The concentration-, size-, and cell type-dependent response to layered black phosphorous is explored to maximise its potential and avoid future problems.
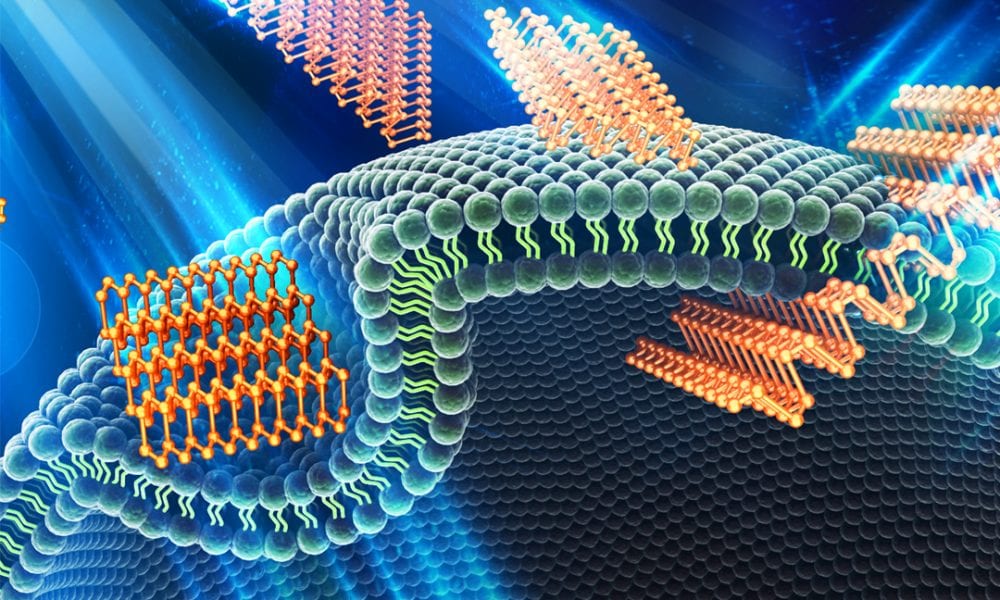

The concentration-, size-, and cell type-dependent response to layered black phosphorous is explored to maximise its potential and avoid future problems.
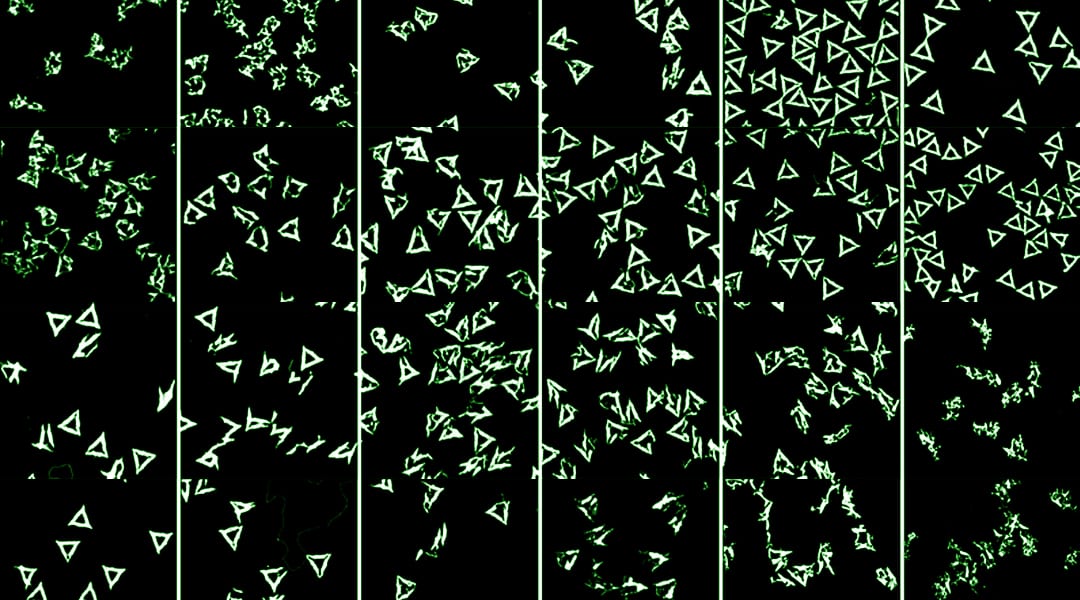

The stability of DNA origami under strongly denaturing conditions is investigated.
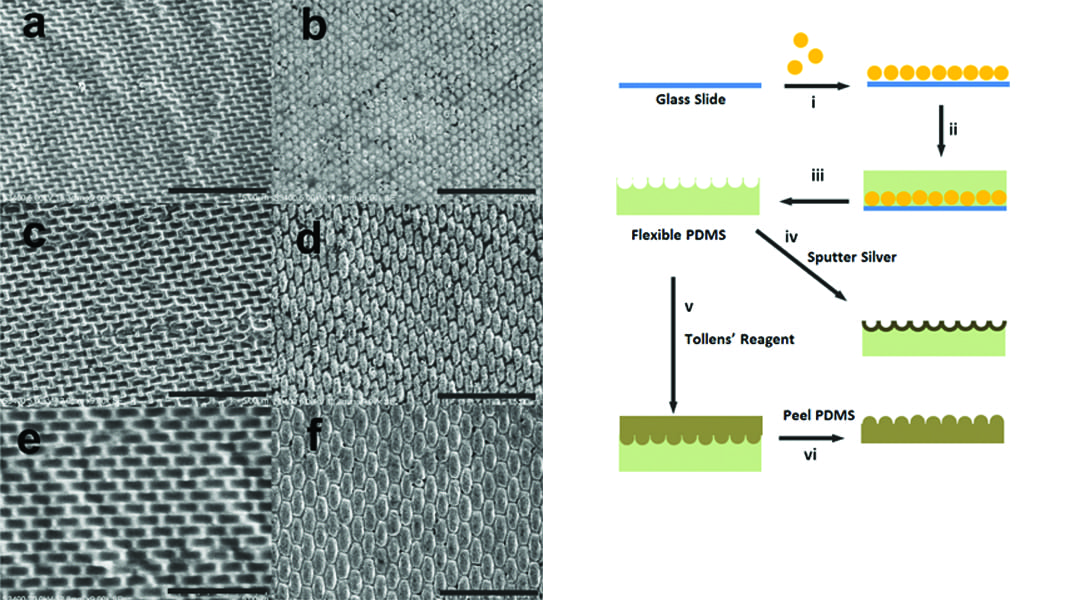
A unique and versatile approach to creating ordered silver nanostructures is presented that allows for feature shape alteration in a simple and inexpensive manner.
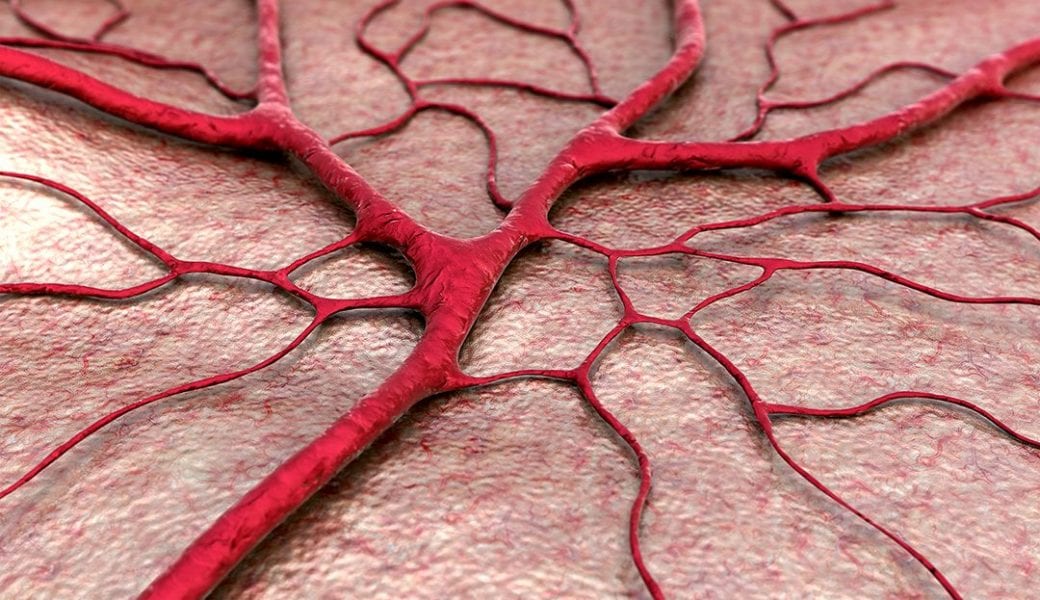
An advanced 4D bioprinting approach uses shape-morphing, biopolymer hydrogels to form the basis for blood vessels and other tubular structures in artificial tissues and organs.

A new study introduces an innovative and cost-effective technique for the plasma functionalization of POSS micro-powders without damaging the nanocage structure they are based on.
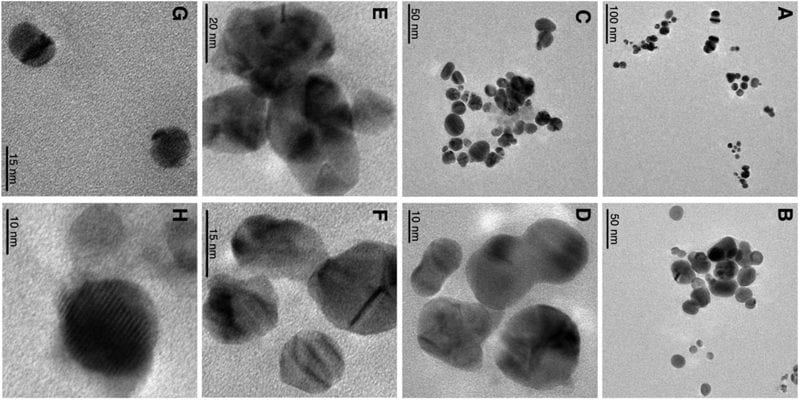
Researchers created a one-step flow-through plasma-reaction system for a cheaper and more sustainable synthesis of silver nanoparticles aimed at large scale production.
A new broad scope journal dedicated to publishing data-driven, scientifically rigorous findings at every stage of basic, translational, clinical and interdisciplinary research in cancer development, progression, treatment, care and outcome.

A team of scientist from the Center for Optical and Electromagnetic Research in China developed a new laser spectroscopy method measuring gas to detect necrosis in the hip joints.
Unlike all other cells in the body, which age and eventually die, a female’s oocytes can give rise to a new individual. Oocytes have, in a sense, achieved immortality. In order to reach this exalted state, each oocyte undergoes a complex program of differentiation within the ovary before it is ovulated and fertilized.

A new type of hybrid hydrogel for tissue regenerative therapy—Anisogel—is developed by Abdolrahman Omidinia-Anarkoli, Laura De Laporte, and co-workers from the Leibniz Institute for Interactive Materials in Aachen, Germany. This low-invasive hydrogel is promising for healing body tissues that consist of an aligned architecture, such as the heart, kidney, muscles, and nerves.