Albert Zink, director at the Institute for Mummy Studies, investigates remains from the past to bring ancient stories to life.
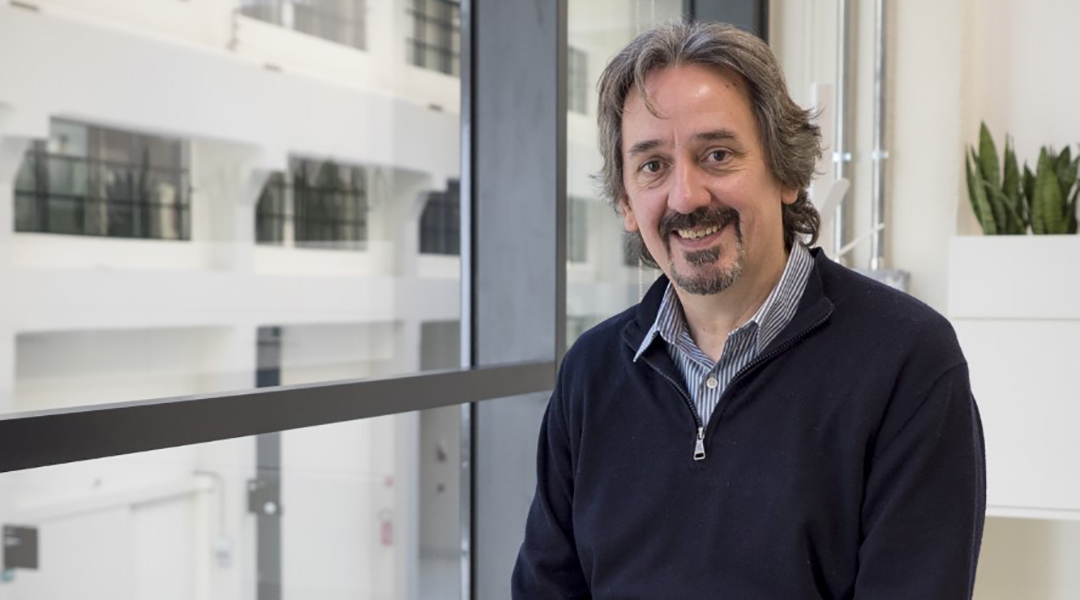


Albert Zink, director at the Institute for Mummy Studies, investigates remains from the past to bring ancient stories to life.
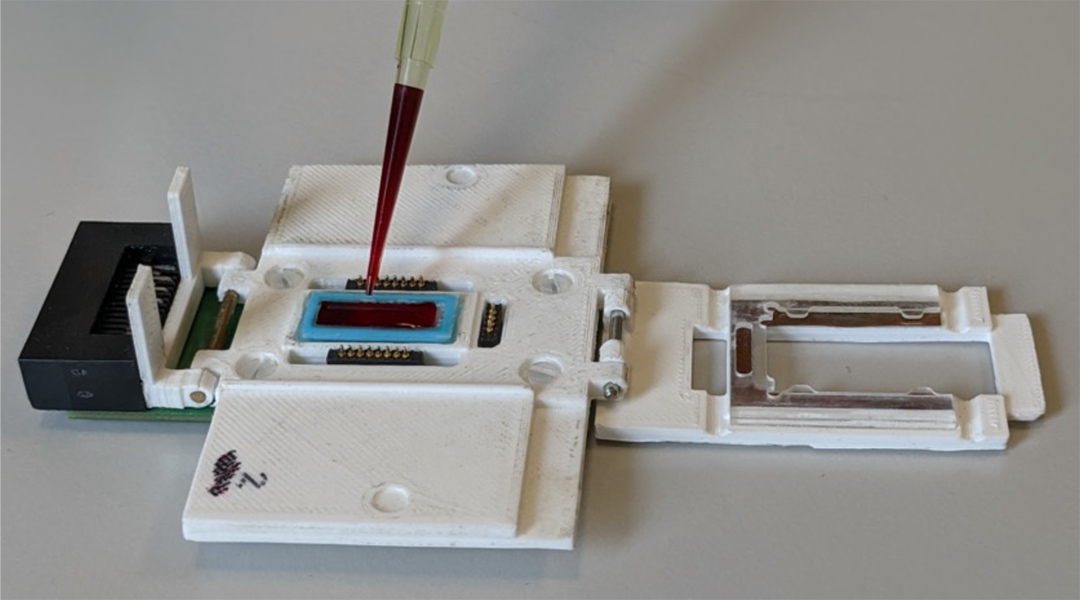
A new lab-on-chip technology enables the rapid and quantitative identification of malaria parasites in the blood for better and more accurate diagnosis in remote regions.
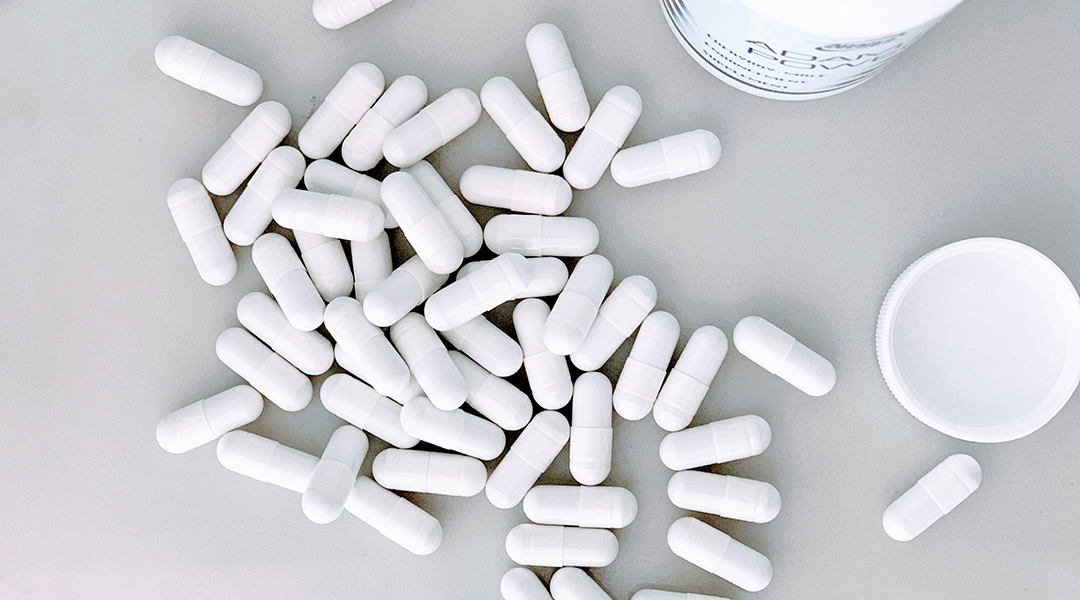
Self-propelling microparticles enhance the dissolution of drugs in the stomach, achieving better bioavailability without the side effects of high dosing.
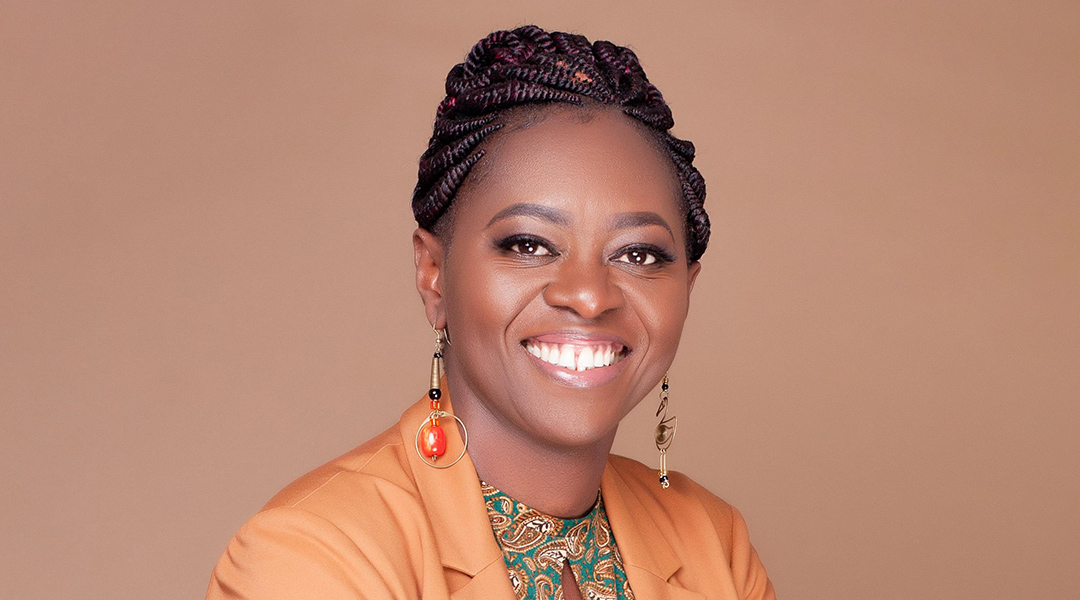

With research groups spread over two continents, Osier is striving to eliminate malaria through her groundbreaking work in immunology, advocacy and awareness.
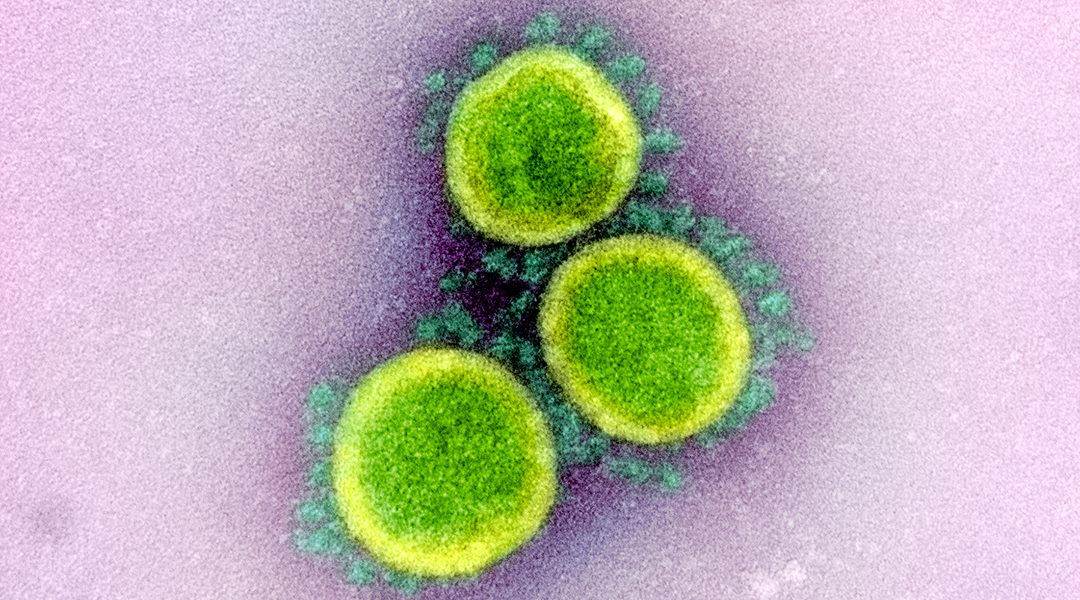
Researchers enhance the immune response against the receptor binding domain of SARS-CoV-2 by presenting it on liposomes, providing a promising strategy for vaccine development targeting this domain.
A recent study discovers that CRISPR can be used for a number of different purposes by diverse biological entities, not just humans and bacteria.
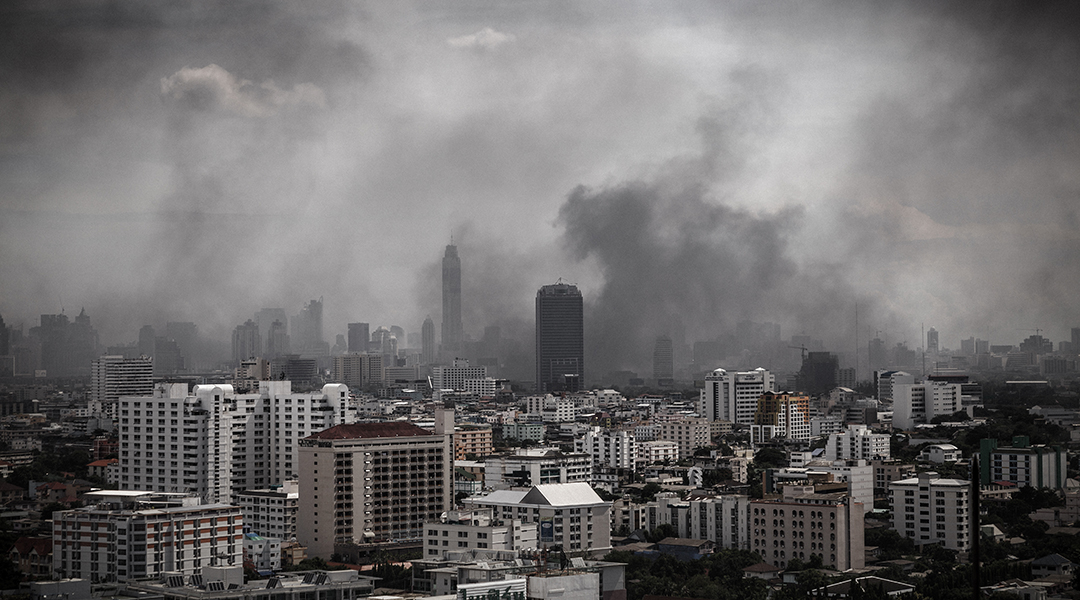

Researchers say people’s lives are shortened by an average of nearly three years from different sources of air pollution
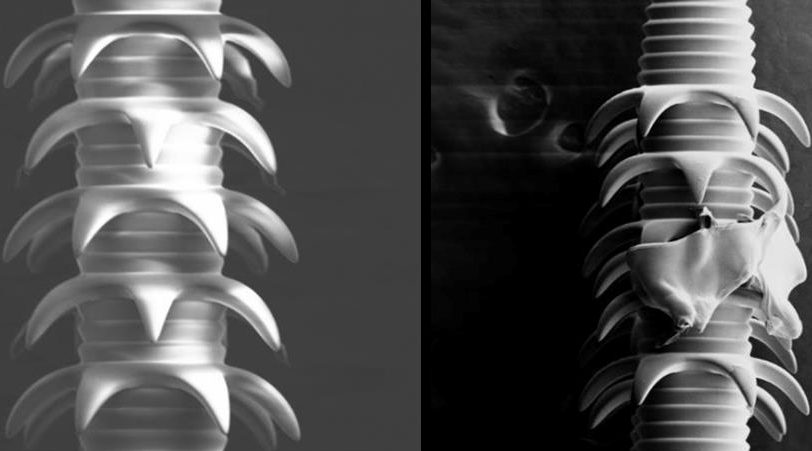
4D-printed microneedles may one day replace conventional hypodermics.
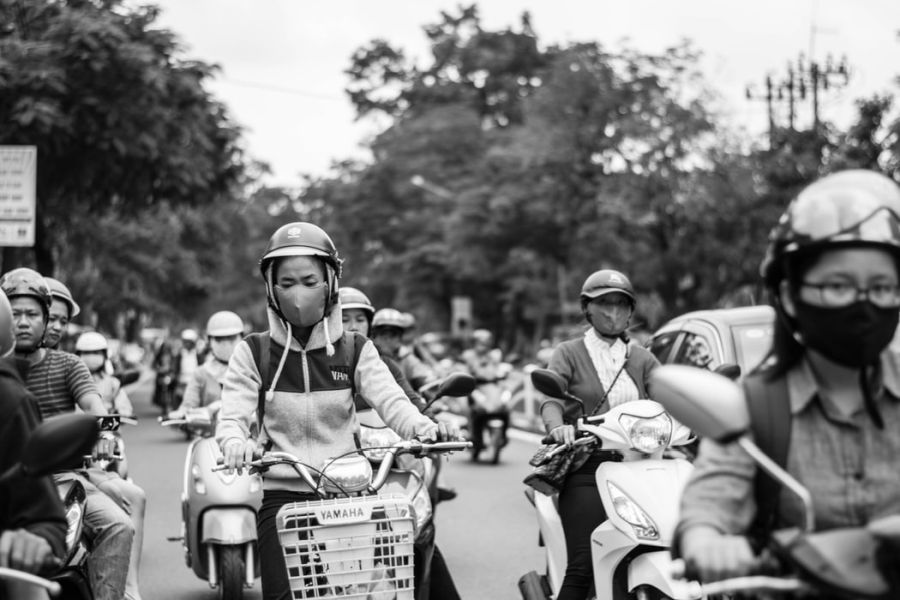

Protecting human health should be a priority in climate change mitigation efforts.
Single stranded RNAs with a free 5′ monophosphate end are susceptible to rapid degradation. Transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs) are stabilized by hairpin structures and by “hiding” their 5′ ends within complex protein structures.