Protein-protected metal nanoclusters have excellent biocompatibility and have received considerable attention as a luminescent probe in a number of fields such as biosensing, bioimaging, and imaging-guided therapy.

Protein-protected metal nanoclusters have excellent biocompatibility and have received considerable attention as a luminescent probe in a number of fields such as biosensing, bioimaging, and imaging-guided therapy.
Photodynamic therapy holds great potential for cancer treatment.

Electrospinning is a useful method for preparing non-woven fabrics, and is finding use in creating complex nanostructures.
Nanotechnology has emerged as an innovative tool in medicine that could alter the landscape in relation to disease treatment and prevention.
Polymers have been shown to improve the biological capabilities of optical contrast agents to improve diagnosis of diseases such as cancer.
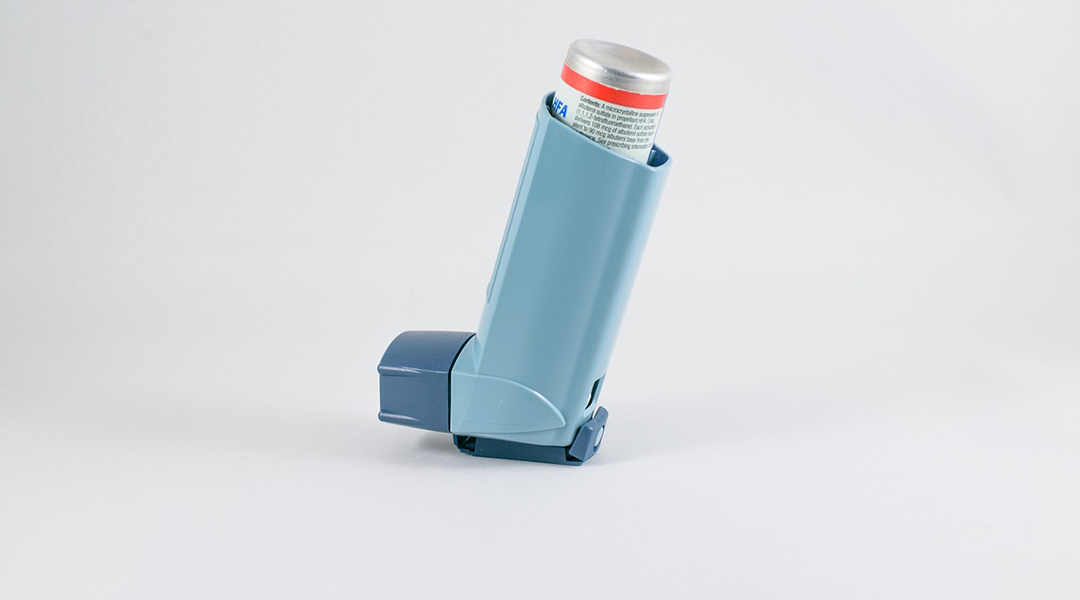

Many nanomaterials can be used to develop inhalable nanomedicines that can be administered with various aerosolization devices.
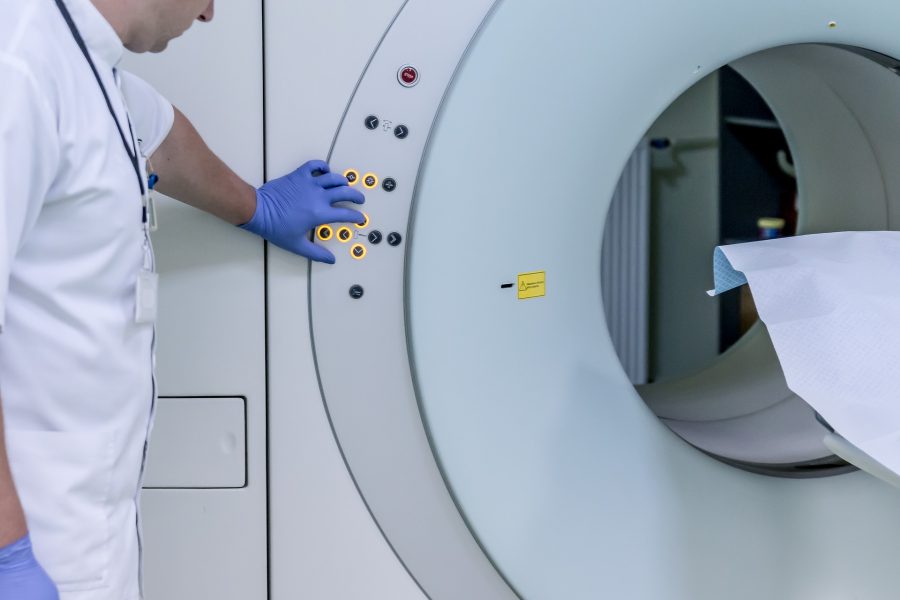
Nanoparticle-based gadolinium contrast agents to improve the safety of MRIs.
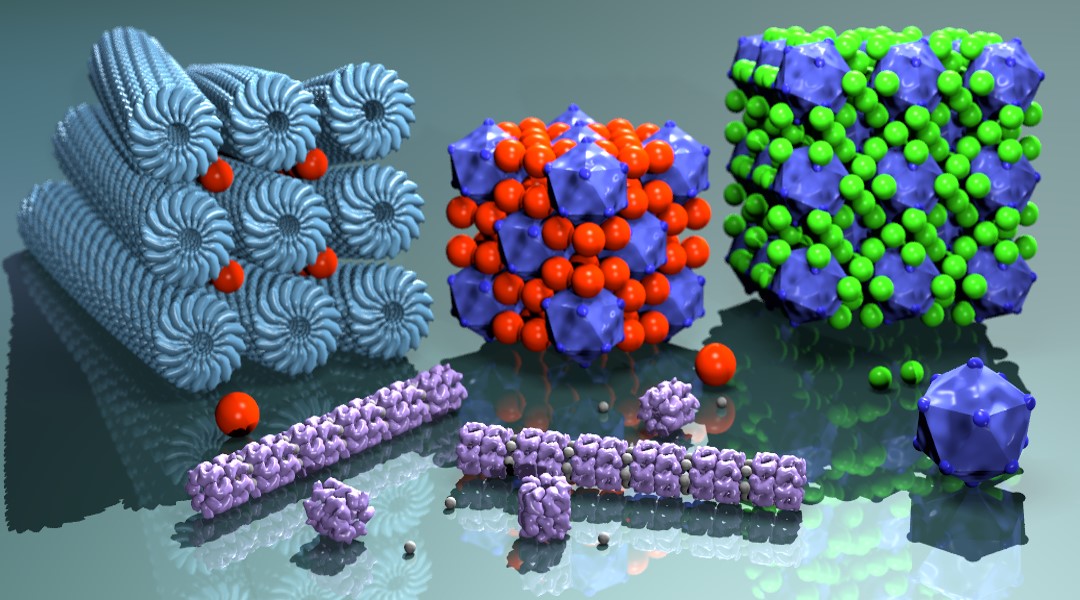
Protein capsids are specialized and versatile natural macromolecules with exceptional properties. These materials have numerous potential applications, including catalysis and drug delivery.
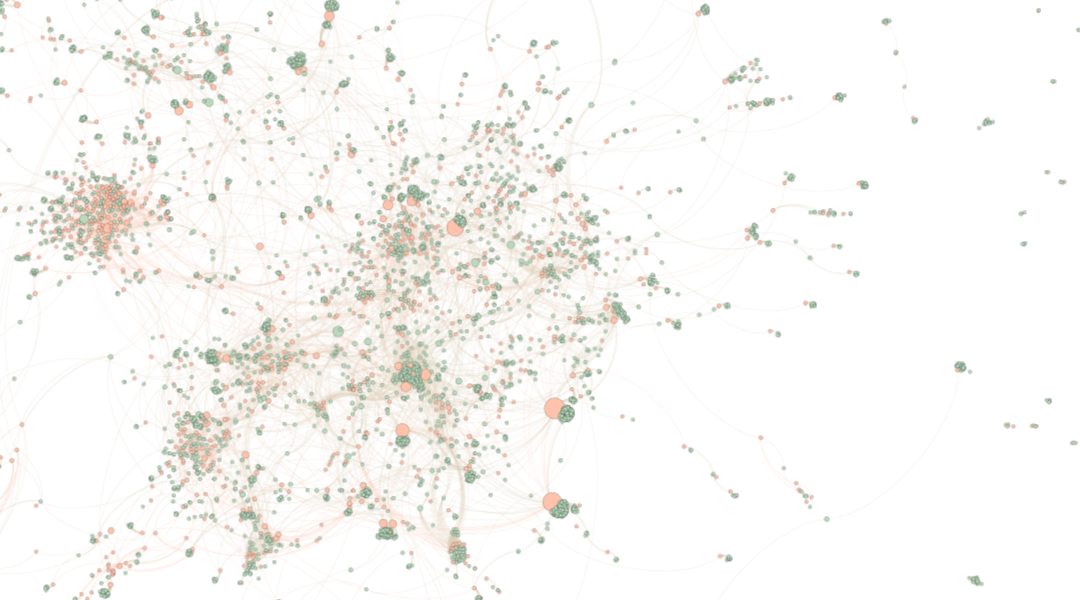
At the core, this WIREs Nanomedicine & Nanobiotechnology review argues that innovators sought to deal with these uncertainties by building upon approved technologies, favoring scientifically crowded fields.

Electroconductive hydrogels resemble the extracellular matrix in tissues, enabling cell growth, proliferation, and migration.