Alexander Poellinger from Charité in Berline researchers the potential of near-infrared imaging using optical contrast agents for diagnosing breast cancer.
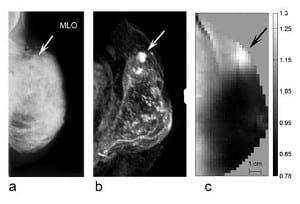

Alexander Poellinger from Charité in Berline researchers the potential of near-infrared imaging using optical contrast agents for diagnosing breast cancer.
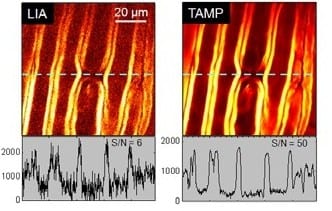
A superior signal to noise ratio for heterodyne detected nonlinear optical imaging can be attained by a newly developed tuned amplifier system in a lock-in free manner, as demonstrated through stimulated Raman scattering imaging of live cells and tissues.

The issue aims to provide a representative and comprehensive overview on the broad range of current biophotonics on-chip, spanning the full range from chip fabrication to applications in biomedical sensing and related fields.
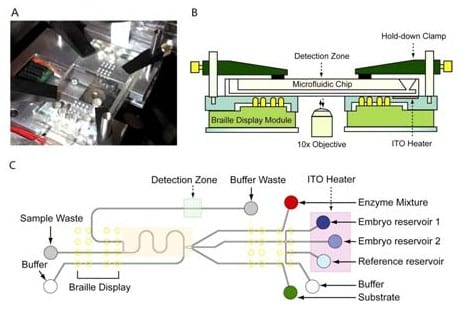
Lab-on-a-chip method, when combined with biophotonics, can be used to assay for metabolites, to separate gametes via optoelectrical tweezers, or to improve the vitrification of oocytes.
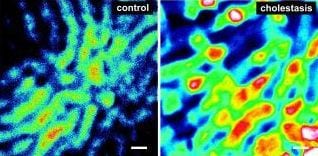
What happens in the liver during cholestasis? A novel in vivo imaging technique based on fluorescence microscopy delivers insight into the hepatic excretory function in rat.
Coherent Raman scattering methods have one key advantage over spontaneous Raman microscopy: speed. The (sub-)microsecond pixel dwell times offered by narrowband CRS imaging methods have initiated a new era of chemical imaging applications in biology and biomedicine.
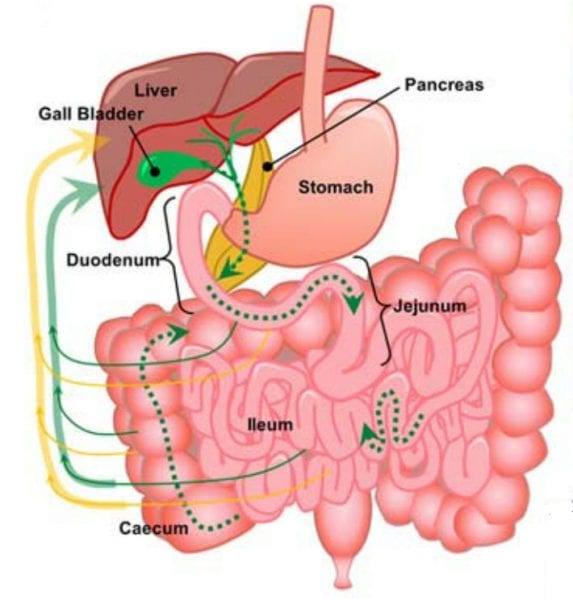
Which pathways do nanomedicines take after they have been swallowed? Scientists find a recirculation pathway of polymeric micelles using multimodal nonlinear optical microscopy.
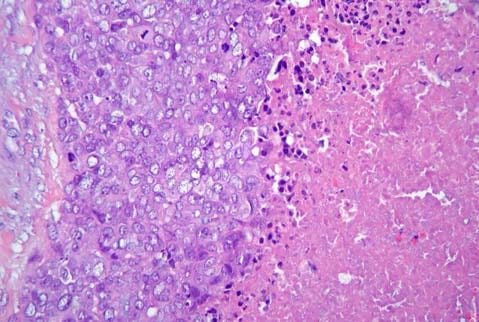
Are modern molecular classification methods for breast carcinomas reasonable? Austrian scientists challenge the clinical relevance of the term “basal-like” breast cancer subtype.
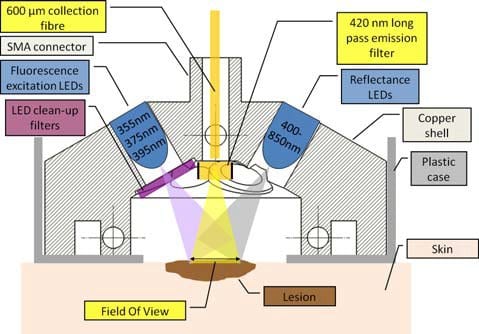
A biopsy is a painful and scarring but often unavoidable procedure. Now, scientists have reported promising results of autofluorescence and reflectance measurements of tissue as a noninvasive approach for basal cell carcinoma diagnosis.
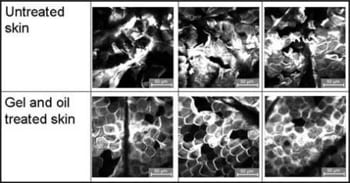
Transepidermal water loss measurement is the standard method to characterize epidermal barrier function. However, it can be affected by a broad range of exogenous and endogenous factors – in vivo laser scanning microscopy may be a superior method.