The future will witness a gradual shift in which computational models will play a progressively larger role in identifying new materials for specific purposes.
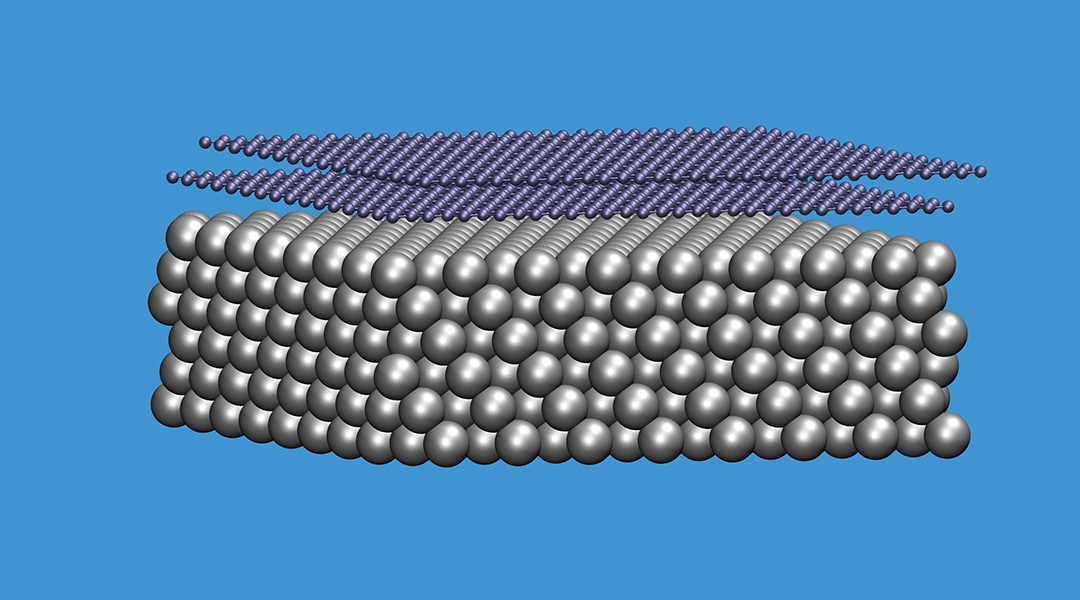

The future will witness a gradual shift in which computational models will play a progressively larger role in identifying new materials for specific purposes.
New quantum algorithms will have dramatic impact in computational molecular biology and bioinformatics and promise to impact a number of life science applications.
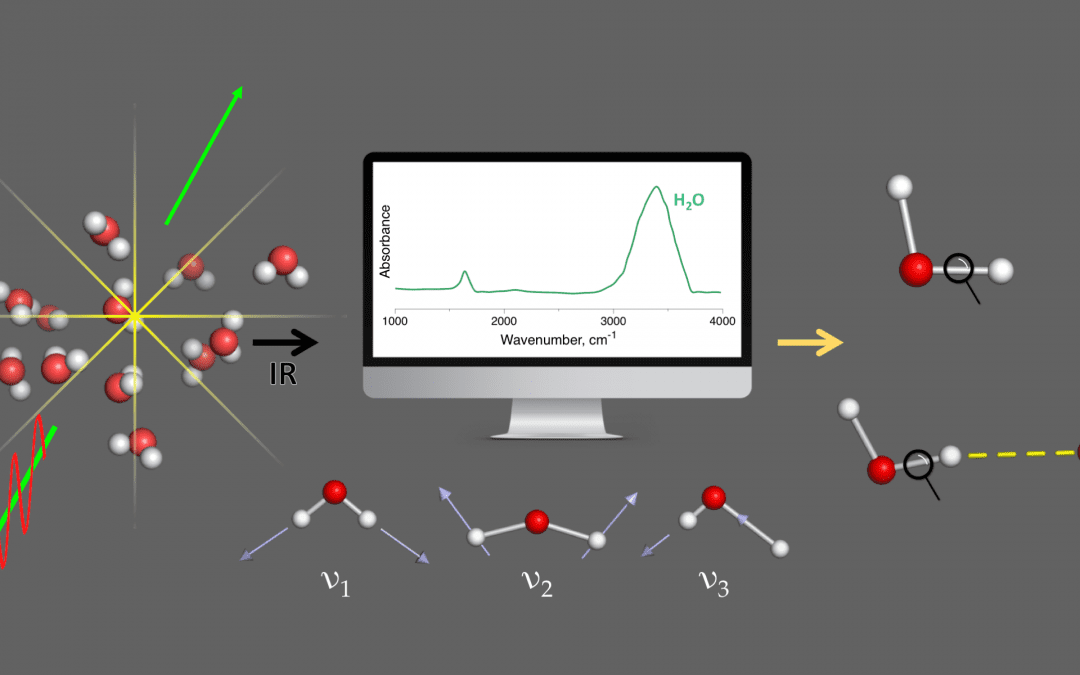
The local vibrational mode theory has raised vibrational spectroscopy to a new level.

Convolutional neural networks provide stronger predictive performances for pharmacological assays compared to traditional machine learning models.

Computer modeling decodes the chemistry carried out by complex DNA repair enzymes to remove DNA damage caused by environmental exposure.
Computational screens allow researchers to efficiently determine how different elemental combinations can alter material properties to quickly identify 2D materials for next generation battery anodes.
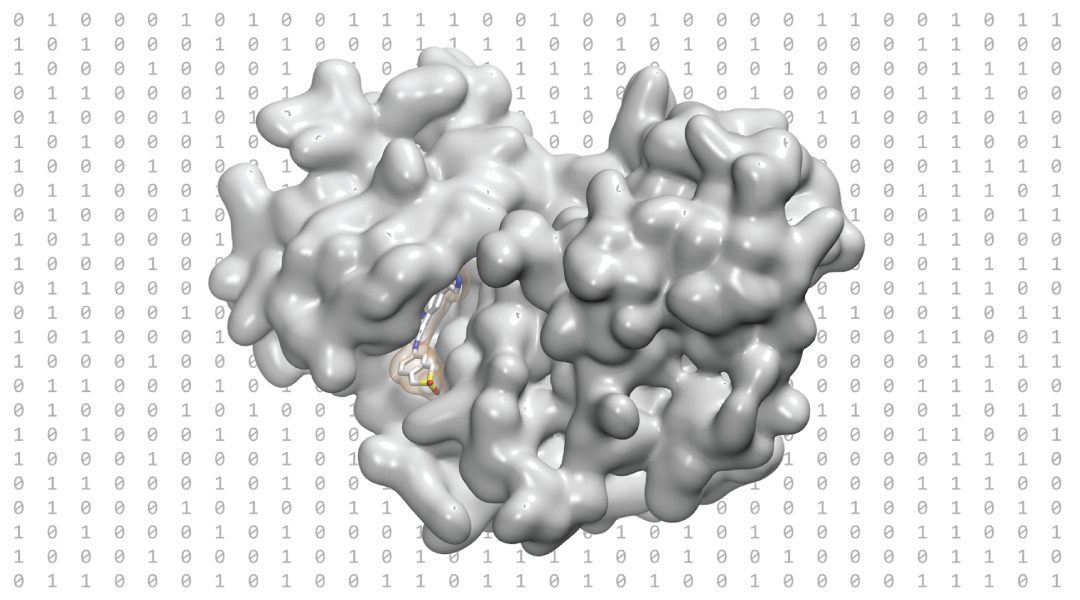
Researchers from Freie Universität Berlin explore the impact of 3D pharmacophores on drug discovery, as well as recent developments in the field.
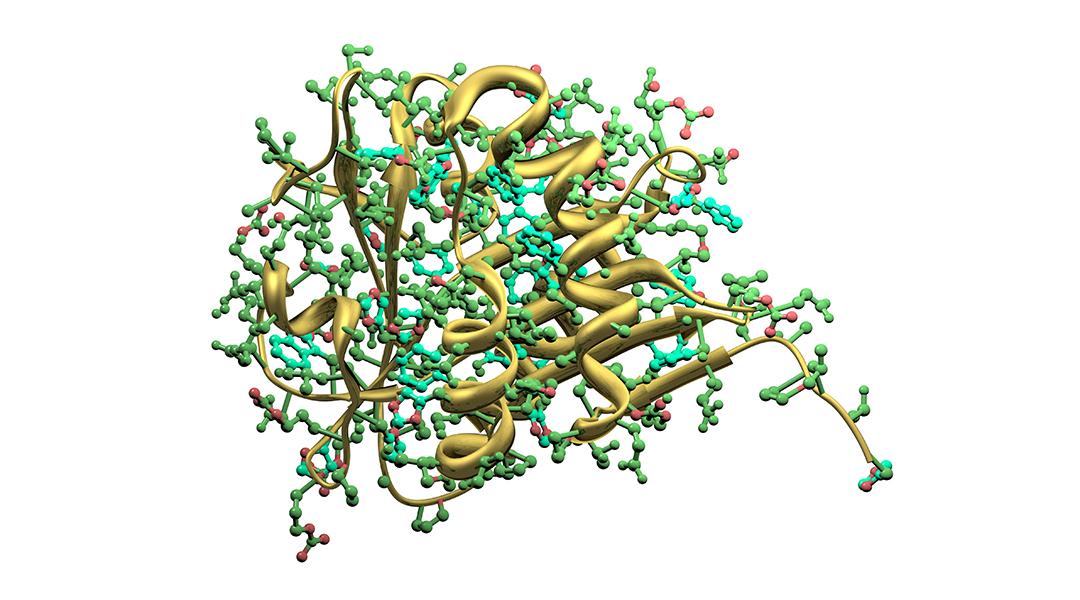
Artificial enzymes promise to not only help us understand the complex functioning of enzymes, but will create a new generation of biosystems for sustainable chemistry practices.

Machine learning significantly reduces the time and cost involved in drug screening.
Recent progress in density functional theory provide new insights for chemical concepts like electrophilicity, nucleophilicity, regioselectivity, stereoselectivity, and more.