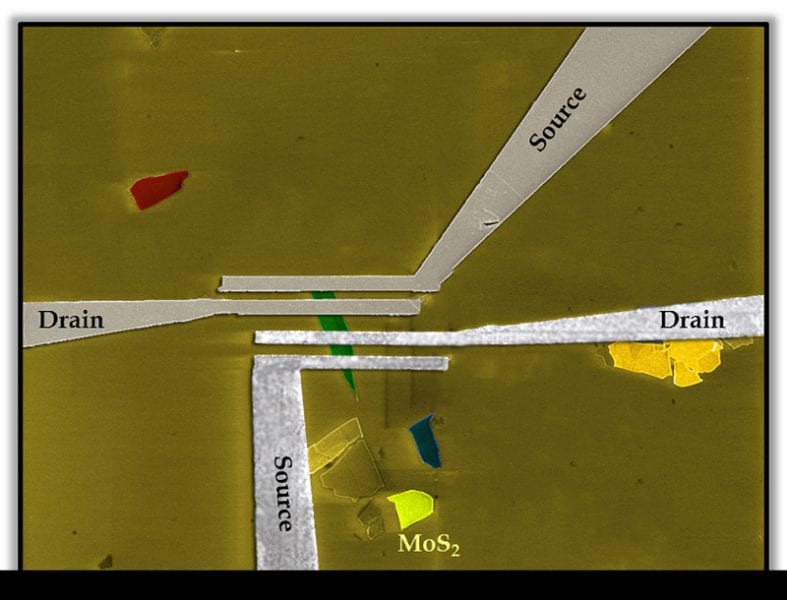
2D nanocrystals developed for future computing applications
Technology is based on metal di-chalogenides, which are emerging as potential candidates to replace current CMOS materials.
Applied Nanotech awarded new printed electronics patents
Both patents are related to their copper inks, which have the potential to replace existing silver inks that are commonplace in the marketplace.

Microtransistor will improve study of the human brain
French scientists have produced the world’s first microscopic, organic transistors that can amplify and record signals from within the brain itself.
Bozhi Tian awarded Searle Scholar grant for nanoelectronics research
Project is titled “Silicon-based Biomaterials for an Electrical Study of Single-Neuron Dynamics.”
Ultrathin optoelectronics help researchers explore the brain
Ultrathin, flexible optoelectronic devices – including LEDs the size of individual neurons – are lighting the way for scientists in optogenetics and beyond.
Optical circuits from polycrystalline diamond
Pernice group at KIT use polycrystalline diamond for the fabrication of wafer-based optomechanical circuits.

Single-atom germanium films could advance electronics research
Thin germanium films, with properties similar to graphene, could lead to lighter, faster electronics.
Intermolecular Joins SEMATECH’s Lithography and Front End Processes Programs
Companies have agreed to co-develop new methods to reduce overall cost of ownership for Extreme UltraViolet and lithography.
Researchers take a step towards optical transistors
McGill researchers demonstrate new way to control light in semiconductor nanocrystals.






