Researchers use stick insect locomotion as inspiration for machine learning approaches to teaching robots how to walk.
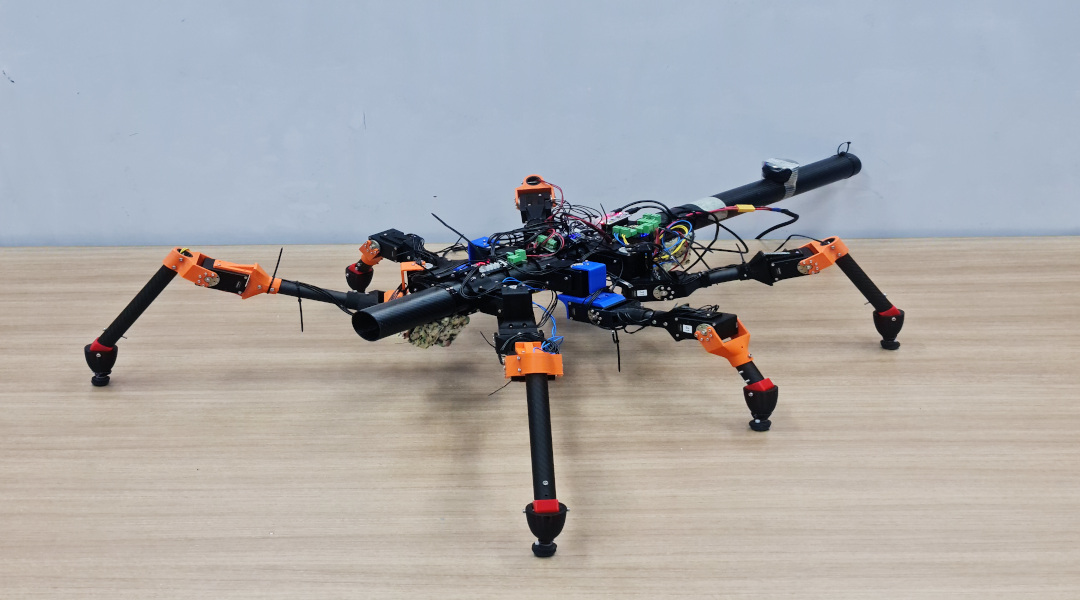


Researchers use stick insect locomotion as inspiration for machine learning approaches to teaching robots how to walk.
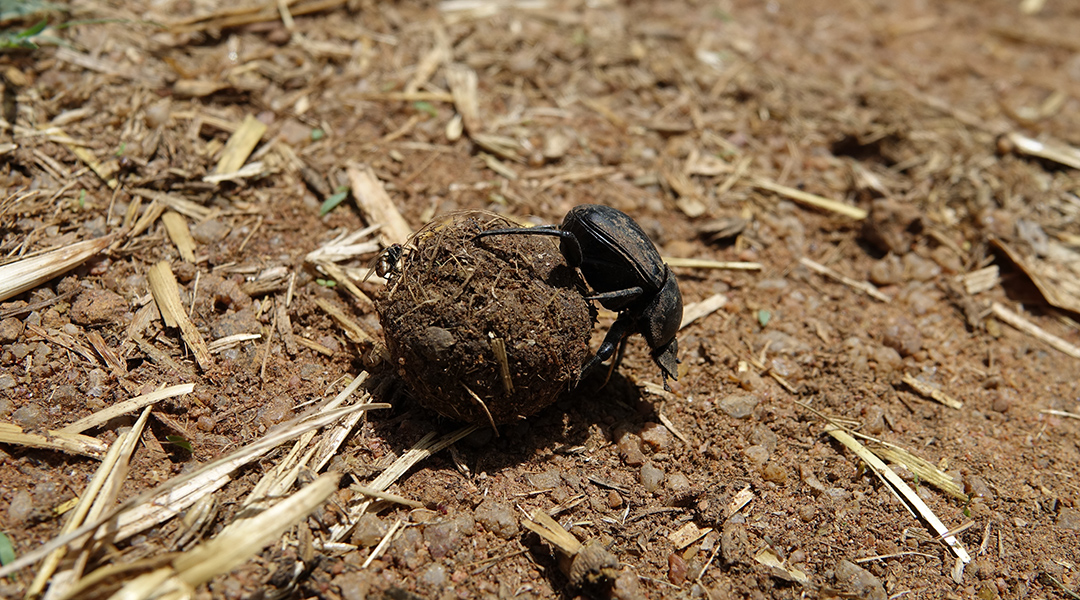

A numerical model helps scientists understand how particularities of different terrains affect the trajectory and behavior of dung beetles.

The debate around COVID-19 boosters is highly nuanced, but a new computational model could help better inform policy around such measures in an evolving pandemic.

A new simulator can accurately model COVID-19 and the effects of different mitigation strategies, which researchers say could help guide new policies to combat the pandemic.
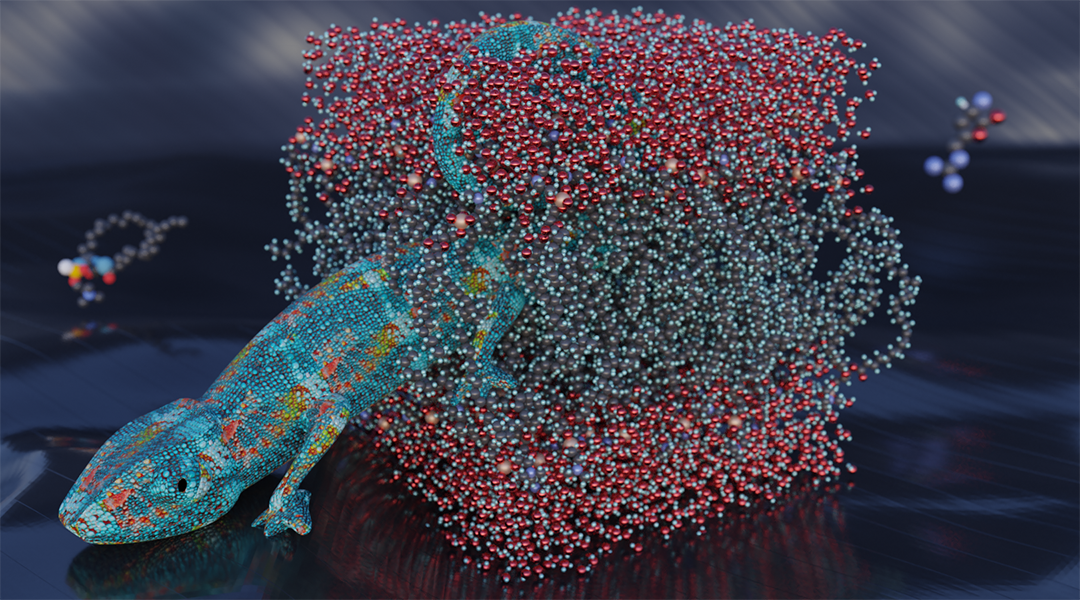
Computational methods allow researchers to delve deeper into molecular processes, beyond what can easily be achieved with current experimental techniques.

A new study shows fundamental limitations to the computer-based simulation of chaotic systems with implications in climate change modeling, weather forecasts, and machine learning.

Computational materials design is shown to be essential for the discovery of new and novel materials of the future.
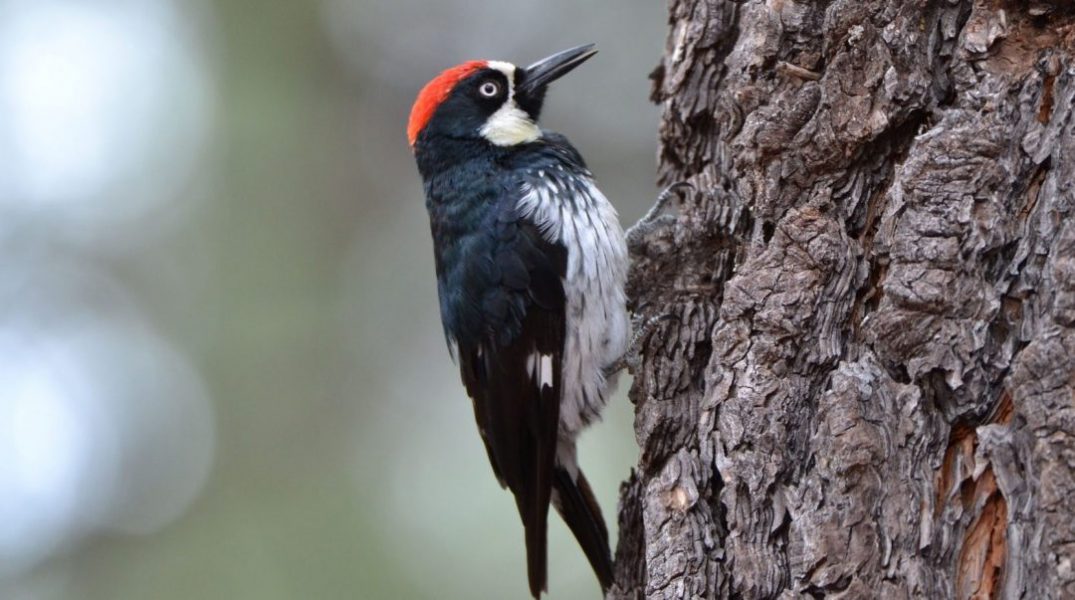

A combination of experiments and simulations show how woodpeckers are protected from concussion by the structure of their skull.
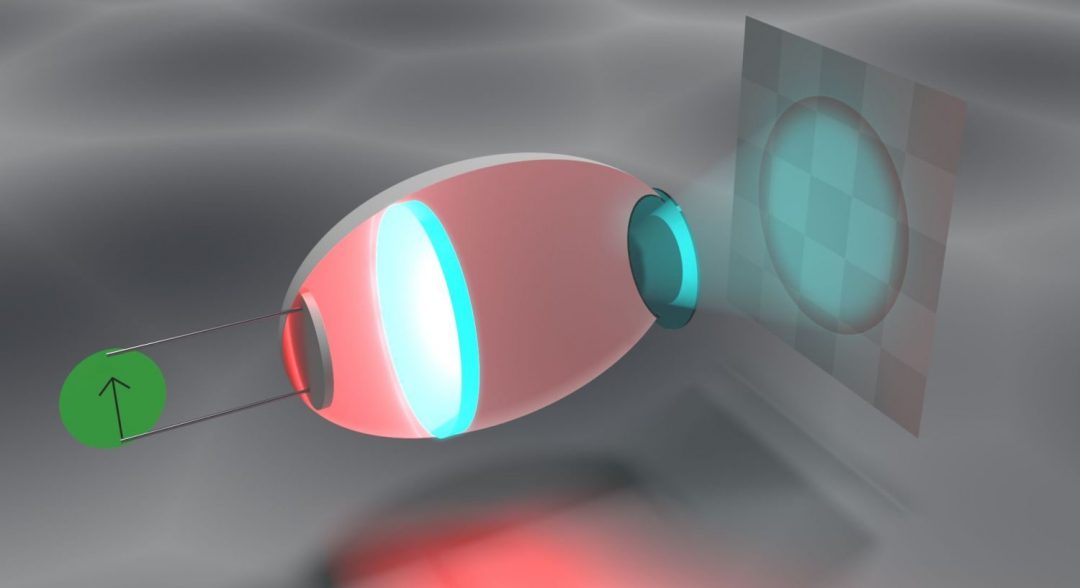
New predictions for efficiently making blue lighting from red lighting.
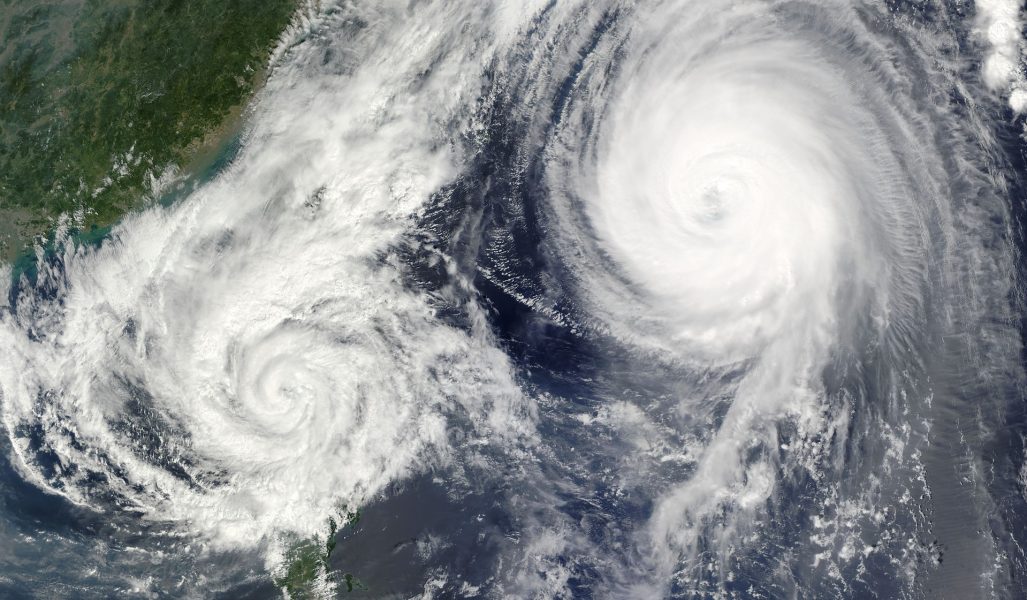

Systemic risks tend to be underestimated and do not attract the same amount of attention as catastrophic events.