Inexpensive and stable: Water could form the basis for future particularly inexpensive rechargeable batteries.

Inexpensive and stable: Water could form the basis for future particularly inexpensive rechargeable batteries.
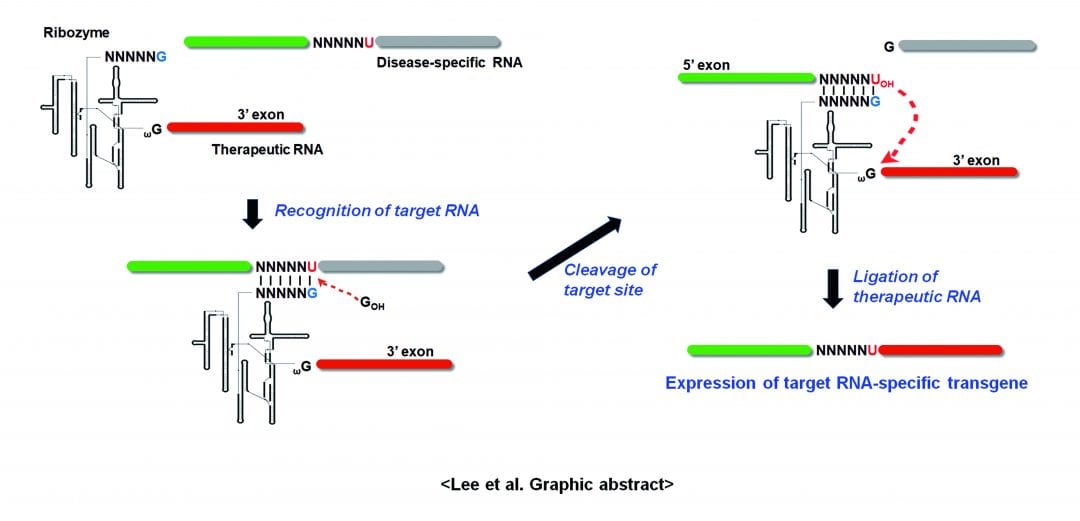
Group I intron-based trans-splicing ribozyme specifically recognizes disease-specific RNA, removes the sequence downstream of the target site, and replaces it with a 3’-exon encoding a therapeutic/reporter RNA sequence, inducing therapeutic/reporter activity selectively in the target RNA-expressing cells.
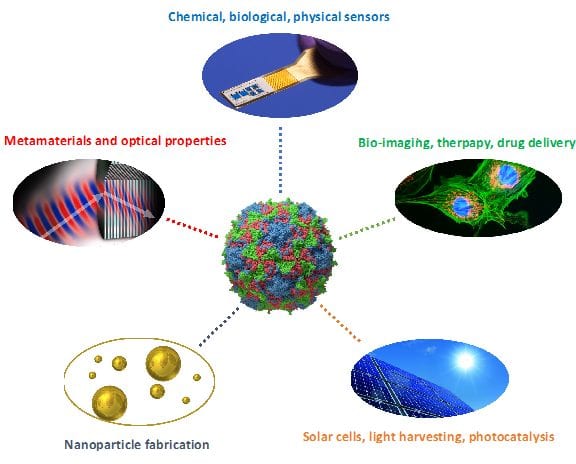
Researchers are taking advantage of 4 billion years of viral evolution to produce robust protein cages for a wide range of applications in nanotechnology.
A team of North American researchers developed an epi-SRS imaging platform for functional imaging of VSMCs in fresh coronary arteries which could support in developing new strategies for cardiovascular disease treatment.
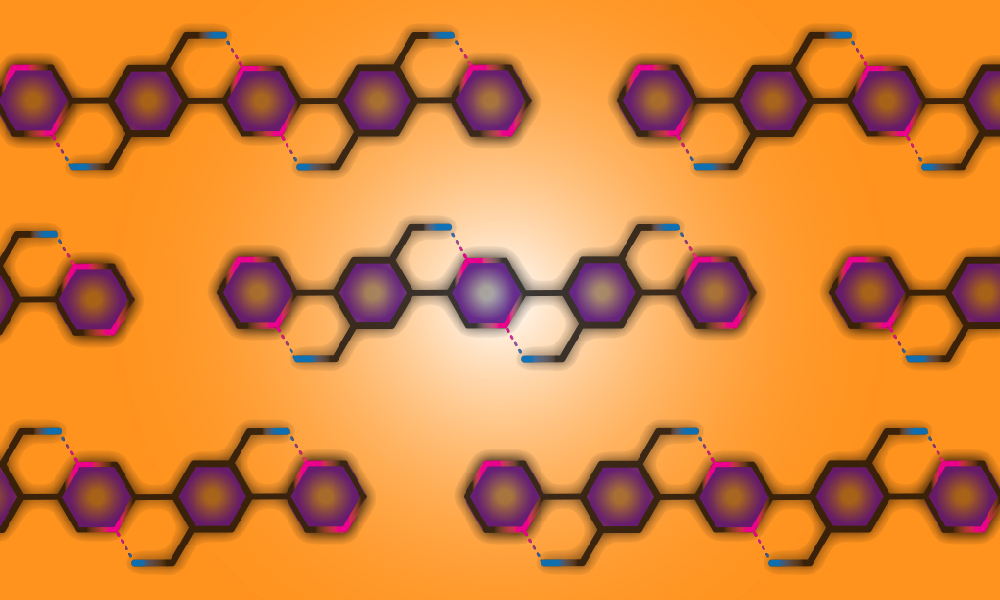
Prof. Lei Fang reviews how co-planar conformation in π-conjugated systems can be locked by using dynamic noncovalent bonds.

The burgeoning development and sustained production of advances in the booming field of solar-to-energy conversion have inspired a Special Issue specifically dedicated to “Artificial Photosynthesis: Mimicking Nature for Renewable Energy Production” – guest editors Wee-Jun Ong, Zhiqun Lin and Kazunari Domen.
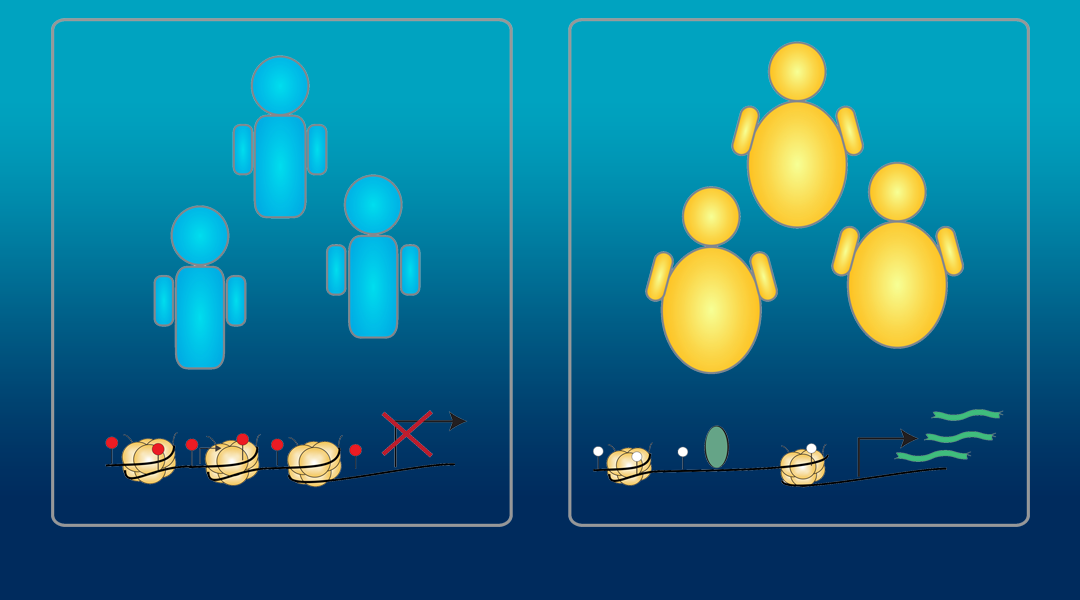
Modifications to chromatin are associated with the development of metabolic diseases, including Type 2 diabetes and obesity. There is evidence that these chromatin modifications can lead to long-term disease risk and increased disease risk for offspring.
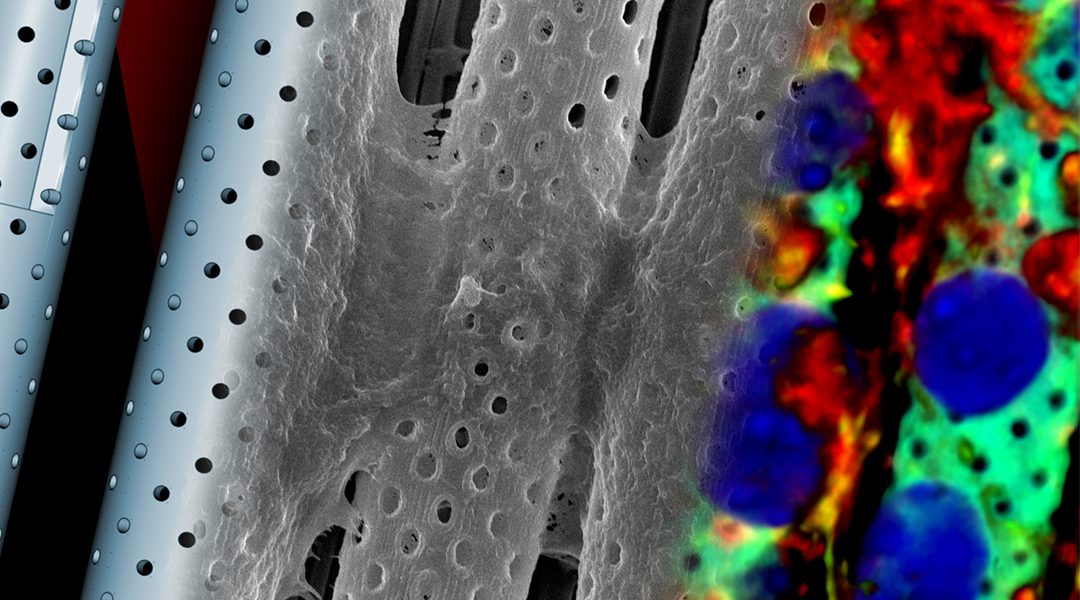
Bioinspired, biohybrid device design and fabrication strategy for investigating the ability of therapeutics to cross the blood brain barrier.
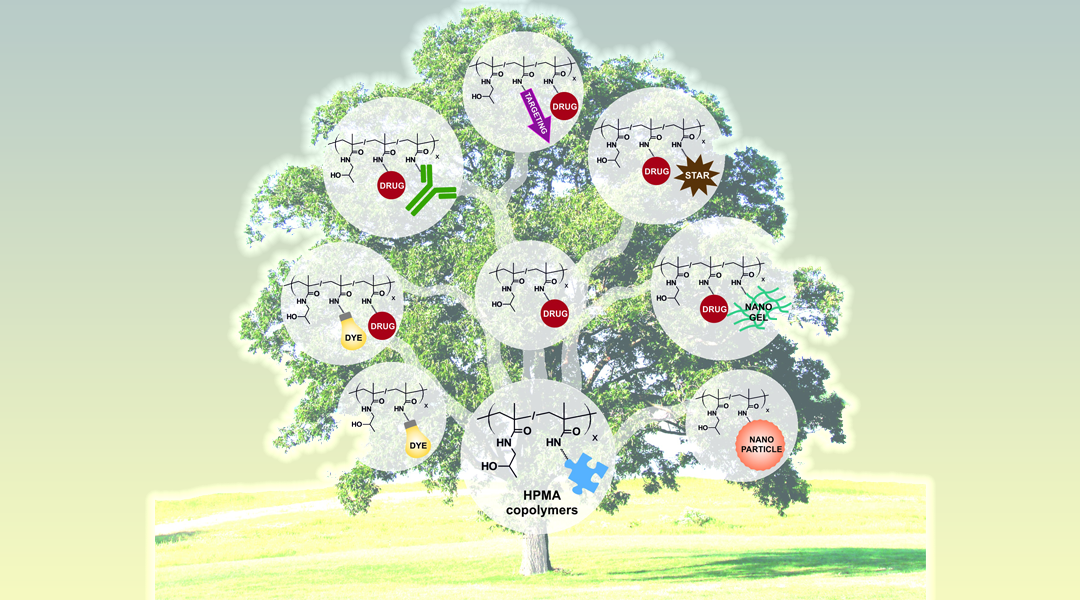
The current special issue in Macromolecular Bioscience is published on the occasion of Professor Karel Ulbrich’s 70th birthday
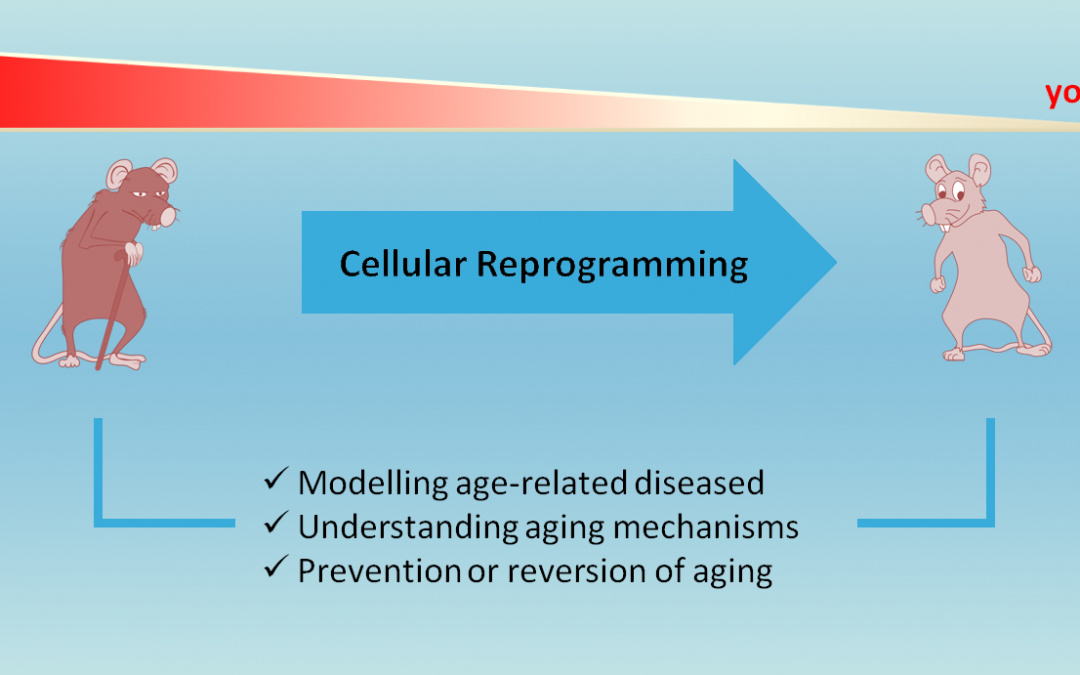
This rise in the elderly population brings forward the concept of healthy aging and encourages scientists to conduct extensive research in cellular reprogramming.