Scientists are investigating how fullerene nanomaterials can be used as antivirals against different variants of SARS-CoV-2 and other viruses.
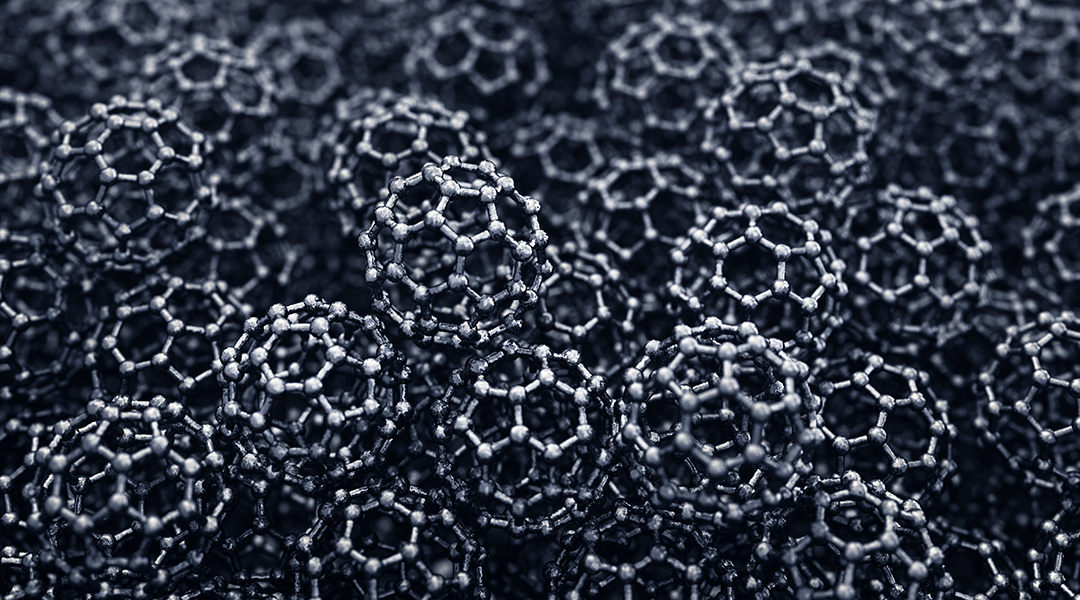


Scientists are investigating how fullerene nanomaterials can be used as antivirals against different variants of SARS-CoV-2 and other viruses.
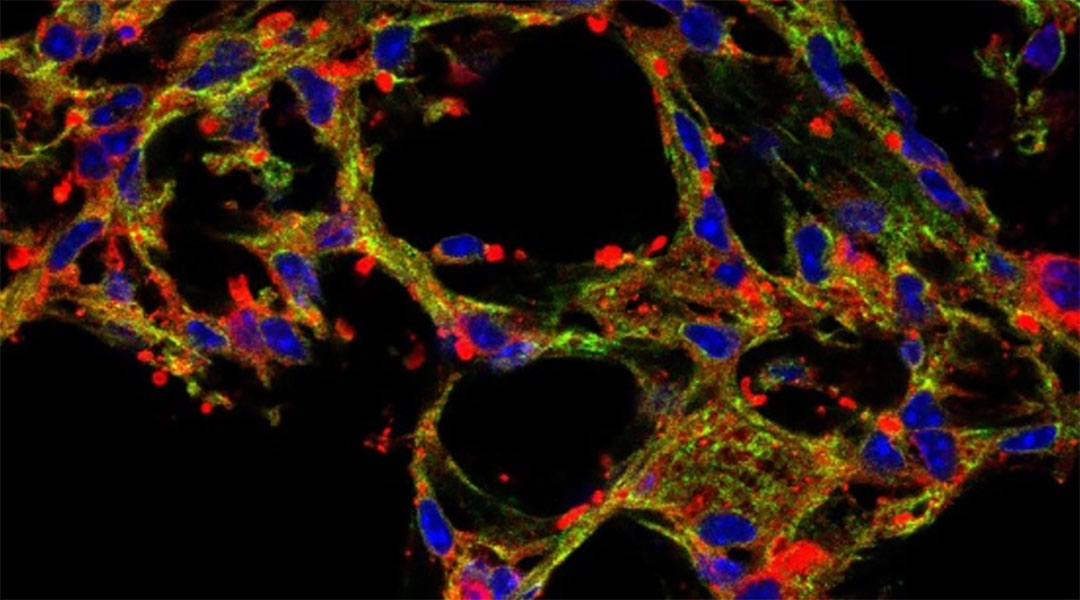
An inhaled drug carrier helps minimize side effects while delivering drugs to the lungs to treat diseases such as pulmonary fibrosis.
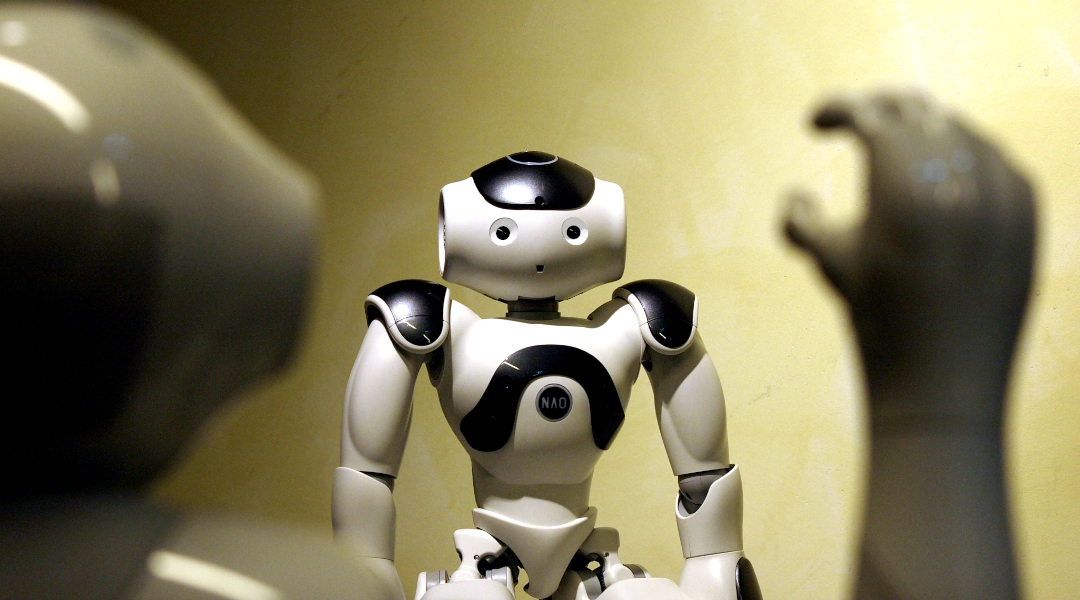

Event cameras mimic the human eye to allow robots to navigate their environment, and a new approach helps minimize computational costs.
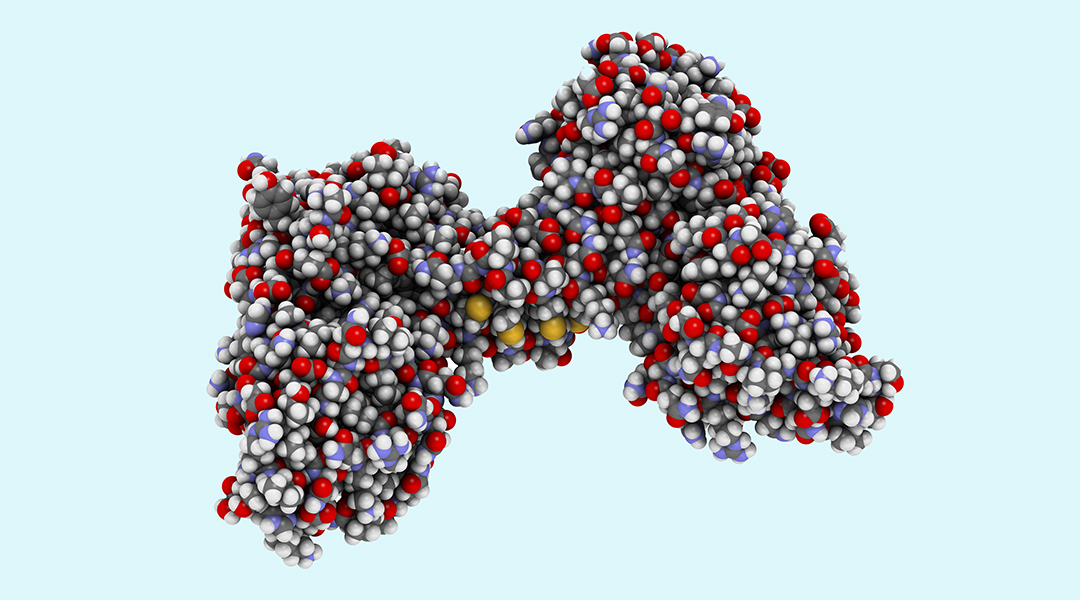
Important findings from an animal study have prompted the exploration of a gene therapy for Duchenne muscular dystrophy in an ongoing human trial.
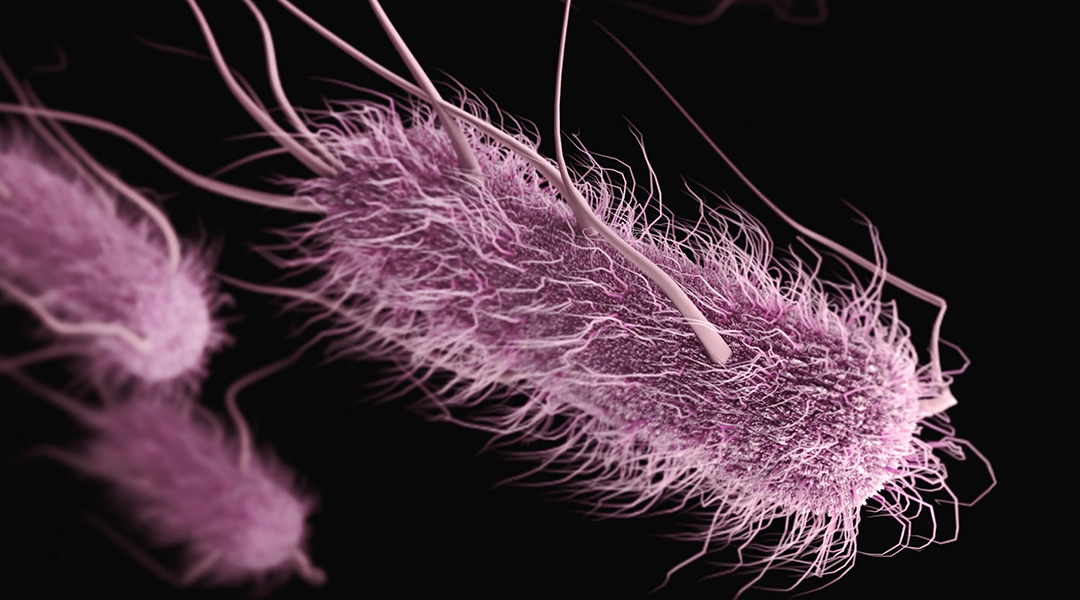
Incorporating polymer skeletons inside bacteria stops them from replicating and results in cyborg cells that are half living, half artificial.
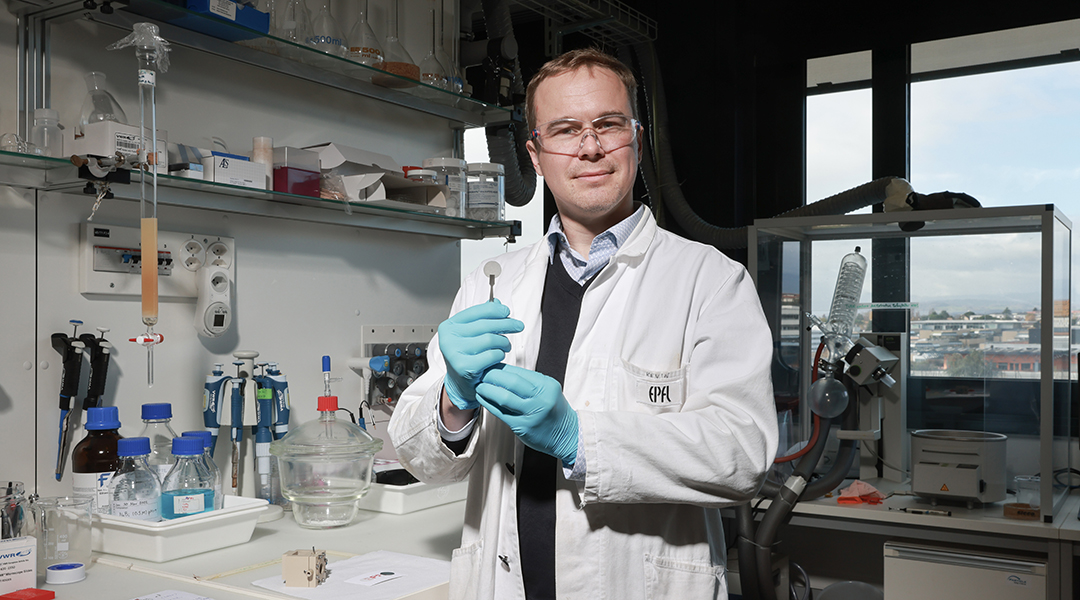

Taking inspiration from plants, researchers demonstrate a proof-of-concept device that extracts hydrogen fuel from humidity using sunlight.
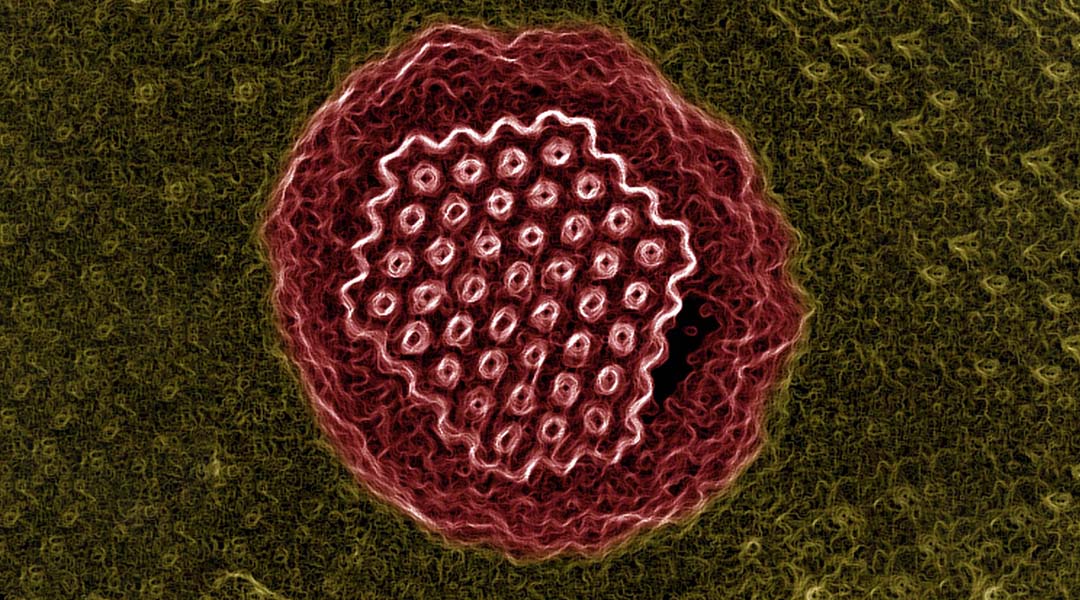
How seven ancient viruses ranging in age from 27,000 to 48,500 years were recovered from the Siberian permafrost, and what researchers hope to learn from them.
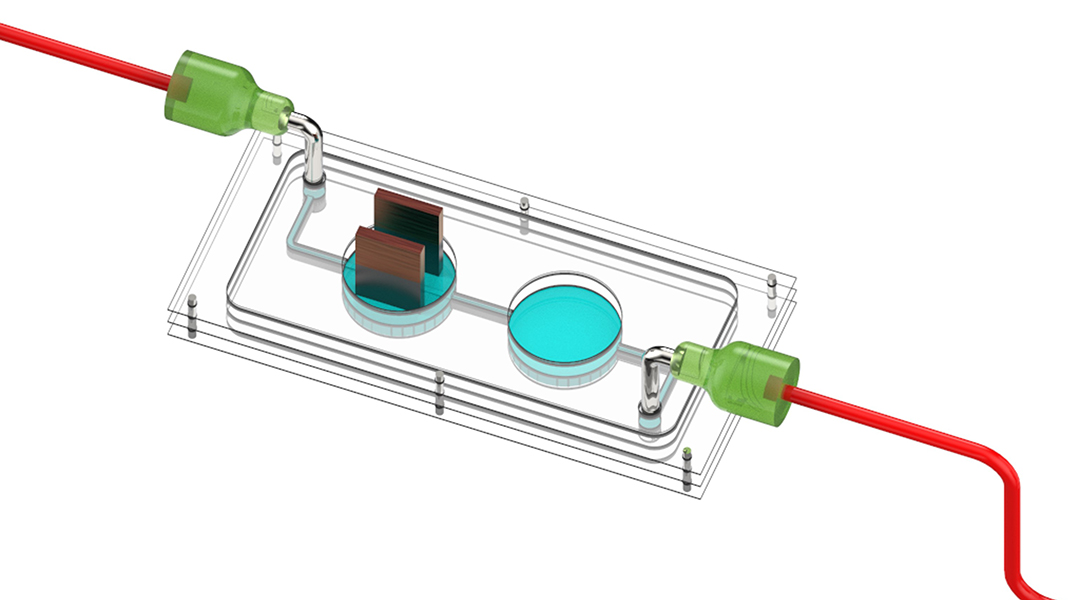
The device provides a powerful tool for studying and treating diabetes, allowing personalized modelling by using patients’ own cells.
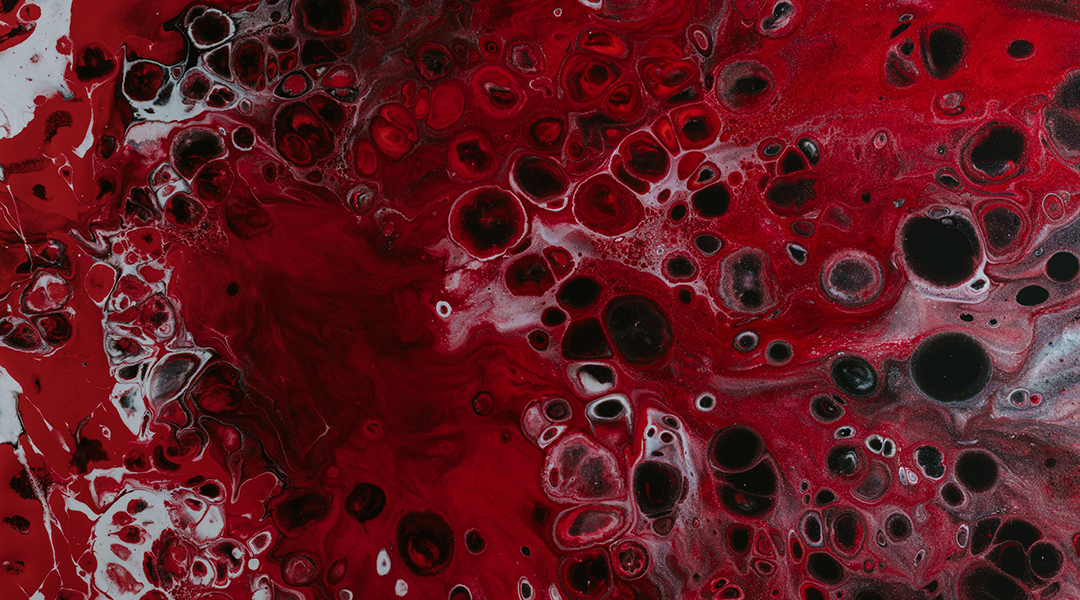

Blood coagulation is a common but delicate physiological behavior and is inspiring new porous materials.
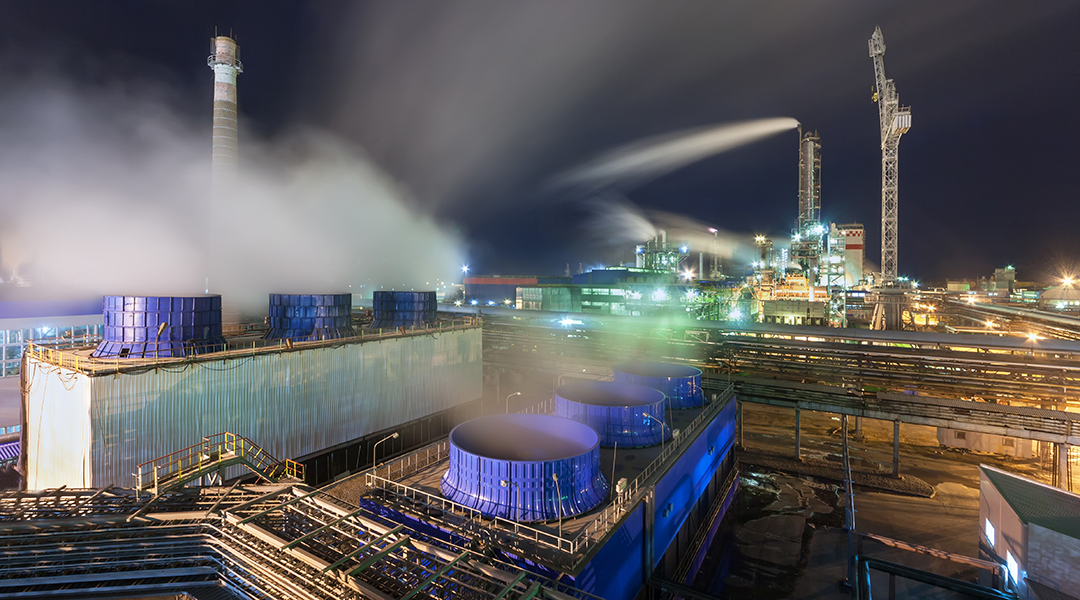

With a fossil fuel–derived climate catastrophe on our doorstep, many see ammonia as a possible alternative fuel source.