P(VDF-CTFE)-PTU composite with significantly elevated statistical breakdown field and the promoted charge-discharge efficiency has been successfully synthesized.
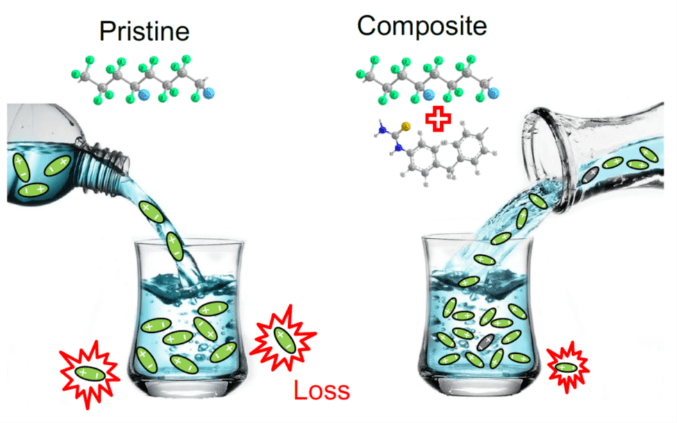

P(VDF-CTFE)-PTU composite with significantly elevated statistical breakdown field and the promoted charge-discharge efficiency has been successfully synthesized.
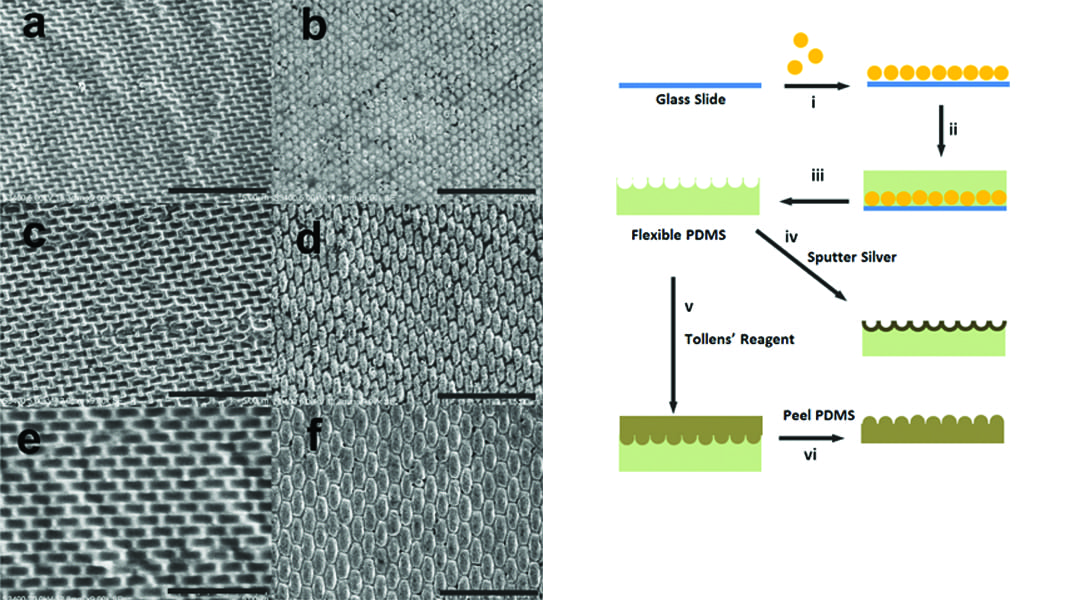
A unique and versatile approach to creating ordered silver nanostructures is presented that allows for feature shape alteration in a simple and inexpensive manner.
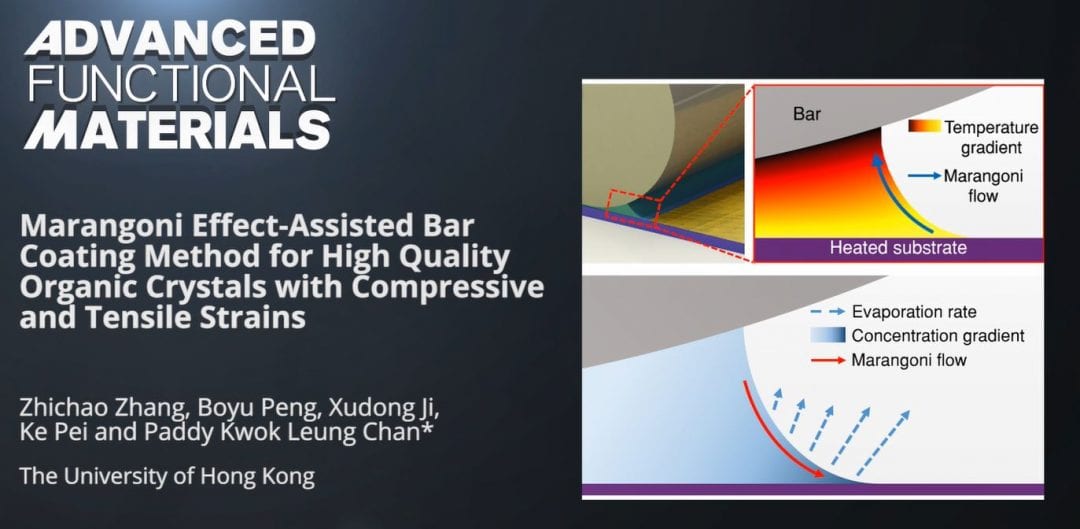
Researchers from the University of Hong Kong report how solution shearing of organic semiconductor crystals is influenced by a surface tension gradient. Using a Marangoni-effect-assisted bar coating method, ultrathin, uniform layers of crystals with large domain sizes are obtained that show excellent performance in organic field-effect transistors.
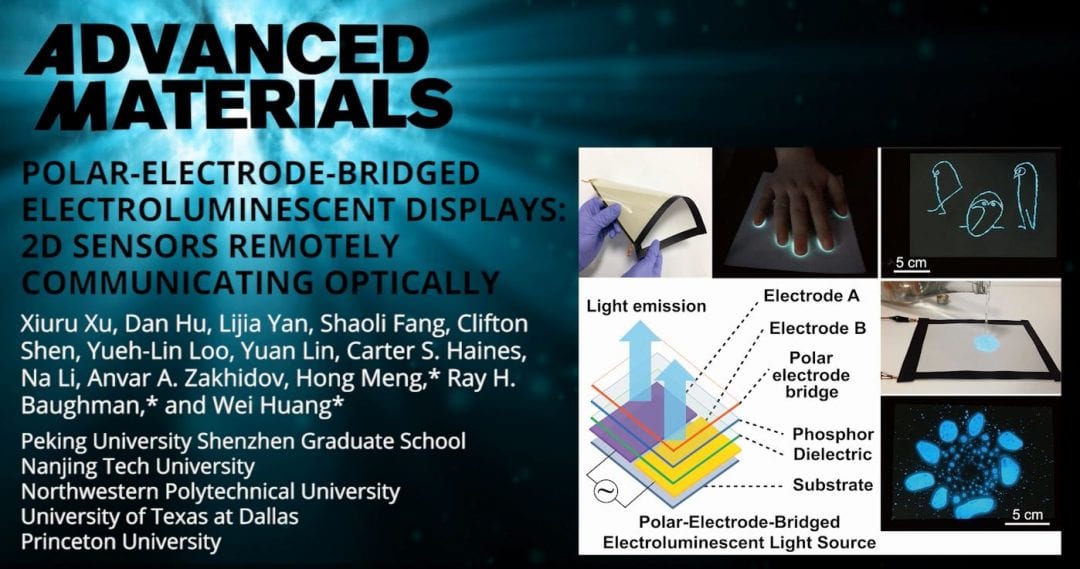
Researchers introduce a new device concept for electroluminescent displays, which does not require transparent electrodes and can be used as remotely readable, spatially-responsive sensors that emit light in response to the accumulation and distribution of materials on the device surface.
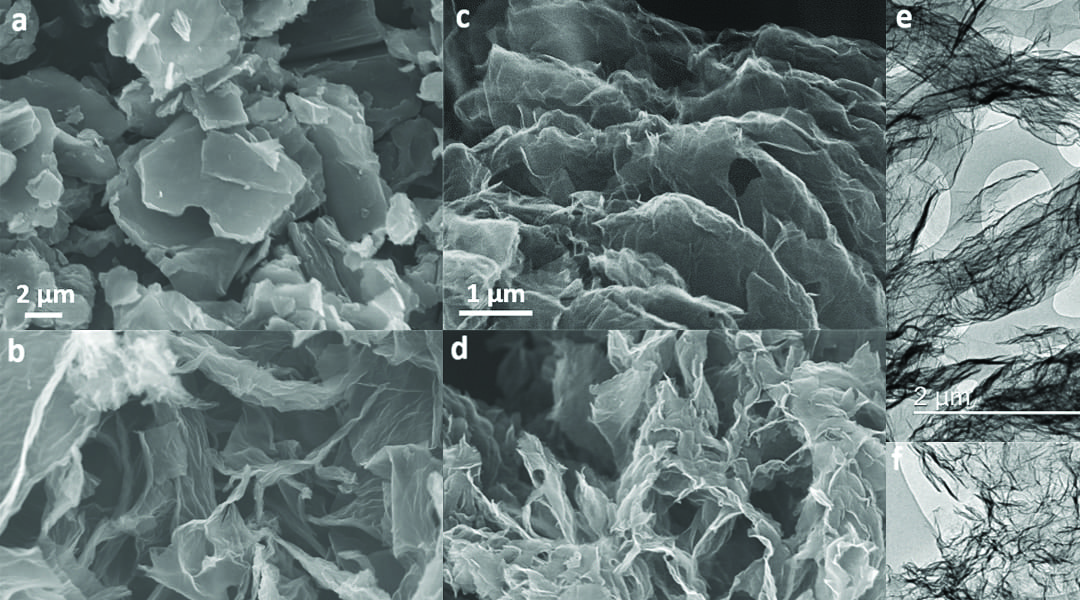
An effective synthesis strategy via a flash-freezing and freeze-dry approach is presented, to synthesis 3D GO structures that exhibit fully accessible hierarchical porous networks for supercapacitor applications.
Guest editors Kyung Eun Lee and Sang Ouk Kim present important recent contributions to the field of Graphene Oxide Liquid Crystals and discuss how this research field will develop in the coming years.

A wearable liquid-embedded microfluidic tactile sensor capable of haptic perception has been prepared.
Chuanbo Gao and co-workers present a mild, robust and effective strategy to remove capping ligands from noble metal nanocrystals for surface-enhanced Raman scattering and catalytic applications.
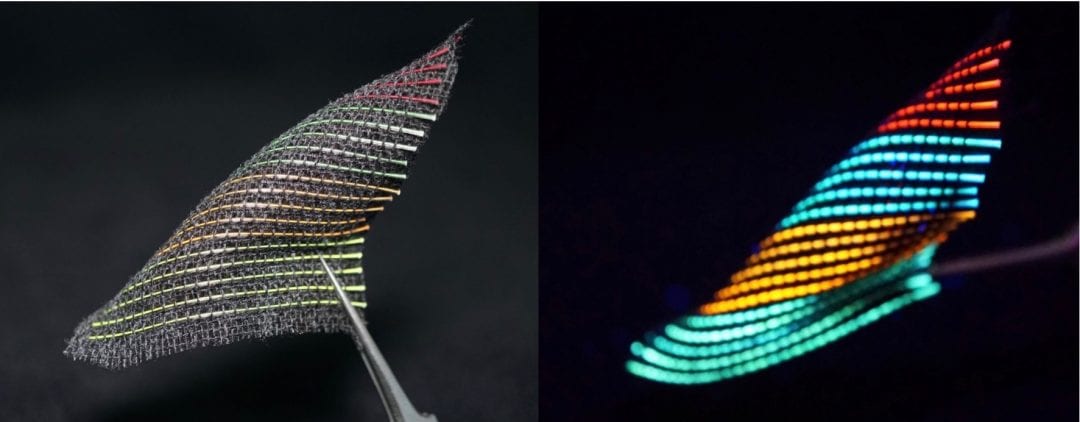
A novel family of colorful fluorescent supercapacitor fibers allows for continuous energy storage in flexible systems used in the dark.
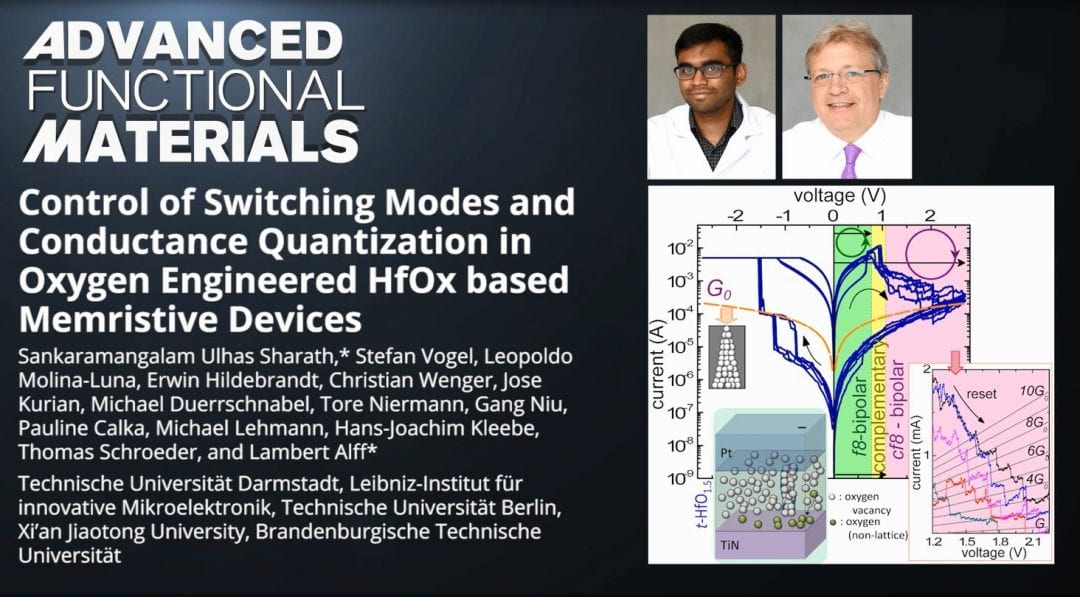
Lambert Alff and his team from Darmstadt University of Technology (TU Darmstadt) in Germany, along with their collaborators, propose a novel unified model for hafnium-oxide resistive random access memory (RRAM) based on the role of oxygen vacancy defects.